PPBstats is a freely available package based on the R software for
Participatory Plant Breeding statisticial analyses. It performs analyses
on the data collected during PPB programs at four levels:
- network of seed management,
- agronomic trials,
- organoleptic tests and
- molecular analyses.
The objectives of PPBstats are
- to have a single package capable of performing several analyses required for PPB programmes with comprehensive documentation, and
- to create a community working on PPB programmes in order to improve the package, exchange on how to process data from PPB programmes and develop good practices.
library(PPBstats)
Descriptive analysis can be done regarding:
- unipart network for seed lots analysis
- unipart network for location analysis
- bipart network analysis
Below an example on unipart network for seed lots analysis:
# get data
data(data_network_unipart_sl)
# format data for the package
net_unipart_sl = format_data_PPBstats(
type = "data_network",
data = data_network_unipart_sl,
network_part = "unipart",
vertex_type = "seed_lots")
# Display outputs
plot(net_unipart_sl, plot_type = "network", organize_sl = TRUE)
## [[1]]
## [[1]]$network
Other examples can be found in the book.
Statistical analysis can be done
- To compare different germplasms on each location for selection:
- classic anova,
- spatial analysis,
- mixed models,
- bayesian hierarchical model intra-location.
- To study response of germplasm over several locations for selection:
- AMMI and GGE,
- bayesian hierarchical model G×E.
- To study specific research questions on one farm or more
- response to selection
- local adaptation with two models: home away and local foreign
- intra germplasm variance
- To run multivariate analysis
Below an example on GGE model:
# get data
data(data_model_GxE)
# format data for the package
data_model_GxE = format_data_PPBstats(data_model_GxE, type = "data_agro")
Once the data are formated, the model is run
# run the GGE model
out_gge = model_GxE(data_model_GxE, variable = "y1", gxe_analysis = "GGE")
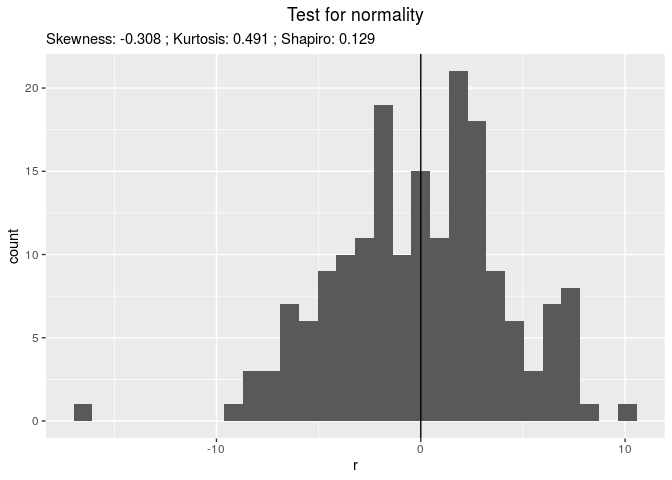
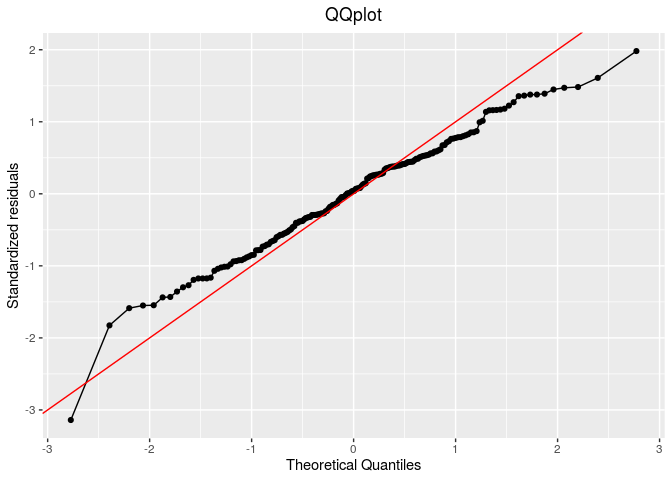
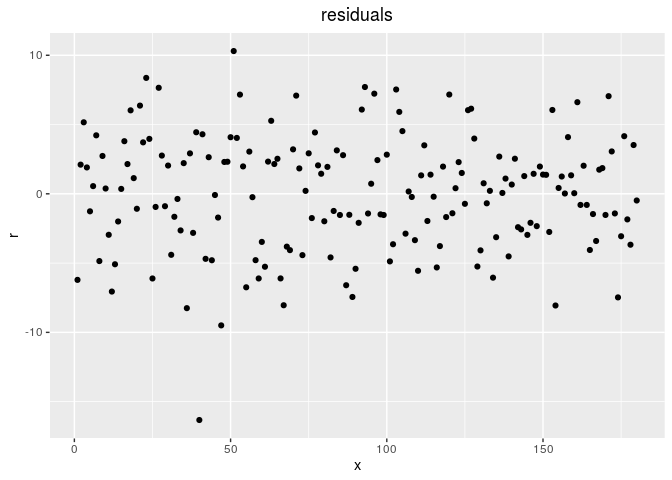
Then, check it, for example with residuals
# check if the model went well
out_check_gge = check_model(out_gge)
p_out_check_gge = plot(out_check_gge)
p_out_check_gge$residuals
## $histogram
##
## $qqplot
##
## $points
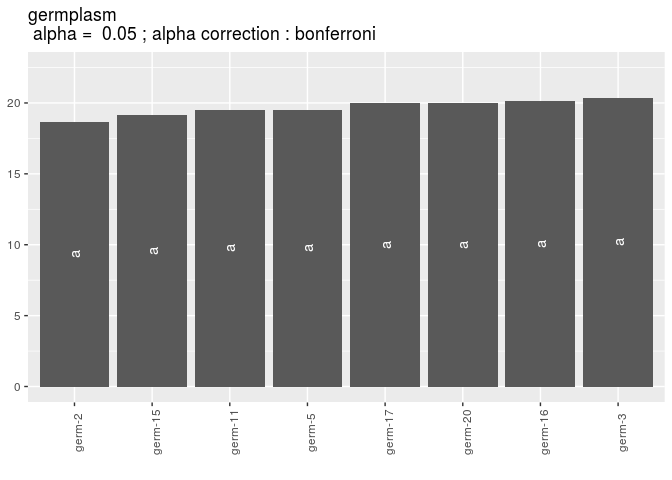
Then, compare means
# get mean comparisons
out_mean_comparisons_gge = mean_comparisons(out_check_gge, p.adj = "bonferroni")
p_out_mean_comparisons_gge = plot(out_mean_comparisons_gge)
p_out_mean_comparisons_gge$germplasm$`1`
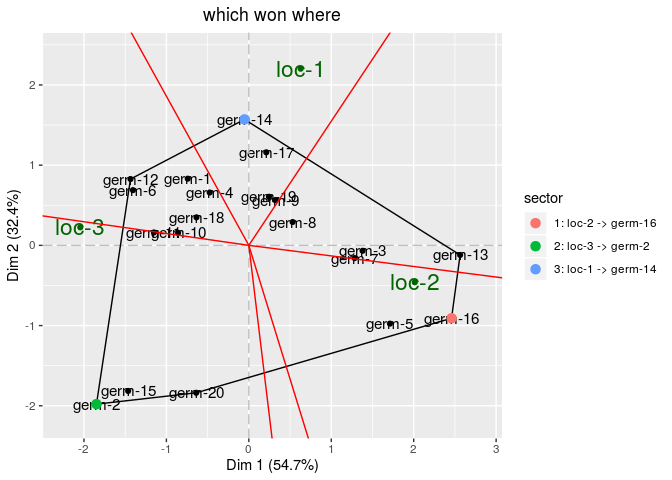
Then, look at biplot
# get biplot
out_biplot_gge = biplot_data(out_check_gge)
p_out_biplot_gge = plot(out_biplot_gge)
p_out_biplot_gge$biplot$which_won_where
Sensory analysis can be done on
- hedonic analysis
- napping analysis
- rank analysis
Below an example on hedonic analysis
# get data
data(data_hedonic)
# format data for the package
data_hedonic = format_data_PPBstats(data_hedonic, type = "data_organo_hedonic", threshold = 2)
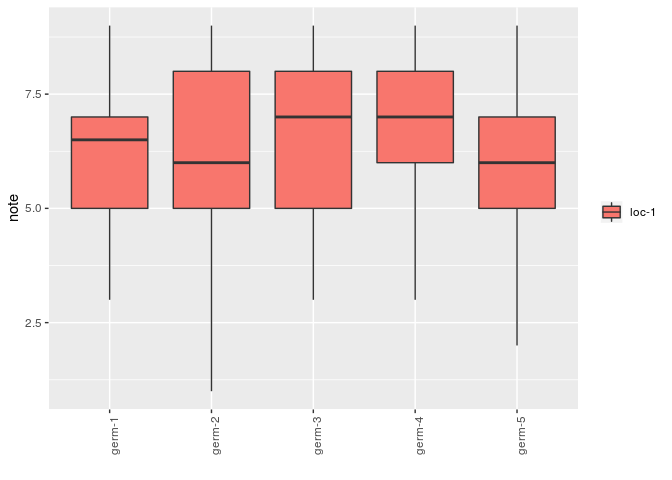
# descriptive analysis
p_note = plot(data_hedonic, plot_type = "boxplot", x_axis = "germplasm",
in_col = "location", vec_variables = "note"
)
p_note$note$`germplasm-1|location-1`
descriptors = data_hedonic$descriptors
p_des = plot(data_hedonic, plot_type = "radar", in_col = "germplasm",
vec_variables = descriptors
)
p_des$`all-variables`
A model can also be run.
Under development …
A full tutorial of PPBstats is available in the book on the website.
Exchange information about the R package PPBstats
You can subscribe to this mailing list to have news on the R package
PPBstats and share questions and remarks
Subscribe : https://framalistes.org/sympa/subscribe/ppbstats