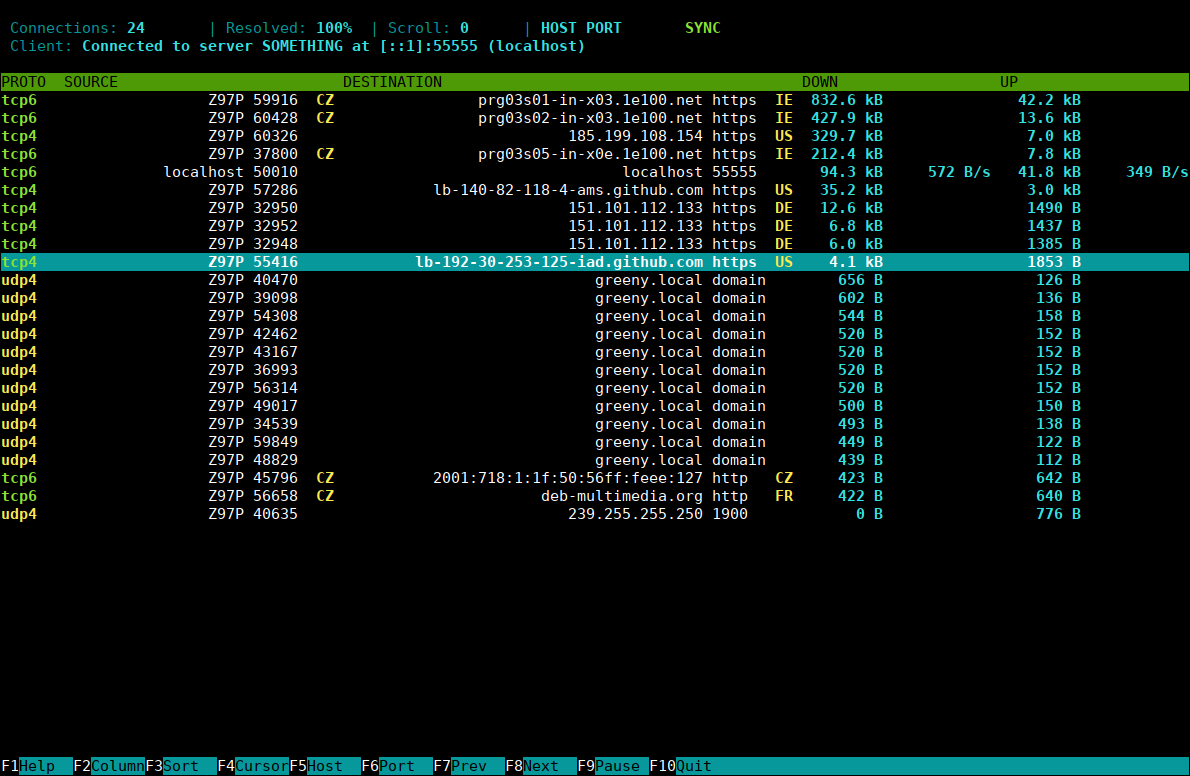
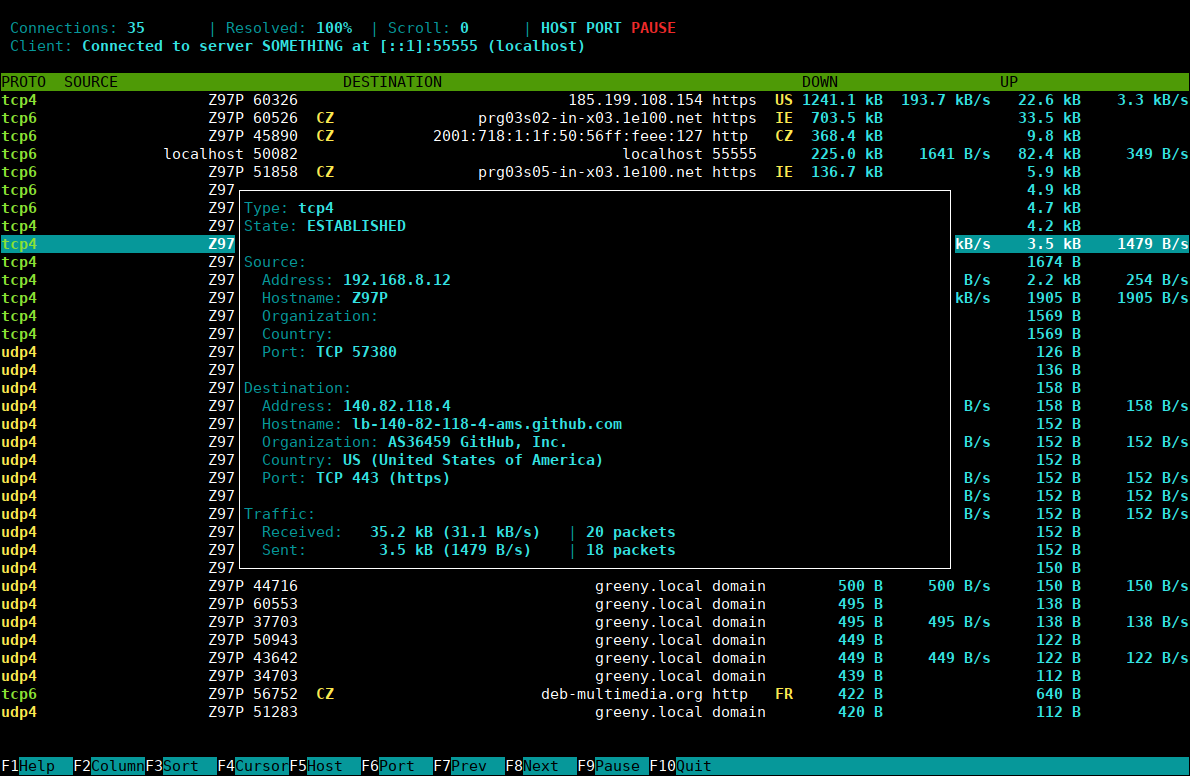
ConnTop is an interactive tool for monitoring network traffic in real-time. It allows user to view and examine active connections on the system. The current version runs only on Linux-based systems, but it's designed as cross-platform tool, so adding support for other platforms in future should be quite easy. Note that this is a fairly new project without long-term testing, so be careful when using it in a production environment.
- Optional client-server mode
- Automatically obtains additional information - hostname, ASN, organization, country, service name
- Uses local GeoIP database to quickly obtain AS and country information
- Uses Netfilter connection tracking table (conntrack) to acquire traffic data effectively
- Terminal UI (curses library) with design inspired by htop
- Connection list updates can be paused at any time, allowing user to inspect currently active connections in detail
- Configurable connection list columns with sort feature
To build it, you need CMake, C++17 compiler (GCC >= 7 or Clang >= 3.9), and the following libraries:
libnetfilter-conntracklibmaxminddbcurses
If you are going to build only dedicated server, libmaxminddb and curses libraries are not required.
You may also need git to obtain the source code from this repository.
On Debian GNU/Linux and its derivatives (Ubuntu, Mint, ...), you can use the following command to install all required tools and libraries:
sudo apt install build-essential cmake git libnetfilter-conntrack-dev libmaxminddb-dev libncurses-dev
Download the source code:
git clone https://github.com/ccomrade/conntop
You can also manually download zip file with the source code and extract it.
Now create empty build directory and move to it:
mkdir conntop-build
cd conntop-build
Generate build files inside the empty build directory with the following command. At this point you can also set various build
options with -D<option>=<value> parameter. See below for list of supported build options.
cmake ../conntop
If the build files were generated successfully, you can now build the source code:
make
The resulting conntop or conntopd executable can be found in the build directory. You can now start using it. If you want to
install it on your system, use the following command:
sudo cp conntop /usr/local/bin/
To install dedicated server executable, use the following command instead:
sudo cp conntopd /usr/local/sbin/
CONNTOP_DEDICATED: Set to1to build conntop dedicated server (conntopd).CONNTOP_USE_OWN_LIBMAXMINDDB: Set to1if your system doesn't providelibmaxminddblibrary.
Complete list of build options provided by CMake can be found here.
Check the following steps before using conntop.
You can skip this step on systems where you want to use only the conntop client.
Linux kernel contains connection tracking table (conntrack) that is used by conntop to acquire traffic data. This table is active only when something inside the kernel requires it. For example, when stateful firewall is enabled. In older versions of Linux kernel, it's possible to activate the connection tracking table by loading its kernel modules. This doesn't work anymore since kernel version 4.14.
So, to activate the connection tracking table, you need to enable firewall (or NAT). If firewall is not already enabled on your
system, you can enable it with iptables or preferably with modern nftables, or
any front-end tool built on top of them. By default, the connection tracking table doesn't provide number of packets and bytes.
To enable it, you need to set the acct parameter of the nf_conntrack kernel module to 1. You can do this, for example, by
creating netfilter.conf file inside /etc/modprobe.d/ with the following content:
options nf_conntrack acct=1
If the connection tracking table is not active, conntop will work but won't be able to obtain any traffic data. Similarly, when
the acct parameter is not set to 1, conntop won't be able to obtain number of received and sent packets and bytes.
You can skip this step on systems where you want to use only the conntop server.
Local GeoIP database is optional and is used to obtain additional information about network addresses. The database is expected in MaxMind DB binary format, and the following paths are used to search for its files:
$HOME/.local/share/GeoIP
/usr/local/share/GeoIP
/var/lib/GeoIP
The current version of conntop can use the following database files:
GeoLite2-Country.mmdb
GeoLite2-ASN.mmdb
To obtain the GeoIP database, geoipupdate tool can be used. On Debian GNU/Linux and its derivatives (Ubuntu, Mint, ...) with enabled contrib packages, you can install it with the following command:
sudo apt install geoipupdate
It periodically checks and downloads database updates. Don't forget to edit its configuration file /etc/GeoIP.conf to enable all
database editions used by conntop.
You can also download the GeoIP database manually from here.
To start monitoring network traffic, simply launch conntop as follows:
sudo conntop
If you are not sure how to control it, press F1.
You can also start conntop server and connect to it with conntop client from another computer. This mode is intended to be used for monitoring network traffic on devices where running whole application is not possible for performance reasons (for example, small computer used as a router). Server can handle multiple clients at once and it only collects traffic data without resolving any additional information or doing any connection list operations that can be done on client.
To launch conntop server, use the following command:
sudo conntop --server
Or use dedicated server:
sudo conntopd
To specify server listen address, use --listen=<address> parameter. You can use this parameter multiple times to specify more
than one listen address. When no listen address is specified, server listens on loopback only. If you want server to listen on
all addresses, use --listen-any parameter instead.
Now with server running, you can start client that connects to it:
conntop --connect=<server-address>
To change port of both client and server, use --port=<port> parameter.
To obtain list of all available command line options with short description, use the following command:
conntop --help
- Connection list group mode
- Connection list ghost mode
- Integrated WHOIS client
- Automatically identify and highlight local and other special addresses
- Resolve process name for local connections
- Add list with local listening sockets and calculate total traffic for each one
- Additional protocols (ICMP, SCTP, ...)
- Network interface statistics mode
- Add pcap API collector
- Manual (man page)
- GUI (probably Qt)
- Shell autocompletion script
- Add static build option
- Add install target rules
- Add support for multi-collector and multi-UI build
- Add unit tests for certain classes
- Windows support + WinAPI GUI
- Improve client-server protocol message parsing (validate each message against JSON schema during parsing)
- Prevent rare exit delay caused by resolver thread blocked in some resolve function (timeout takes few seconds)
- Automatically remove unused addresses and ports on server to save some memory
- Automatically put server to sleep mode when no client is connected and collector is "dumpable"
- Create some modern C++ thing to replace designated initializers (non-standard extension in C++)
- Send modifications of RapidJSON library to upstream (or use another JSON library)
- Add changelog file
This program is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or (at your option) any later version.
This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU General Public License for more details.
You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License along with this program. If not, see https://www.gnu.org/licenses/.