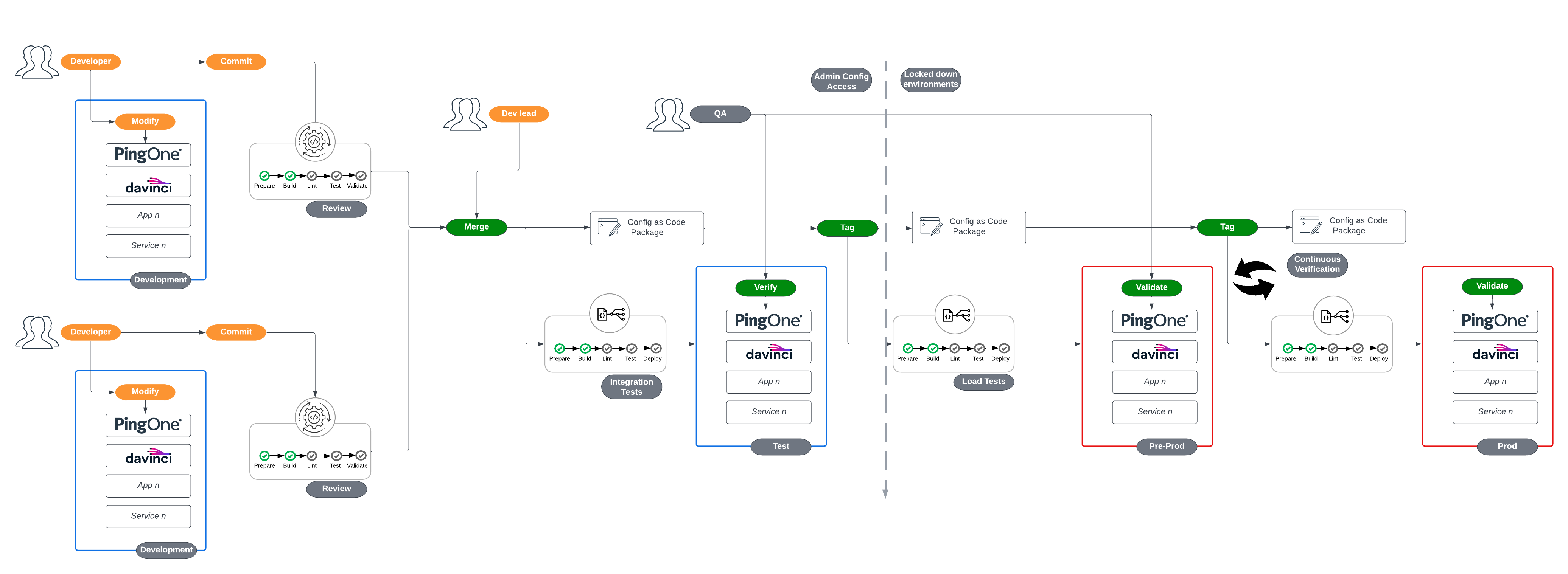
The intention of this repository is to present a simplified reference demonstrating how a CICD pipeline might work for Ping Identity solutions. The configuration managed in this repository covers "platform" components that are complementary to the infrastructure and application example pipeline repositories.
Infrastructure - Components dealing with deploying software onto self-managed Kubernetes infrastructure and any configuration that must be delivered directly via the filesystem.
Platform - Components dealing with deploying configuration to self-managed or hosted services that will be shared and leveraged by upstream applications.
Application - Delivery and configuration of a client application that relies on core services from Platform and Infrastructure.
The use cases and features shown in this repository are an implementation of the guidance provided from Ping Identity's Terraform Best Practices and Getting Started with Configuration Promotion at Ping documents.
In this repository, the processes and features shown in a GitOps process of developing and delivering a new feature include:
- Feature Request Template
- On-demand development environment deployment
- Building a feature in development environment (PingOne UI)
- Extracting feature configuration to be stored as code
- Validating the extracted configuration from the developer perspective
- Validating that the suggested configuration adheres to contribution guidelines
- Review process of suggested change
- Approval of change and automatic deployment into higher environments
After completing the next few sections, you will have the following items configured before you deploy the prod environment into your PingOne account for the first time:
A worker application in the "Administrators" environment of PingOne (you can use another environment if you choose). This worker application will have the following roles:
Environment Adminfor your organizationOrganization Adminfor your organizationIdentity Data Adminfor the environments necessary, which are the environment in which the application is located (Administrators in this example), and the Davinci Administrator environment where the Davinci Admin User is located. As new environments are created by the pipeline, this application will be granted this role in those environments as well.
Information needed from this application (Applications > Applications > <application_name> > Overview):
Client ID- This value will be assigned to TF_VAR_pingone_client_id in the localsecrets file (line 2)Client Secret- This value will be assigned to TF_VAR_pingone_client_secret in the localsecrets file (line 3)Environment ID- This value will be assigned to TF_VAR_pingone_environment_id in the localsecrets file (line 4)
Information needed from the environment in which the application resides (Environment > Settings > Environment Properties):
Region- This value will be assigned to TF_VAR_pingone_region in the localsecrets file (line 5)License ID- This value will be assigned to TF_VAR_pingone_license_id in the localsecrets file (line 6)
An environment with the following characteristics:
- PingOne SSO and PingOne DaVinci services enabled
- A group for Davinci Administrators with the 'DaVinci Admin' role for the DaVinci Administrator environment
- A user in the Davinci Administrator environment that is a member of the Davinci Administrators group
Information needed from the user in the Davinci Administrator environment (Directory > Users > <user_name>):
Username- This value will be assigned to TF_VAR_pingone_username in the localsecrets file (line 8)Password- This value will be assigned to TF_VAR_pingone_password in the localsecrets file (line 9). This password is created when you create and confirm the user.
Information needed from the environment in which the application resides (Environment > Settings > Environment Properties):
Environment ID- This value will be assigned to TF_VAR_davinci_environment_id in the localsecrets file (line 10)
Information needed from the group in the Davinci Administrator environment (Directory > Groups > <group_name>):
Group ID- This value will be assigned to TF_VAR_pingone_davinci_terraform_group_id in the localsecrets file (line 12)
An AWS S3 bucket for storing Terraform state, and a user with permissions as specified in the Terraform documentation for an S3 backend.
Note -The bucket should have folders for prod, qa and dev before your first pipeline attempt.
Information needed from the AWS S3 bucket and user:
AWS Access Key ID- This value for the user will be assigned to AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID in the localsecrets file (line 14)AWS Secret Access Key- This value for the user will be assigned to AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY in the localsecrets file (line 15)Bucket Name- This value will be assigned to TF_VAR_tf_state_bucket in the localsecrets file (line 17)Bucket region- This value will be assigned to TF_VAR_tf_state_region in the localsecrets file (line 19)
To be successful in recreating the use cases supported by this pipeline, there are initial steps that should be completed prior to configuring this repository:
- A PingOne trial or paid account configured according to the PingOne Terraform access and DaVinci Terraform access guidelines.
Note - For PingOne, meeting these requirements means you should have credentials for a worker app residing in the "Administrators" environment that has organization-level scoped roles. For DaVinci, you should have credentials for a user in a non-"Administrators" environment that is part of a group specifically intended to be used by command-line tools or APIs with environment-level scoped roles. This demonstration will add roles to the DaVinci command-line group and will fail if roles are not scoped properly.
Click the Use this template button at the top right of this page to create your own repository. After the repository is created, clone it to your local machine to continue. The rest of this guide will assume you are working from the root of the cloned repository.
Note - A pipeline will run and fail when the repository is created. This result is expected as the pipeline is attempting to deploy and the necessary configuration has not been performed.
The use cases in this repository follow the flow in this diagram:
There are a few items to configure before you can use this repository effectively.
In order to avoid committing private information stored in terraform state to a code repository such as Github, and to have an efficient developer experience, it is a best practice to use a remote backend for Terraform state. As such, this example uses AWS S3 for remote state management.
To avoid potential conflicts, there is no default information provided in this repository for the S3 bucket. The bucket name and region must be configured in the following files:
- Your localsecrets file (see the Github Actions Secrets section below)
- scripts/local_feature_deploy.sh
Details on appropriate permissions for the S3 bucket and corresponding AWS IAM user can be found on Hashicorp's S3 Backend documentation
The Github cli: gh will need to be configured for your repository. Run the command gh auth login and follow the prompts. You will need an access token for your Github account as instructed:
gh auth login
? What account do you want to log into? GitHub.com
? You're already logged into github.com. Do you want to re-authenticate? Yes
? What is your preferred protocol for Git operations? HTTPS
? Authenticate Git with your GitHub credentials? Yes
? How would you like to authenticate GitHub CLI? Paste an authentication token
Tip: you can generate a Personal Access Token here https://github.com/settings/tokens
The minimum required scopes are 'repo', 'read:org', 'workflow'.
? Paste your authentication token: ****************************************
- gh config set -h github.com git_protocol https
✓ Configured git protocol
✓ Logged in as <User>The Github pipeline actions will depend on sourcing some secrets as ephemeral environment variables. To prepare the secrets in the repository:
cp secretstemplate localsecretsFill in localsecrets accordingly.
Note,
secretstemplateis intended to be a template file,localsecretsis a file that contains credentials but is part of .gitignore and should never be committed into the repository.
Run the following to upload localsecrets to Github:
_secrets="$(base64 -i localsecrets)"
gh secret set --app actions TERRAFORM_ENV_BASE64 --body $_secrets
unset _secretsNote - On a Mac, if you have installed the base64 application using brew, there will be a file content failure in the pipeline stemming from the first command shown above. Use the default version of base64 by specifying the path explicitly:
_secrets="$(/usr/bin/base64 -i localsecrets)"
The final step before creating new features is to deploy the static environments prod and qa.
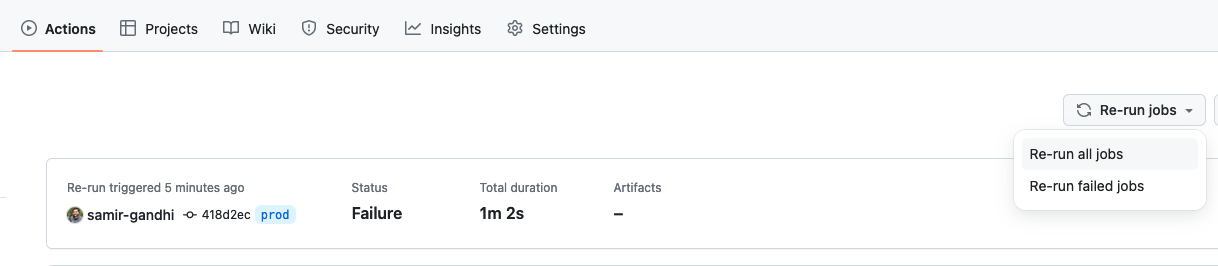
Under the Actions section in Github, locate the failed Initial commit workflow run from the creation of the repository. Click "Re-run jobs" and choose "Re-run all jobs". If your secrets are configured correctly, this should result in the successful deployment of a new environment named "prod" in your PingOne account.
To deploy the qa environment, simply create and push a new branch from prod with the name qa:
git checkout prod
git pull origin prod
git checkout -b qa
git push origin qaNow that the repository and pipeline are configured, the standard git flow can be followed. To experience the developer's perspective, the following steps will revolve around the use case of adding a new OIDC web application configuration into the PingOne production environment.
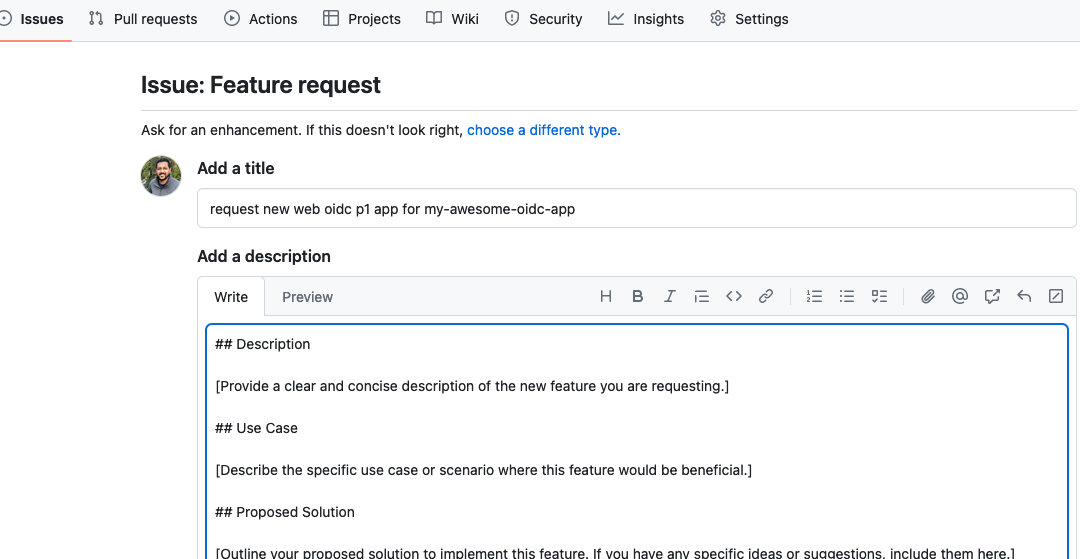
- Create a GitHub Issue for a new feature request via the UI. GitHub Issue Templates help ensure the requestor provides appropriate information on the issue. Note: The GitHub issue name will be used to create the PingOne environment.
- Click "Create a branch" and choose "Checkout Locally" for GitHub to create a development branch and PingOne environment on your behalf.
-
After the Github Actions pipeline completes, log in to your PingOne account with a user that has appropriate roles. This user may be the organization administrator with which you signed up for the trial or a development user if you have configured roles for it. PingOne should show a new environment with a name similar to your GitHub issue title.
-
Build the requested configuration by navigating into the environment: Applications > Applications > Click the blue + and provide the information:
- Application Name: my-awesome-oidc-web-app
- Application Type: OIDC Web App
-
Click Save and toggle the Enable switch. On the screen where the application is enabled, the Environment ID and application Client ID will also be shown. Capture these for use in the import process.
-
Typically the next step would be to provide the application details to the developer team for testing. This process is skipped in here for brevity.
-
After the application creation is "tested" manually, the new configuration must be added to the Terraform configuration. This addition will happen in a few steps, starting with creating and testing the configuration in the
./terraform/devfolder.
a. Terraform provides a tool to help generate configuration for resources built directly in the environment. To leverage this tool as a developer, an import block will be added to ./terraform/dev/imports.tf. Create this file now, adding lines similar to the following:
import {
to = pingone_application.my_awesome_oidc_web_app
id = "environment_id/client_id"
}Note: This file is not intended to be committed to Github and is included in .gitignore. To understand the values to be provided in the id attribute of any resource, the developer should refer to that resources documentation on registry.terraform.io.
b. Run the generate command to generate output. In this repo, the generate command is wrapped in the deploy script:
./scripts/local_feature_deploy.sh --generateWARNING! Be sure you have updated the local_feature_deploy.sh script to include the correct values for the bucket_name and region variables.
This command will create a file with the generated output at ./terraform/dev/generated-platform.tf
However, the command line should have also returned an error similar to the following:
Planning failed. Terraform encountered an error while generating this plan.
╷
│ Error: expected refresh_token_duration to be in the range (60 - 2147483647), got 0
│
│ with pingone_application.my_awesome_oidc_web_app,
│ on generated-platform.tf line 22:
│ (source code not available)
│
╵
╷
│ Error: expected refresh_token_rolling_duration to be in the range (60 - 2147483647), got 0
│
│ with pingone_application.my_awesome_oidc_web_app,
│ on generated-platform.tf line 23:
│ (source code not available)
Terraform's import feature may frequently return errors due to complications with resource schemas. When this occurs the developer is typically able to correct the issue by reading the error.
c. To resolve the error, two attributes in the generated configuration must be updated:
refresh_token_duration = 0
refresh_token_rolling_duration = 0becomes
refresh_token_duration = 60
refresh_token_rolling_duration = 60d. After correcting the generated configuration, run the script again to import the resource into terraform's managed state:
./scripts/local_feature_deploy.sh
Initializing the backend...
Initializing modules...
... trimmed extra lines ...
support_unsigned_request_object = false
token_endpoint_authn_method = "CLIENT_SECRET_BASIC"
type = "WEB_APP"
}
}
Plan: 1 to import, 0 to add, 1 to change, 0 to destroy.
Do you want to perform these actions?
Terraform will perform the actions described above.
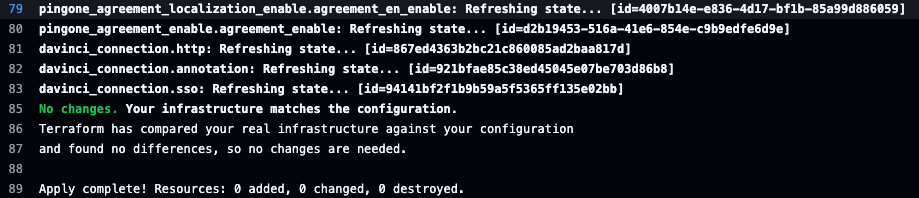
Only 'yes' will be accepted to approve.e. Accept the plan by typing yes and allow it to complete. When finished, the deploy script can be run again to confirm there are no missed changes and signal that this configuration is ready to move into the base module.
- Copy the new configuration into the base module at
/terraform/pingone_platform.tf. Note, because this configuration is general for each environment, the environment_id attribute must be updated accordingly. The final new resource should look similar to:
resource "pingone_application" "my_awesome_oidc_web_app" {
access_control_role_type = null
description = null
enabled = true
environment_id = pingone_environment.target_environment.id
hidden_from_app_portal = false
login_page_url = null
name = "my awesome oidc web app"
tags = []
oidc_options {
additional_refresh_token_replay_protection_enabled = true
allow_wildcards_in_redirect_uris = false
grant_types = ["AUTHORIZATION_CODE"]
home_page_url = null
initiate_login_uri = null
jwks = null
jwks_url = null
par_requirement = "OPTIONAL"
par_timeout = 60
pkce_enforcement = "OPTIONAL"
post_logout_redirect_uris = []
redirect_uris = []
refresh_token_duration = 60
refresh_token_rolling_duration = 60
refresh_token_rolling_grace_period_duration = 0
require_signed_request_object = false
response_types = ["CODE"]
support_unsigned_request_object = false
target_link_uri = null
token_endpoint_authn_method = "CLIENT_SECRET_BASIC"
type = "WEB_APP"
}
}- A
git statuscommand should show the file changed with your new configuration:
git status
On branch 1-request-new-web-oidc-p1-app-for-my-awesome-oidc-app
Your branch is ahead of 'origin/1-request-new-web-oidc-p1-app-for-my-awesome-oidc-app' by 1 commit.
(use "git push" to publish your local commits)
Changes not staged for commit:
(use "git add <file>..." to update what will be committed)
(use "git restore <file>..." to discard changes in working directory)
modified: terraform/pingone_platform.tf
no changes added to commit (use "git add" and/or "git commit -a")- Before committing and pushing changes to GitHub, it is important to run the local development validations to ensure the proposed configuration meets the defined standards. In this case, those validates are called via
make devcheck:
make devcheck
==> Formatting Terraform code with terraform fmt...
==> Checking Terraform code with terraform fmt...
==> Validating Terraform code with terraform validate...
Success! The configuration is valid.
==> Checking Terraform code with tflint...
==> Checking Terraform code with trivy...
2024-04-10T00:34:09.630-0600 INFO Misconfiguration scanning is enabled
2024-04-10T00:34:13.544-0600 INFO Detected config files: 7- Now that the configuration is completely ready, perform the typical file management cycle: git add, git commit, and git push the changes to GitHub. This push to GitHub will trigger the "Feature Deploy Push" action. However, if you inspect the
Deploystep, there should be no change needed because your local environment is using the same remote backend terraform state as the pipeline, so the pushed change to the feature branch matches what was created by running the local deploy script.
Note - From this point forward, the configuration deployment should not include any more manual changes in the UI of higher environments. PingOne Administrators or Developers may have access to the UI, but it should be for reviewing, not making, changes.
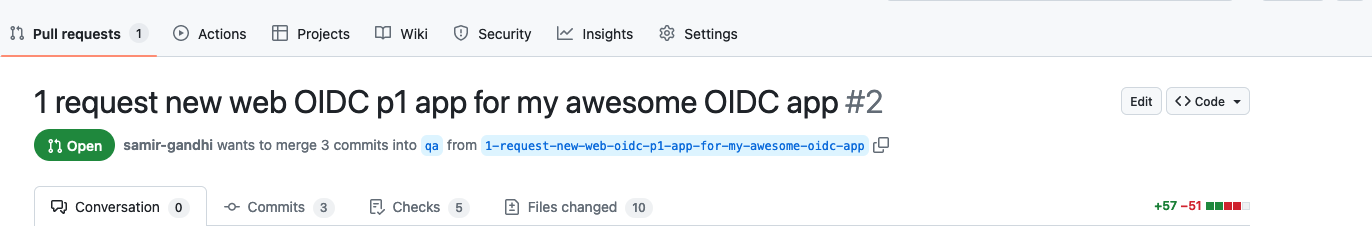
- Open a Pull request for the feature branch to be merged into the qa branch. This pull request will trigger an action that runs validations similar to what occured in
make devcheckas well as an importantterraform plancommand. The result of the terraform plan is what the reviewer of the pull request should focus on. In this case, the plan should show one new resource would be created if the pull request is merged.
-
When satisfied with the code review, merge the pull request into the qa branch. This merge triggers an action that will deploy the new change.
-
Finally, to get the feature into the production environment, the same pull request, review, and merge process will occur. The only difference in this situation is merging the qa branch into the prod branch.
-
After the merge to prod finishes and is the issue is considered complete, the GitHub isssue can be closed and the development branch can be deleted. When the development branch is deleted, a GitHub Action will be triggered to delete the corresponding PingOne Environment leaving only the qa and prod environments relevant to this example.