Kube-OVN integrates the OVN-based Network Virtualization with Kubernetes. It offers an advanced Container Network Fabric for Enterprises. It provides the most functions and very easy to use and operate.
- Namespaced Subnets: Each Namespace can have a unique Subnet (backed by a Logical Switch). Pods within the Namespace will have IP addresses allocated from the Subnet. It's also possible for multiple Namespaces to share a Subnet.
- Subnet Isolation: Can configure a Subnet to deny any traffic from source IP addresses not within the same Subnet. Can whitelist specific IP addresses and IP ranges.
- Network Policy: Kube-OVN implements networking.k8s.io/NetworkPolicy API by ovn ACL.
- Static IP Addresses for Workloads: Allocate random or static IP addresses to workloads.
- Dynamic QoS: Configure Pod Ingress/Egress traffic rate limits on the fly.
- Embedded Load Balancers: Replace kube-proxy with the OVN embedded distributed L2 Load Balancer.
- Distributed Gateways: Every Node can act as a Gateway to provide external network connectivity.
- Namespaced Gateways: Every Namespace can have a dedicated Gateway for Egress traffic.
- Direct External Connectivity:Pod IP can be exposed to external network directly.
- Traffic Mirror: Duplicated container network traffic for monitoring and diagnosing.
- IPv6 Support: Kube-OVN supports ipv6-only mode pod network.
- TroubleShooting Tools: Handy tools to diagnose, trace, monitor and dump container network traffic to help troubleshooting complicate network issues.
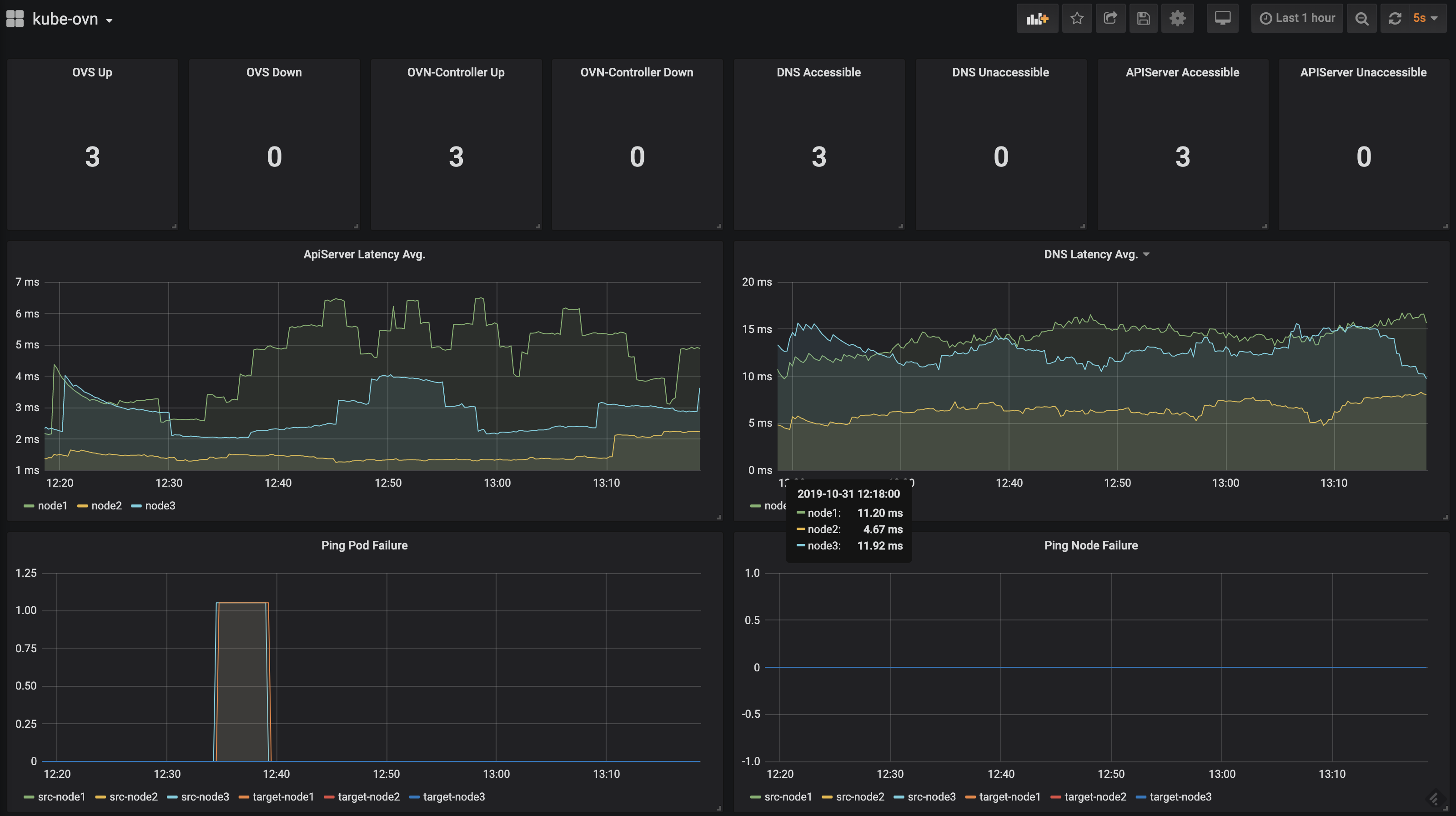
- Prometheus & Grafana Integration: Exposing network quality metrics like pod/node/service/dns connectivity/latency in Prometheus format.
- Hardware Offloading and DPDK Support
- Policy-based QoS
- More Metrics and Traffic Graph
- More Diagnosis and Tracing Tools
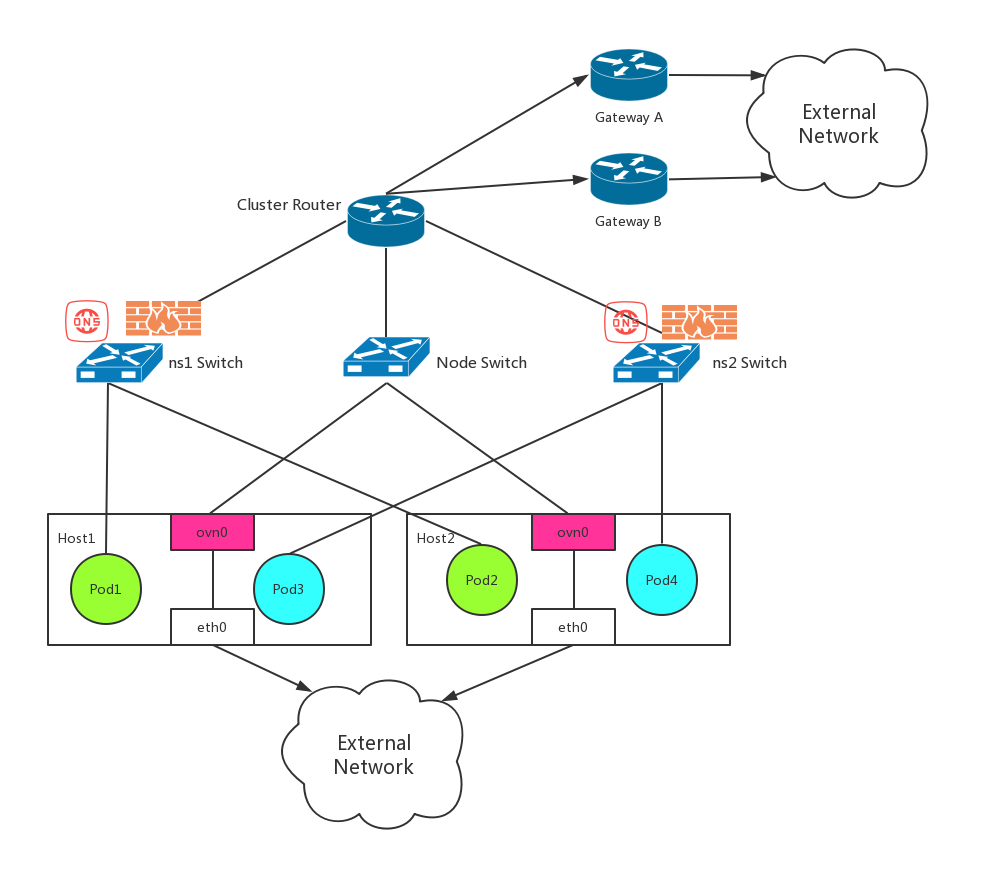
The Switch, Router, Firewall showed in the diagram below are all distributed on all Nodes. There is no single point of failure for in cluster network.
Kube-OVN offers prometheus integration with grafana dashboards to visualise network quality.
Kube-OVN is easy to install with all necessary components/dependencies included. If you already has a Kubernetes cluster without any cni plugin, please refer to the Installation Guide.
If you want to install Kubernetes from scratch, you can try kubespray or for Chinese users try kubeasz to deploy a production ready Kubernetes cluster with Kube-OVN embedded.
- Namespaced Subnets
- Subnet Isolation
- Static IP
- Dynamic QoS
- Gateway and Direct connect
- Traffic Mirror
- Webhook
- IPv6
- Tracing/Diagnose/Dump Traffic with Kubectl Plugin
- Prometheus Integration
Different CNI Implementation has different function scope and network topology. There is no single implementation that can resolve all network problems. In this section, we compare Kube-OVN to some other options to give users a better understanding to assess which network will fit into your infrastructure.
ovn-kubernetes is developed by the ovn community to integration ovn for Kubernetes. As both projects use OVN/OVS as the data plane, they have some same function sets and architecture. The main differences come from the network topology and gateway implementation.
ovn-kubernetes implements a subnet-per-node network topology. That means each node will have a fixed cidr range and the ip allocation is fulfilled by each node when the pod has been invoked by kubelet.
Kube-OVN implements a subnet-per-namespace network topology. That means a cidr can spread the entire cluster nodes, and the ip allocation is done by kube-ovn-controller at a central place. And then kube-ovn can apply lots of network configurations at subnet level, like cidr, gw, exclede_ips, nat and so on. This topology also gives Kube-OVN more ability to control how ip should be allocated, on top of this topology, Kube-OVN can allocate static ip for workloads.
We believe the subnet-per-namespace topology will give more flexibility to evolve the network.
On the gateway side, ovn-kubernetes uses native ovn gateway concept to control the traffic. The native ovn gateway relies on a dedicated nic or needs to transfer the nic ip to another device to bind the nic to the ovs bridge. This implementation can reach better performance, however not all environments meet the network requirement,s especially in the cloud.
Kube-OVN uses policy-route, ipset, and iptables to implement the gateway functions that all by software, which can fit more infrastructure and give more flexibility to more function.
Calico is an open-source networking and network security solution for containers, virtual machines, and native host-based workloads. It's known for its good performance and security policy.
The main difference from the design point is the encapsulation method. Calico use no encapsulation or lightweight IPIP encapsulation and Kube-OVN uses geneve to encapsulate packets. No encapsulation can achieve better network performance for both throughput and latency. However, as this method will expose pod network directly to the underlay network with it comes with the burden on deploy and maintain. In some managed network environment where BGP and IPIP is not allowed, encapsulation is a must.
Use encapsulation can lower the requirement on network, and isolate container and underlay network from logical. We can use the overlay technology to build a much complex network concept, like router, gateway, and vpc. For performance, ovs can make use of hardware offload and DPDK to enhance throughput and latency.
From the function set, Kube-OVN can offer some more abilities like static ip, QoS and traffic mirror. The subnet in Kube-OVN and ippool in Calico share some same function set.
Mail: mengxin#alauda.io
微信交流群请加 liumengxinfly,并注明 Kube-OVN