This project implements a simulated IPMI Server and manipulate Oracle VirtualBox VM. The main purpose of this project is to solve that there is not enough server during server provisioning service development, so it maps the relationship between BMC chip (via IPMI) and Virtual Machines, so that the developer can do their test with minimal environment (One machine) if they use IPMI protocol as the tool to manipulate servers in their provisioning service implementation.
Note: This project supports only IPMI v1.5 currently.
- Operations
- Chassis Power On
- Chassis Power Off
- Chassis Power Reset / Cycle
- Chassis Power Soft
- Chassis Set system boot device (PXE, Disk, local CD/DVD)
- App Authentication
- Session Management and Validation
Other operations (e.g. sensor, etc.) will be added if necessary.
- Running
- Oracle VirtualBox 5.x
- Build
- Go 1.6.2
Please make sure that you have installed Go in your environment, and all the environment variable GOBIN, GOPATH, and GOROOT have been setup properly.
Then:
- Get this project source files
$ cd ${GOPATH}/src
$ go get github.com/rmxymh/infra-ecosphere
$ cd infra-ecoshphere- Prepare for dependencies
$ go get github.com/rmxymh/go-virtualbox
$ go get github.com/htruong/go-md2
$ go get github.com/gorilla/mux
$ go get github.com/jmcvetta/napping- Build: infra-ecosphere main package is located at ${GOPATH}/src/github.com/rmxymh/infra-ecosphere/infra-ecosphere
$ go installThen you can find your executable file is under $GOBIN.
Config file is written in json format and it describes the following:
- The relationship between BMC IP address and Oracle VirtualBox VM name
- BMC Account
The format is as the following, and if you want more detailed information about it, you can refer to "Configuration" in utils/config.go, where the structure that stores the configuration:
{
"Nodes": [
{
"BMCIP": <BMC_IP>,
"VMName": <Virtual_Machine_Name>
}
],
"BMCUsers": [
{
"Username": <BMC_Username>,
"Password": <BMC_Password>
}
],
"WebAPIPort": <WEB_API_SERVER_LISTEN_PORT>
}More detailed example:
{
"Nodes": [
{
"BMCIP": "127.0.1.1",
"VMName": "TestVM01"
},
{
"BMCIP": "127.0.1.2",
"VMName": "TestVM02"
},
{
"BMCIP": "127.0.1.3",
"VMName": ""
}
],
"BMCUsers": [
{
"Username": "admin",
"Password": "admin"
}
],
"WebAPIPort": 9090
}It indicate that we have 1 BMC username and password pair, and we have 3 Virtual Machines that we want to map the simulated BMC:
- TestVM01: A Virtual Machine whose simulated BMC IP is 127.0.1.1
- TestVM02: A Virtual Machine whose simulated BMC IP is 127.0.1.2
- Note: we can find that BMC IP 127.0.1.3 maps to empty VMName. This configuration means that 127.0.1.3 maps to a mock VM, and it will response mocked IPMI response messages and does not affect any VM. This function is useful for large-scale IPMI command test.
Here we need to be aware that:
- This project DOESN'T implement any packet forwarding mechanism, and it only implements UDP servers here, so we need to make sure that those IP address can be listened and reachable by your command sender.
- Here we have two suggested methods for assigning BMC IP:
- IP Alias on interfaces in your machine which runs this program.
- Use loopback IP address. (127.0.0.0/8)
After you have prepared for the configuration file in the same path as your executable file, just execute the executable file:
$ cd $GOBIN
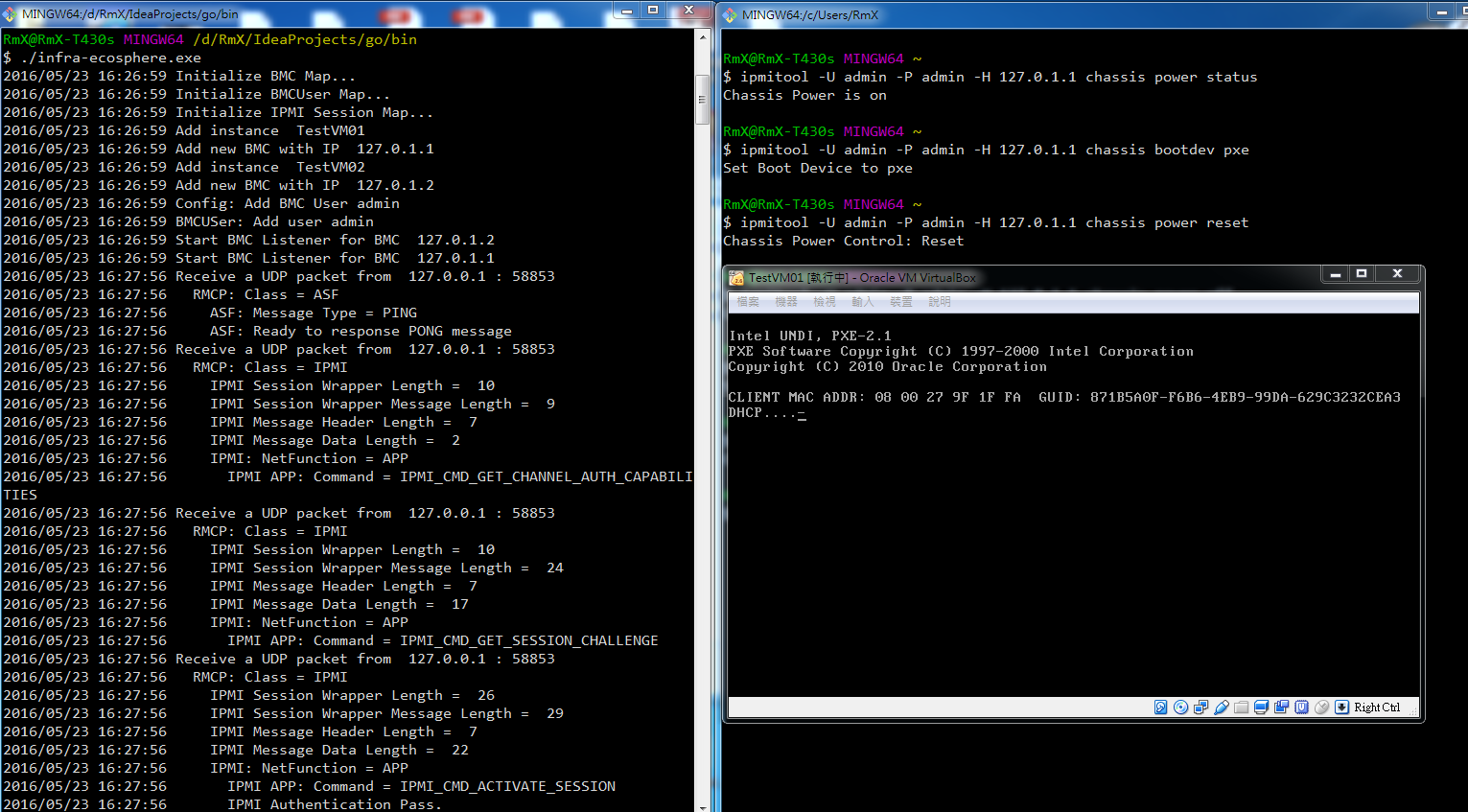
$ ./infra-ecosphereAfter the program is running, you can use IPMI related utilities, such as ipmitool, to operate your VM. For instance:
$ ipmitool -U admin -P admin -H 127.0.1.1 chassis power statusBesides, you can operate VM via REST APIs, and currently this project supports the following APIs:
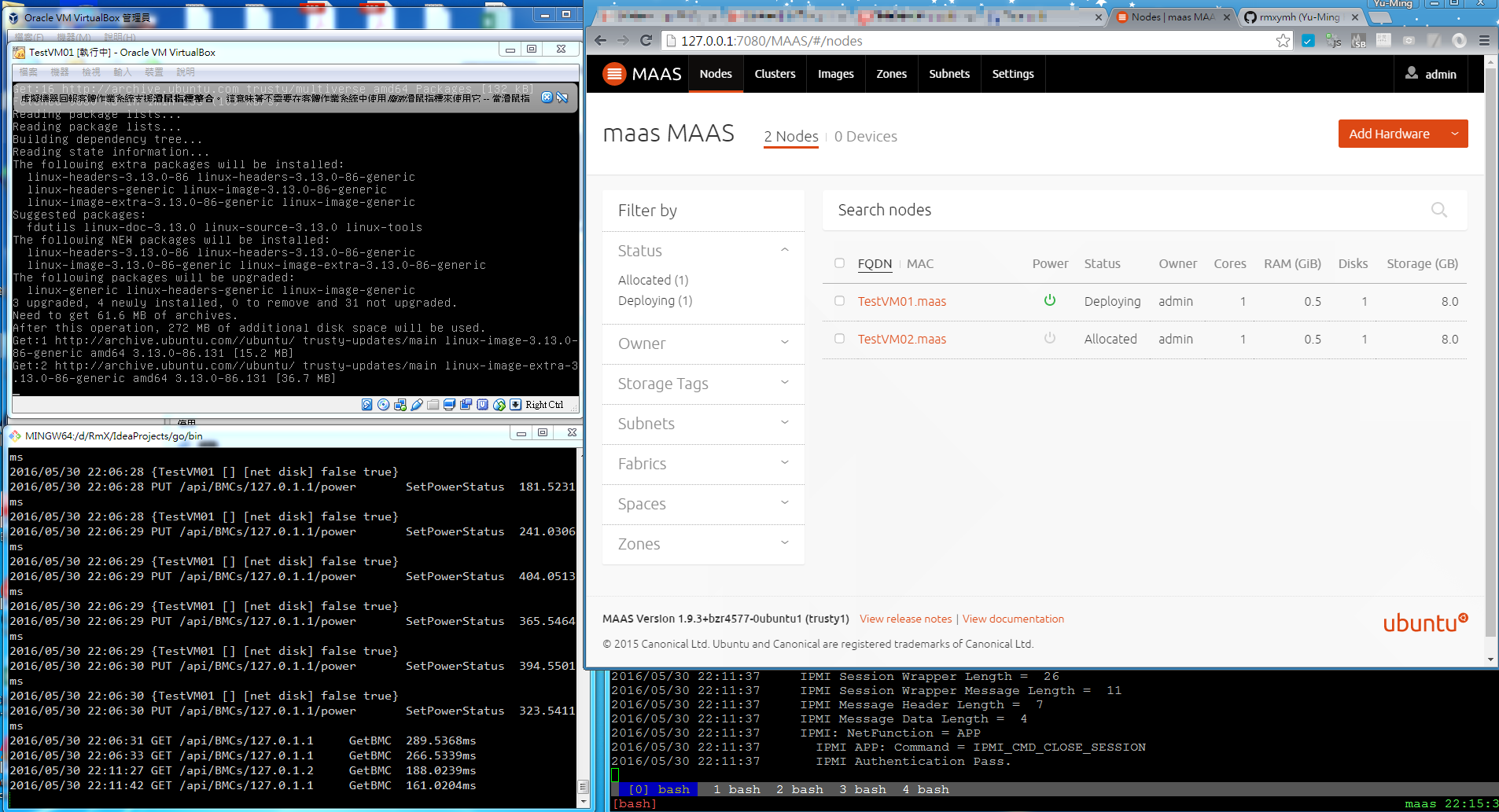
- Get all BMC information: GET /api/BMCs
- Get the information of the specified BMC: GET /api/BMCs/<BMC_IP>
- Send power operation to the BMC: PUT /api/BMCs/<BMC_IP>/power
- Set boot device to the BMC: PUT /api/BMCs/<BMC_IP>/bootdev
For more detailed information, you can find it from Web README.md
If you want to leverage packet deserialize function of ipmi package, you can use the following three function to register your callback:
func IPMI_APP_SetHandler(command int, handler IPMI_App_Handler)
func IPMI_CHASSIS_SetHandler(command int, handler IPMI_Chassis_Handler)
func IPMI_CHASSIS_SET_BOOT_OPTION_SetHandler(command int, handler IPMI_Chassis_BootOpt_Handler)
func IPMI_CHASSIS_GET_BOOT_OPTION_SetHandler(command int, handler IPMI_Chassis_BootOpt_Handler)More detail information can be found at func init() in ipmi_app.go, ipmi_chassis.go, and ipmi_chassis_bootopt.go. For the remaining commands, they may be supported in the future. Besides, if you implement them and have willing to contribute, welcome to make pull request, and we will appreciate your great contributions.
IPMI Proxy is a utility as a proxy which help us to pass the IPMI command out and response the result to the sender.
For more detailed information, you can obtain from this link: IPMI Proxy README.md
- Test cases
This source code are, unless otherwise specified, distributed under the terms of the MIT License.
Copyright (c) 2016 Yu-Ming Huang < rmx.z91@gmail.com >