This repository supports the installation of an Apache Spark Performance Dashboard using containers technology. Use for measuring and troubleshooting Apache Spark applications. Tested with Spark 3.0 and 2.4.
Two different installation options are packaged in this repository, use the one that suits your environment best:
- dockerfiles -> Docker build files for a Docker container image, use this to deploy the Spark Dashboard using Docker.
- charts -> a Helm chart for deploying the Spark Dashboard on Kubernetes.
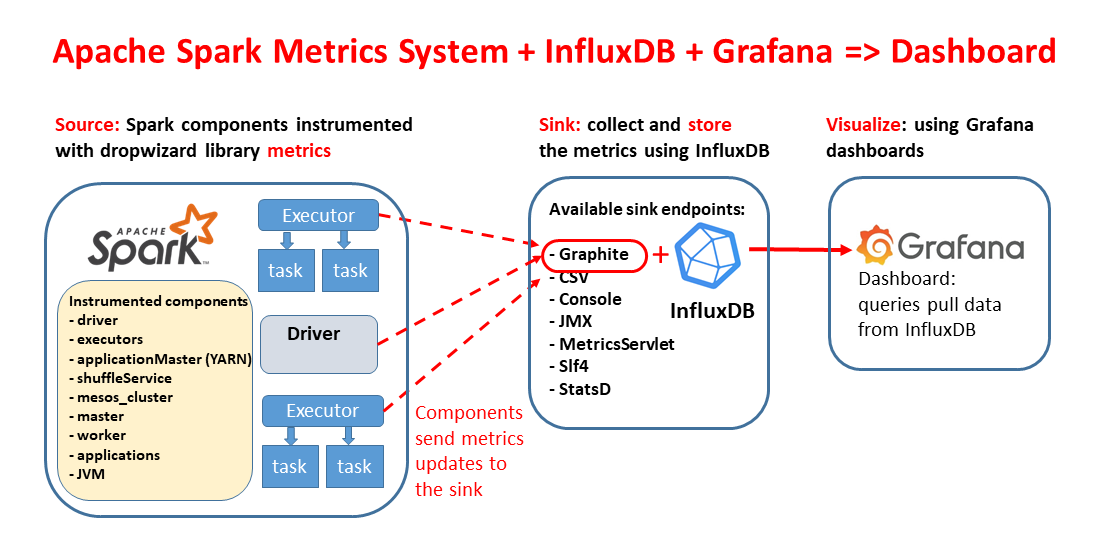
The Spark Dashboard collects and displays Spark workload data exported via the Spark metrics system. Metrics are collected using InfluxDB and displayed using a set of pre-configured Grafana dashboards. Details of how this works at:
- Spark Dashboard Notes
- this blog entry
- Spark Summit Europe 2019 talk
- Data+AI Summit Europe 2020 talk
Note that the provided installation instructions and code are intended as examples for testing and experimenting. Hardening the installation will be necessary for production-quality use.
Authors and contacts: Luca.Canali@cern.ch, Riccardo.Castellotti@cern.ch, additional credits: Michal Bien.
Using Docker:
- Quickstart:
docker run --network=host -d lucacanali/spark-dashboard:v01 - Details: dockerfiles
Using Helm:
- Quickstart:
helm install spark-dashboard https://github.com/cerndb/spark-dashboard/raw/master/charts/spark-dashboard-0.3.0.tgz - Details: charts
You will need to set a few Spark configuration parameter to use this type of instrumentation. In particular, you need to point Spark to write to the InfluxDB instance (to a graphite endpoint).
Docker:
- InfluxDB will use port 2003 (graphite endpoint), and port 8086 (http endpoint) of
your machine/VM (when running using
--network=host). - Note: the endpoints need to be available on the node where you started the Docker container and reachable by Spark executors and driver (mind the firewall).
Helm:
- Find the InfluxDB endpoint IP with
kubectl get service spark-dashboard-influx. Optionally resolve the dns name withnslookupof such IP. For example, the InfluxDB service host name of a test installation is:spark-dashboard-influx.default.svc.cluster.local
Notes:
- More details on how this works and alternative configurations at Spark Dashboard
- The majority of the instrumentation is for the executorSource metrics that are currently only exported when running Spark on a cluster (Kubernets, YARN, Standalone, Mesos). when using this with Spark running in local mode you will only be able to log (and visualize) a smaller subset of metrics,
Example Spark configuration parameters:
# customize, as relevant for your system
INFLUXDB_ENDPOINT=`hostname`
#INFLUXDB_ENDPOINT=spark-dashboard-influx.default.svc.cluster.local
#INFLUXDB_ENDPOINT=10.0.0.1
bin/spark-shell (or spark-submit or pyspark) ...addtitional options...
--conf "spark.metrics.conf.driver.sink.graphite.class"="org.apache.spark.metrics.sink.GraphiteSink" \
--conf "spark.metrics.conf.executor.sink.graphite.class"="org.apache.spark.metrics.sink.GraphiteSink" \
--conf "spark.metrics.conf.driver.sink.graphite.host"=$INFLUXDB_ENDPOINT \
--conf "spark.metrics.conf.executor.sink.graphite.host"=$INFLUXDB_ENDPOINT \
--conf "spark.metrics.conf.*.sink.graphite.port"=2003 \
--conf "spark.metrics.conf.*.sink.graphite.period"=10 \
--conf "spark.metrics.conf.*.sink.graphite.unit"=seconds \
--conf "spark.metrics.conf.*.sink.graphite.prefix"="luca_20200508" \
--conf "spark.metrics.conf.*.source.jvm.class"="org.apache.spark.metrics.source.JvmSource" \
--conf spark.metrics.staticSources.enabled=false \
Optionally, you can add annotation instrumentation to the performance dashboard. This would provide additional info on the queries, jobs and stages start and end times. To activate annotations, add the following additional configuration, needed for collecting and writing extra performance data:
INFLUXDB_HTTP_ENDPOINT="http://`hostname`:8086"
#INFLUXDB_HTTP_ENDPOINT="http://10.0.0.1:8086"
--packages ch.cern.sparkmeasure:spark-measure_2.12:0.16 \
--conf spark.sparkmeasure.influxdbURL=$INFLUXDB_HTTP_ENDPOINT \
--conf spark.extraListeners=ch.cern.sparkmeasure.InfluxDBSink \
Docker:
- The Grafana dashboard is reachable at port 3000 of your machine/VM (when running using
--network=host)
Helm:
- The Grafana dashboard is reachable at port 3000 of the spark-dashboard-service.
See service details:kubectl get service spark-dashboard-grafana
When using NodePort and an internal cluster IP address, this is how you can port forward to the service from the local machine:kubectl port-forward service/spark-dashboard-grafana 3000:3000
Examples:
Notes:
- First logon: use user "admin", with password admin (you can change that after logon)
- Choose one of the provided dashboards (for example Spark_Perf_Dashboard_Spark3-0_v02) and select the user, applicationId and timerange.
- You will need a running Spark application configured to use the dashboard to be able to select and application and display the metrics.
The provided example dashboards are examples based on the authors' usage. Only a subset of the metrics values logged into
InfluxDB are visualized in the provided dashboard.
For a full list of the available metrics see the
documentation of Spark metrics system.
New dashboards can be added by putting them in the relevant grafana_dashboards folder and re-building the container image
(or re-packaging the helm chart).
On Helm: running helm-update is enough to upload it as ConfigMap and make it available to Grafana.
Automatically persisting manual edits is not supported at this time.