Blazing fast, minimal but complete dependency injection library for Unity
Reflex is an Dependency Injection framework for Unity. Making your classes independent of its dependencies, granting better separation of concerns. It achieves that by decoupling the usage of an object from its creation. This helps you to follow SOLID’s dependency inversion and single responsibility principles. Making your project more readable, testable and scalable.
📌 Table Of Contents
- Fast: ~3x faster than VContainer, ~7x faster than Zenject.
- GC Friendly: ~2x less allocations than VContainer, ~9x less allocations than Zenject.
- AOT Support: Basically theres no runtime Emit, so it works fine on IL2CPP builds. [*]
- Contract Table: Allows usages of APIs like
container.All<IDisposable> - Immutable Container: Performant thread safety free of lock plus predictable behavior.
You can install Reflex using any of the following methods:
https://github.com/gustavopsantos/reflex.git?path=/Assets/Reflex/#4.2.0
- In Unity, open Window → Package Manager.
- Press the + button, choose "Add package from git URL..."
- Enter url above and press Add.
openupm install com.gustavopsantos.reflex- Download the .unitypackage from releases page.
- Import Reflex.X.X.X.unitypackage
- Install Reflex
- Create
ProjectInstaller.cswith
using Reflex.Core;
using UnityEngine;
public class ProjectInstaller : MonoBehaviour, IInstaller
{
public void InstallBindings(ContainerDescriptor descriptor)
{
descriptor.AddInstance("Hello");
}
}- In unity project window
- Create directory
Assets/Resources - Select just created
Resourcesdir - Right click, Create → Reflex → ProjectScope
- With just created
ProjectScopeselected - Add
ProjectInstaller.cscreated at step 2 as a component - Create new scene
Greet - Add
GreettoBuild Settings→Scenes In Build - Create
Greeter.cswith
using UnityEngine;
using Reflex.Core;
using System.Collections.Generic;
public class Greeter : IStartable // IStartable will force it to be constructed on container build
{
public Greeter(IEnumerable<string> strings)
{
Debug.Log(string.Join(" ", strings));
}
public void Start()
{
}
}- Inside Greet scene, create a new empty gameobject named
SceneScopeand attachSceneScopecomponent - Create
GreetInstaller.cswith
using Reflex.Core;
using UnityEngine;
public class GreetInstaller : MonoBehaviour, IInstaller
{
public void InstallBindings(ContainerDescriptor descriptor)
{
descriptor.AddInstance("World");
descriptor.AddSingleton(typeof(Greeter), typeof(IStartable)); // IStartable will force it to be constructed on container build
}
}- Add
GreetInstaller.cstoGreet.unitySceneScope - Create new scene
Boot - Add
BoottoBuild Settings→Scenes In Build - Create
Loader.cswith
using Reflex.Core;
using UnityEngine;
using UnityEngine.SceneManagement;
public class Loader : MonoBehaviour
{
private void Start()
{
ReflexSceneManager.LoadScene("Greet", LoadSceneMode.Single, builder =>
{
// This deferred descriptor will run just before Greet.unity SceneScope installers
builder.AddInstance("beautiful");
});
}
}- Assign it to any gameobject at
Bootscene - Thats it, hit play while on
Bootscene - When Greet scene is loaded, there should be 3 instances implementing string contract
- So when Geeter is constructed, you should see log:
Hello beautiful world
Container scoping refers to the ability of being able to create a container inheriting the registrations of its parent container while also being able to extend it.
It is root scope.
It is created just before first scene opens by relying on [RuntimeInitializeOnLoadMethod(RuntimeInitializeLoadType.BeforeSceneLoad)]
To register bindings to it, create a prefab, name it "ProjectScope", put it inside any Resources folder, and attach a "ProjectScope" component to it.
Then, create your installer as MonoBehaviour and implement IInstaller interface.
Remember to attach your installer to the ProjectScope prefab, as ProjectScope searches for every child implementing IInstaller when its time to create the ProjectScope container.
Theres a menu item to ease the process: Assets > Create > Reflex > ProjectScope
Remember to have a single ProjectScope to avoid undesired behaviour.
Note that ProjectScope prefab is not required, in case Reflex do not found ProjectScope, an empty root will be created.
ProjectScope instance will be disposed once app closes/app quits.
Note that unity does not call OnDestroy deterministically, so rule of thum is do not rely on injected dependencies on OnDestroy event functions.
It is scoped from ProjectScope, so it contains everything that ProjectScope do. It is created and injected after Awake, and before Start. To register bindings to it, create a gameobject on desired scene, name it "SceneScope", put it as root game object, and attach a "SceneScope" component to it. Then, create your installer as MonoBehaviour and implement IInstaller interface. Remember to attach your installer to your SceneScope gameobject, as SceneScope searches for every child implementing IInstaller when its time to create the SceneScope container. Theres a menu item to ease the process: GameObject > Reflex > Scene Context Remember to have a single SceneScope to avoid undesired behaviour. Note that SceneScope gameobject is not required, in case Reflex do not found SceneScope, an empty one will be created. SceneScope instance will be disposed once scene is unloaded.
Note that unity does not call OnDestroy deterministically, so rule of thum is do not rely on injected dependencies on OnDestroy event functions.
using var scopedContainer = parentContainer.Scope("Scoped", descriptor =>
{
// Extend your scoped container by adding extra registrations here
});ContainerDescriptor::AddInstance(object instance, params Type[] contracts)Adds an object already contructed by the user to the container as a singleton, everytime the contracts given is asked to be resolved, the same object will be returned.
If object implements IDisposable it will be disposed when its parent Container are disposed.
Theres no need to pass IDisposable as contract to have your object disposed, howerver, if you want to retrieve all IDisposable by any API Single<TContract>, Resolve<TContract> or All<TContract> then yes, you have to specify it.
ContainerDescriptor::AddSingleton(Type concrete, params Type[] contracts)Adds a defered object creation based on the type to be constructed and its contracts.
The object will be constructed lazyli, once first request to resolve any of its contracts is called.
Then same object will always be returned.
If you want your singleton to be constructed just after container build (non-lazyli), add typeof(IStartable) as one of your contracts.
If object implements IDisposable it will be disposed when its parent Container are disposed.
Theres no need to pass IDisposable as contract to have your object disposed, howerver, if you want to retrieve all IDisposable by any API Single<TContract>, Resolve<TContract> or All<TContract> then yes, you have to specify it.
ContainerDescriptor::AddTransient(Type concrete, params Type[] contracts)Adds a defered object creation based on the type to be constructed and its contracts.
The object will be constructed lazyli, once first request to resolve any of its contracts is called.
Then for any request of any contract, a new object will be created, use this carefully.
If object implements IDisposable it will be disposed when its parent Container are disposed.
Theres no need to pass IDisposable as contract to have your object disposed, howerver, if you want to retrieve all IDisposable by any API Single<TContract>, Resolve<TContract> or All<TContract> then yes, you have to specify it.
Note that
IStartablealso works for Transients but pay attention that any resolve API will create a new instance
If your type is non-mono, and its gonna be created by the container, then the most recommended way to inject dependencies into it its by constructor injection. Its simply as just requesting the contracts you need as following example:
private class Foo
{
...
public NumberManager(IInputManager inputManager, IEnumerable<IManager> managers)
{
...
}
}Note that constructor injection relies on
Resolve<TContract>API, so in case theres theres two objects withIInputManagercontract, the last one will be injected.
Attribute injection is the way to go for MonoBehaviours. You can use it to inject fields, writeable properties and methods like following:
class Foo : MonoBehaviour
{
[Inject] private readonly IInputManager _inputManager;
[Inject] public IEnumerable<IManager> Managers { get; private set; }
[Inject]
private void Inject(IEnumerable<int> numbers) // Method name here does not matter
{
...
}
}Note that attribute injection also works on non-mono classes.
Container::Single<TContract> actually validates that theres a single binding implementing given contract, and returns it.
If theres more than one the following exception will be thrown.
InvalidOperationException: Sequence contains more than one element
Its recommended for every binding that you know that there should be a single binding implementing the contract.
Container::Single<TContract> runs no validations, and return the last valid object implementing given contract.
Container::All<TContract> returns all objects implementing given contract.
Example:
private void Documentation_Bindings()
{
var container = new ContainerDescriptor("")
.AddInstance(1)
.AddInstance(2)
.AddInstance(3)
.Build();
Debug.Log(string.Join(", ", container.All<int>())); // Prints: 1, 2, 3
}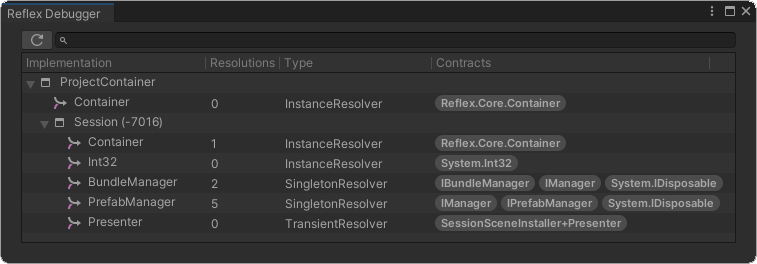
It can be accessed by menu item Reflex → Debugger.
And from there you can check:
- Container Hierarchy
- Implementation
- Contracts
- Resolution Count
- Binding Type
Its a ReflexSettings scriptable object instance, named ReflexSettings that should live inside a Resources folder.
It can be created by asset menu item Assets → Create → Reflex → Settings.
Currently, logging verbosity is configured in this file, and default value is set to Info
Non-Obligatory to have but projects without it will fallback using default settings
Resolving ten thousand times a transient dependency with four levels of chained dependencies. See NestedBenchmarkReflex.cs.
| GC | Time | GC Ratio | Time Ratio | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reflex | 54.7KB | 9.3ms | 1x | 1x |
| Zenject | 512KB | 63.2ms | 9.36x | 6.79x |
| VContainer | 128.9KB | 29.8ms | 2.35x | 3.20x |
| GC | Time | GC Ratio | Time Ratio | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reflex | 140.6KB | 7.4ms | 1x | 1x |
| Zenject | 1024KB | 23.6ms | 7.28x | 3.18x |
| VContainer | 257.8KB | 9.2ms | 1.83x | 1.24x |
| GC | Time | GC Ratio | Time Ratio | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reflex | 109.4KB | 1.2ms | 1x | 1x |
| Zenject | 1024KB | 9.2ms | 9.36x | 7.66x |
| VContainer | 257.8KB | 3.3ms | 2.35x | 2.75x |
| GC | Time | GC Ratio | Time Ratio | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reflex | 140.6KB | 2.9ms | 1x | 1x |
| Zenject | 1024KB | 9.3ms | 7.28x | 3.20x |
| VContainer | 257.8KB | 5.1ms | 1.83x | 1.75x |
If you are taking advantage of reflex to inject IEnumerable<T> in your constructors AND your are building for IL2CPP, you will probably get some exceptions like following:
System.ExecutionEngineException: Attempting to call method 'System.Linq.Enumerable::Cast<ANY-TYPE>' for which no ahead of time (AOT) code was generated.
This happens because compiler does not know at compile time that a specific System.Linq.Enumerable::Cast<T> should be included. And currently Reflex does not implement any type of assembly weaving.
Reflex 4.0.0 had and assembly weaver that was relying on unity UnityEditor.Compilation.CompilationPipeline events and Mono.Cecil. But it was causing conflicts with projects using Burst. So its being removed temporarly until a definitive solution is found. Most probably we are going to weave assemblies the same way unity is doing for Burst as well.
Temporary workaround example:
class NumberManager
{
public IEnumerable<int> Numbers { get; }
public NumberManager(IEnumerable<int> numbers)
{
Numbers = numbers;
}
// https://docs.unity3d.com/Manual/ScriptingRestrictions.html
[Preserve] private static void UsedOnlyForAOTCodeGeneration()
{
Array.Empty<object>().Cast<int>(); // This compiler hint will get rid of: System.ExecutionEngineException: Attempting to call method 'System.Linq.Enumerable::Cast<System.Int32>' for which no ahead of time (AOT) code was generated.
throw new Exception("This method is used for AOT code generation only. Do not call it at runtime.");
}
}Ask your questions and participate in discussions regarding Reflex related and dependency injection topics at the Reflex Discord server.
Reflex is distributed under the terms of the MIT License. A complete version of the license is available in the LICENSE file in this repository. Any contribution made to this project will be licensed under the MIT License.






