This simple test bed is for testing encrypted UDP messages from client and server
using python asyncio tools.
usage: udp-server [-h] [--channel-name-1 CHANNEL_NAME_1] [--channel-key-1 CHANNEL_KEY_1] [--channel-port-1 CHANNEL_PORT_1] [--channel-address-1 CHANNEL_ADDRESS_1]
[--channel-direction-1 CHANNEL_DIRECTION_1] [--channel-send-port-1 CHANNEL_SEND_PORT_1] [--channel-send-address-1 CHANNEL_SEND_ADDRESS_1]
[--channel-name-2 CHANNEL_NAME_2] [--channel-key-2 CHANNEL_KEY_2] [--channel-port-2 CHANNEL_PORT_2] [--channel-address-2 CHANNEL_ADDRESS_2]
[--channel-direction-2 CHANNEL_DIRECTION_2] [--channel-send-port-2 CHANNEL_SEND_PORT_2] [--channel-send-address-2 CHANNEL_SEND_ADDRESS_2]
[--channel-name-3 CHANNEL_NAME_3] [--channel-key-3 CHANNEL_KEY_3] [--channel-port-3 CHANNEL_PORT_3] [--channel-address-3 CHANNEL_ADDRESS_3]
[--channel-direction-3 CHANNEL_DIRECTION_3] [--channel-send-port-3 CHANNEL_SEND_PORT_3] [--channel-send-address-3 CHANNEL_SEND_ADDRESS_3]
Example UDP server application
options:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
channel-1:
--channel-name-1 CHANNEL_NAME_1
name of the channel on index 1
--channel-key-1 CHANNEL_KEY_1
key of the channel on index 1
--channel-port-1 CHANNEL_PORT_1
port for channel on index 1
--channel-address-1 CHANNEL_ADDRESS_1
address for channel on index 1
--channel-direction-1 CHANNEL_DIRECTION_1
direction of channel on index 1
--channel-send-port-1 CHANNEL_SEND_PORT_1
send data to port from channel on index 1
--channel-send-address-1 CHANNEL_SEND_ADDRESS_1
send data to address from channel on index 1
channel-2:
--channel-name-2 CHANNEL_NAME_2
name of the channel on index 2
--channel-key-2 CHANNEL_KEY_2
key of the channel on index 2
--channel-port-2 CHANNEL_PORT_2
port for channel on index 2
--channel-address-2 CHANNEL_ADDRESS_2
address for channel on index 2
--channel-direction-2 CHANNEL_DIRECTION_2
direction of channel on index 2
--channel-send-port-2 CHANNEL_SEND_PORT_2
send data to port from channel on index 2
--channel-send-address-2 CHANNEL_SEND_ADDRESS_2
send data to address from channel on index 2
channel-3:
--channel-name-3 CHANNEL_NAME_3
name of the channel on index 3
--channel-key-3 CHANNEL_KEY_3
key of the channel on index 3
--channel-port-3 CHANNEL_PORT_3
port for channel on index 3
--channel-address-3 CHANNEL_ADDRESS_3
address for channel on index 3
--channel-direction-3 CHANNEL_DIRECTION_3
direction of channel on index 3
--channel-send-port-3 CHANNEL_SEND_PORT_3
send data to port from channel on index 3
--channel-send-address-3 CHANNEL_SEND_ADDRESS_3
send data to address from channel on index 3
Example:
Launch an encryption channel:
udp-server \
--channel-name-1 SA1 \
--channel-key-1 my-secret-key \
--channel-direction-1 encrypt \
--channel-address-1 127.0.0.1 \
--channel-port-1 5005 \
--channel-send-address-1 127.0.0.1 \
--channel-send-port-1 5025
2024-04-02 19:40:26,423 udp.channel [INFO] Running SA1 for encrypt on 127.0.0.1:5005 -> 127.0.0.1:5025
2024-04-02 19:40:26,424 udp.channel [INFO] Channel SA1 is connected
In separate terminal, launch a receive client:
udp-client \
--channel-name SA1 \
--channel-key my-secret-key \
--channel-direction encrypt \
--channel-address 127.0.0.1 \
--channel-port 5025 \
--channel-function receive
2024-04-02 19:40:59,141 udp.channel [INFO] Channel SA1 is connected
2024-04-02 19:41:12,073 udp.client.__main__ [INFO] Data received from ('127.0.0.1', 5005)
2024-04-02 19:41:12,075 udp.client.__main__ [INFO] Data received was "Channel message 3ff14f5a-c663-45d4-8f84-17e54d2c4033 from SA1 on 1712101272"
2024-04-02 19:41:13,073 udp.client.__main__ [INFO] Data received from ('127.0.0.1', 5005)
2024-04-02 19:41:13,073 udp.client.__main__ [INFO] Data received was "Channel message 95ff6e3c-1bad-44af-9346-28320cd2cdbc from SA1 on 1712101273"
2024-04-02 19:41:14,075 udp.client.__main__ [INFO] Data received from ('127.0.0.1', 5005)
2024-04-02 19:41:14,076 udp.client.__main__ [INFO] Data received was "Channel message e4192b60-3049-4456-95a6-c3de69b70689 from SA1 on 1712101274"
In a separate terminal, launch a send client:
udp-client \
--channel-name SA1 \
--channel-key my-secret-key \
--channel-direction decrypt \
--channel-address 127.0.0.1 \
--channel-port 5005 \
--channel-function send
Once the send client is activated, you will see messages propagate:
Receiver
2024-04-02 19:40:59,141 udp.channel [INFO] Channel SA1 is connected
2024-04-02 19:41:12,075 udp.client.__main__ [INFO] Data received was "Channel message 3ff14f5a-c663-45d4-8f84-17e54d2c4033 from SA1 on 1712101272"
2024-04-02 19:41:13,073 udp.client.__main__ [INFO] Data received was "Channel message 95ff6e3c-1bad-44af-9346-28320cd2cdbc from SA1 on 1712101273"
2024-04-02 19:41:14,076 udp.client.__main__ [INFO] Data received was "Channel message e4192b60-3049-4456-95a6-c3de69b70689 from SA1 on 1712101274"
Sender
2024-04-02 19:41:12,070 udp.channel [INFO] Channel SA1 is connected
2024-04-02 19:41:12,070 udp.client.__main__ [INFO] Sending Channel message 3ff14f5a-c663-45d4-8f84-17e54d2c4033 from SA1 on 1712101272
2024-04-02 19:41:13,072 udp.client.__main__ [INFO] Sending Channel message 95ff6e3c-1bad-44af-9346-28320cd2cdbc from SA1 on 1712101273
2024-04-02 19:41:14,074 udp.client.__main__ [INFO] Sending Channel message e4192b60-3049-4456-95a6-c3de69b70689 from SA1 on 1712101274
This trivial example demonstrates a sender sending plain text data to the server, which routes encrypted data to the receiver. The receiver with knowledge of how to decrypt the data. Now change the SA on the server:
2024-04-02 19:46:48,178 udp.channel [INFO] Channel SA1 is connected
2024-04-02 19:46:51,854 udp.client.__main__ [INFO] Data received from ('127.0.0.1', 5005)
Exception in callback _SelectorDatagramTransport._read_ready()
handle: <Handle _SelectorDatagramTransport._read_ready()>
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "/usr/lib/python3.10/asyncio/events.py", line 80, in _run
self._context.run(self._callback, *self._args)
File "/usr/lib/python3.10/asyncio/selector_events.py", line 1035, in _read_ready
self._protocol.datagram_received(data, addr)
File "/home/philcali/code/udp-sandbox/udp/client/__main__.py", line 20, in datagram_received
output = self.decrypt(data)
File "/home/philcali/code/udp-sandbox/udp/channel/__init__.py", line 56, in decrypt
plaintext = aes.decrypt_and_verify(
File "/home/philcali/.local/lib/python3.10/site-packages/Crypto/Cipher/_mode_gcm.py", line 567, in decrypt_and_verify
self.verify(received_mac_tag)
File "/home/philcali/.local/lib/python3.10/site-packages/Crypto/Cipher/_mode_gcm.py", line 508, in verify
raise ValueError("MAC check failed")
ValueError: MAC check failed
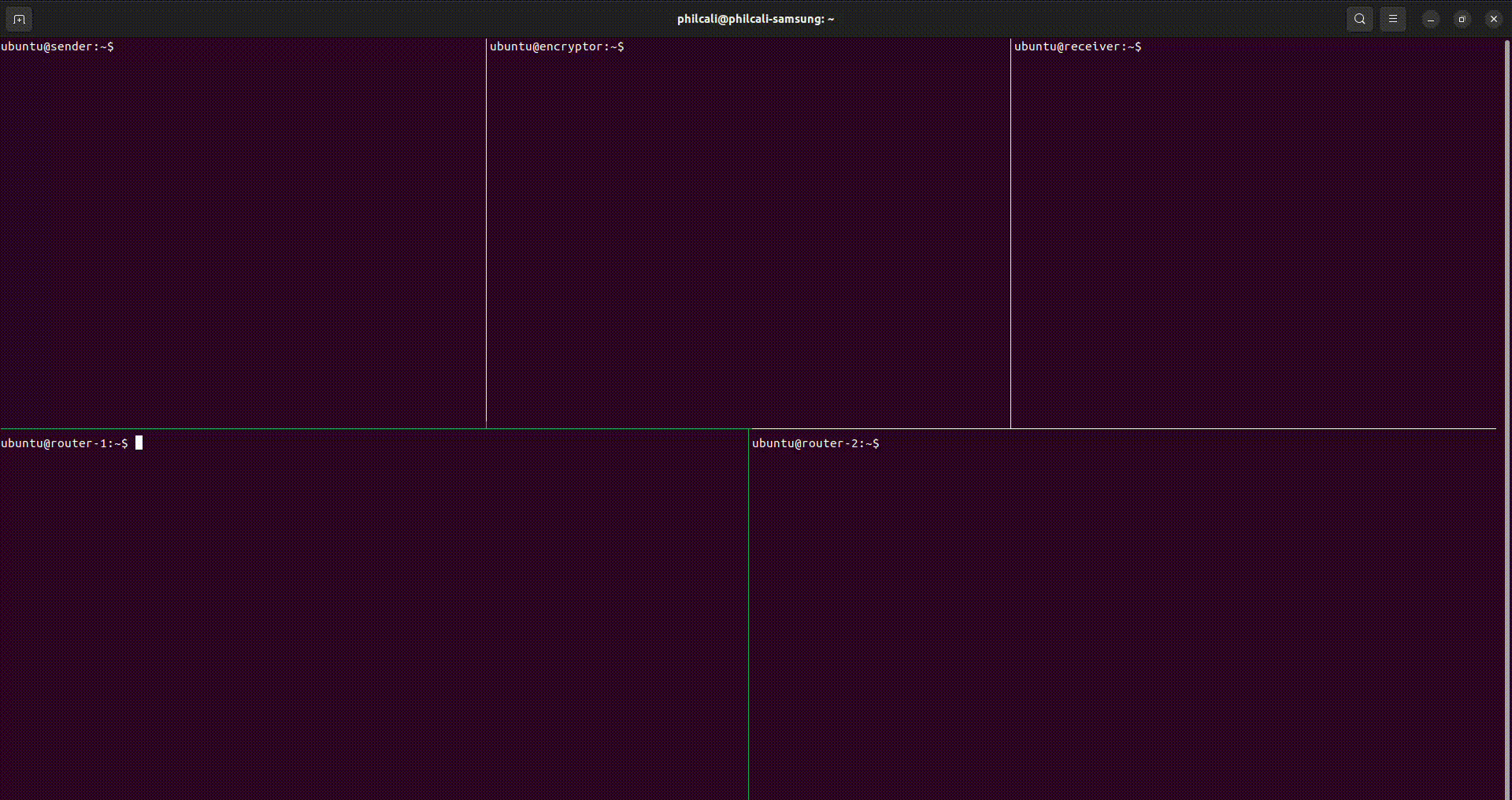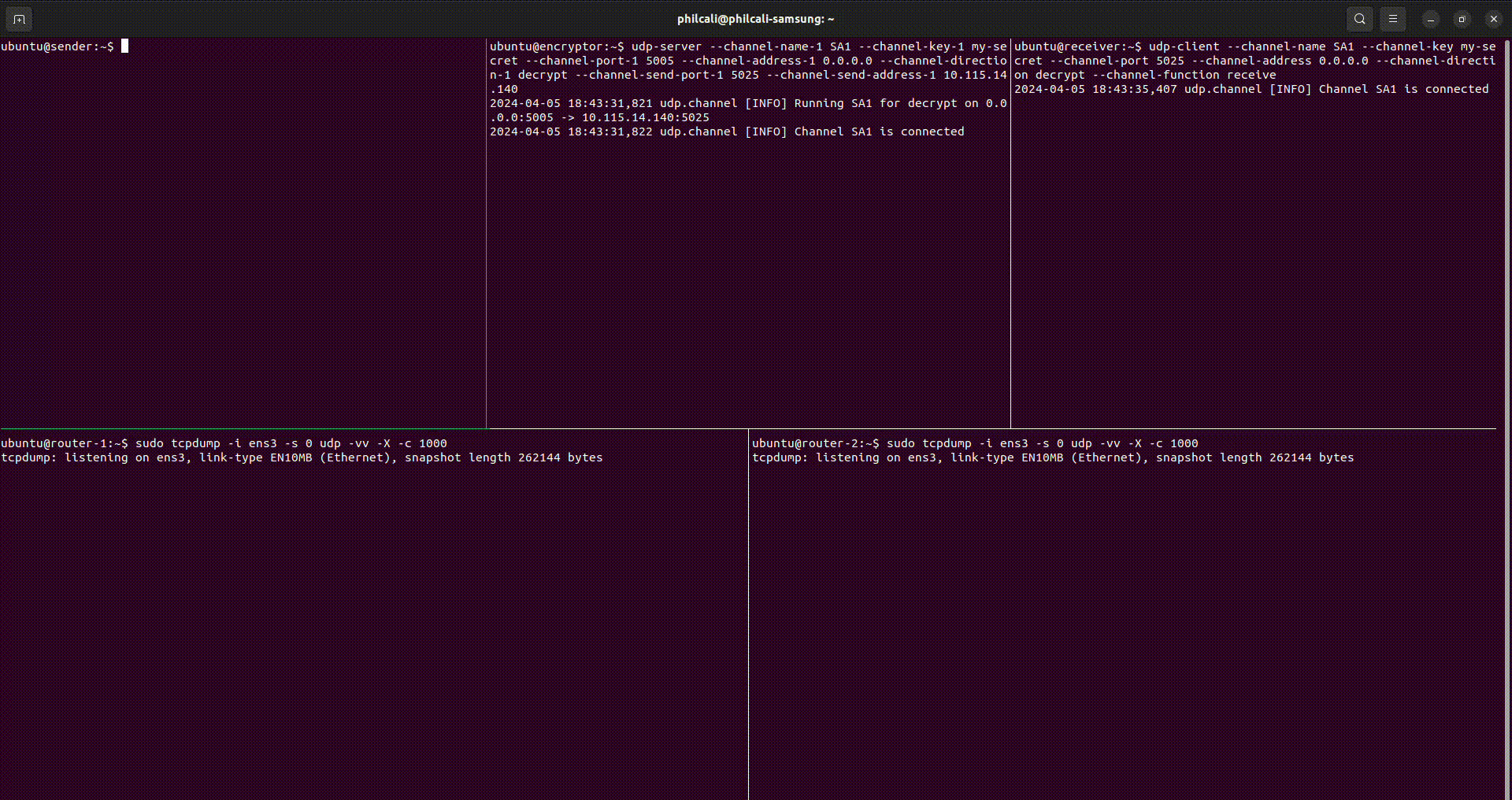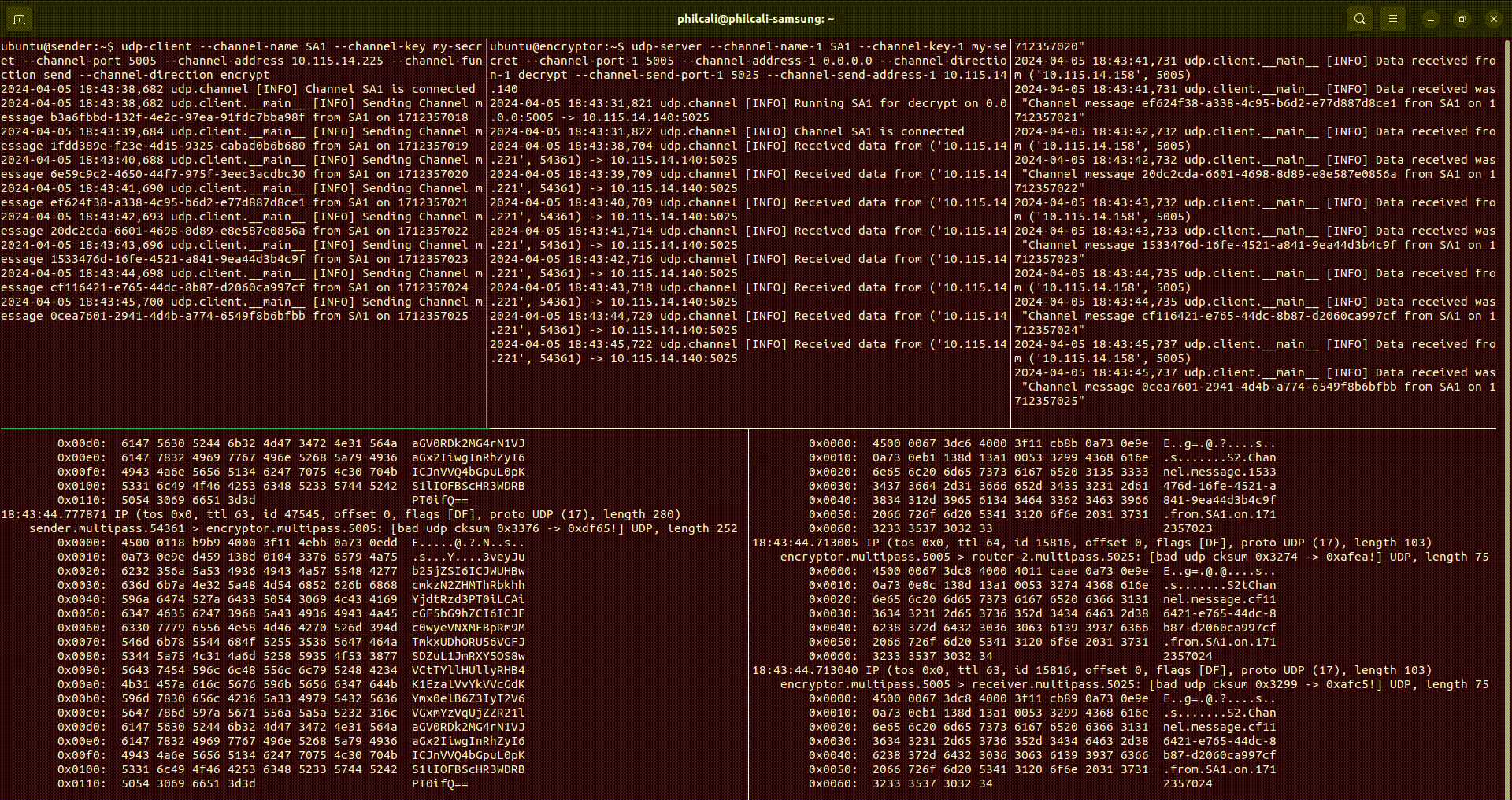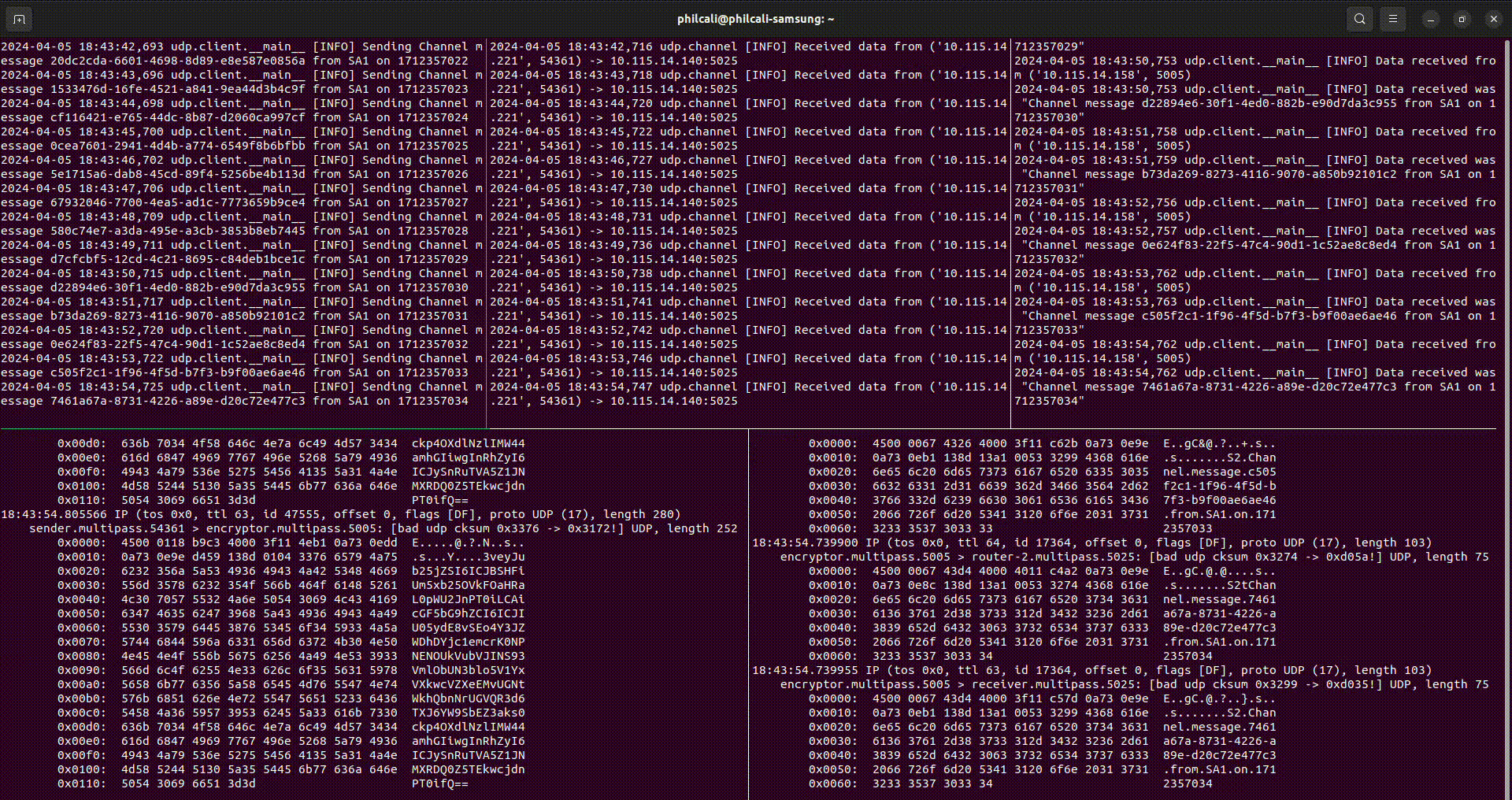
In the above video, you can see five terminal windows that represent machines doing various tasks:
- Top left: this is a sender instance sending data. Encrypted data is sent to router
- Bottom left: this is a router instance that forwards packets to the server. The
tcpdumpdemonstrates that data is encoded and encrypted UDP - Top center: this is the server instance receiving data. Server will receive encrypted data and forward to router
- Bottom right: this is a router instance that forwards packets to the
receiver. The
tcpdumpdemonstrates that data is plain text - Top right: this is a receiver instance that catches data. Receiver will output plain text data.
In ubuntu, spin up five vm's using multipass:
for vm in sender receiver encryptor router-1 router-2; do
multipass launch -n "$vm"
doneReceiver - Sender - Encryptor
Prepare compute instances with the udp-sandbox installation:
multipass shell $instance # where instance is sender, receiver, and encryptor
sudo apt-get install -y python3-pip
git clone https://github.com/philcali/udp-sandbox.git
cd udp-sandbox
python3 -m pip install -e .Routers
Prepare the router instances:
Router 1
multipass shell router-1
DPORT=5005
DEST="<encryptor.ip>"Router 2
multipass shell router-2
DPORT=5025
DEST="<receiver.ip>"Routing Config
sudo iptables -F
sudo iptables -t nat -F
sudo iptables -X
sudo iptables -t nat -A PREROUTING -p udp --dport "$DPORT" -j DNAT --to-destination "$DEST:$DPORT"
sudo iptables-save
sudo apt-get install iptables-persistentReceiver
multipass shell receiver
udp-client \
--channel-name SA1 \
--channel-key my-secret \
--channel-port 5025 \
--channel-address 0.0.0.0 \
--channel-direction decrypt \
--channel-function receiveRouter
multipass shell router-1
sudo tcpdump -i ens3 -s 0 udp -vv -X -c 1000Encryptor
multipass shell encryptor
udp-server \
--channel-name-1 SA1 \
--channel-key-1 my-secret \
--channel-port-1 5005 \
--channel-address-1 0.0.0.0 \
--channel-direction-1 decrypt \
--channel-send-port-1 5025 \
--channel-send-address-1 <router-2.ip>Sender
multipass shell sender
udp-client \
--channel-name SA1 \
--channel-key my-secret \
--channel-port 5005 \
--channel-address <router-1.ip> \
--channel-function send \
--channel-direction encryptOnce the sender begins, you should see output similar to the above video.
multipass stop --all
multipass delete --all
multipass purge