ScriptGui
Data driven Windows gui for command line scripts. Check also the python implementation: usage-gui
Description
This C++ application is a standalone graphical interface toolkit for giving command line scripts a intuitive user input. The user can fill the fields then click "Run" to call the associated script (a file in the same directory and with the same base name) with the parameters selected as the command line arguments.
Ex.:
myscript.exe
myscript.py
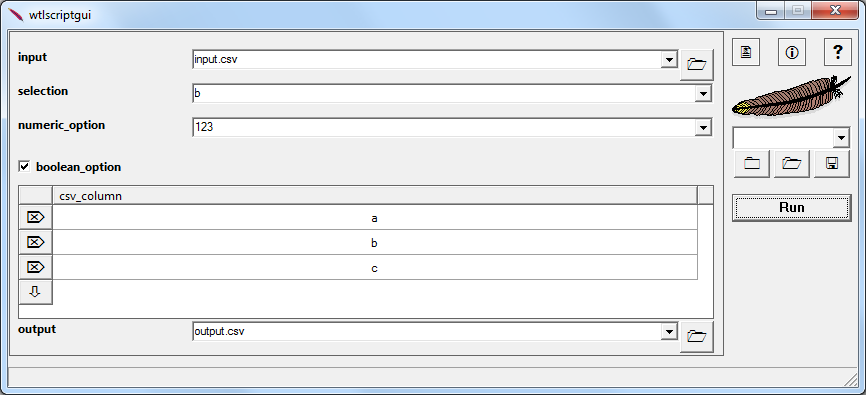
Screenshot
Features
- Fully standalone. The only runtime libraries required are MSVCxx. Current release was compiled using MSVC2010 (v10.0) libraries, which are included by default on Windows 7 and up. You could compile with the static library for complete runtime independence, but that would add around 60k to executable size.
- 64 bit and 32 bits versions.
- Data driven. You copy the same executable for each script that requires a interface, there is no need to (re)compile this project. The entire interface is defined with a single line with special control templates on the target script. This template line can be a comment line, so the active code is unchanged. The only thing you must ensure is to somewhere the script will read the command line parameters which will contain the user input.
- Flexible. Any language that can somehow read the command line arguments can be supported. Custom handlers may be easily implemented. Like the DLL handler that executes its functions dynamically with
LoadLibrary(). - Small. This application does not use toolkits that add a huge footprint to the executable. The entire app is a single executable with ~ 130 Kb (64bits) or ~90 Kb (32bits). It may be be larger, due to resources like the logo and icon.
- Future proof and backward compatible. This interface uses the Win32 API, which is guaranteed to work on all contemporary desktop Windows versions.
- Simple. The arguments are passed as simple text.
- Save and load parameters as named sets. Those parameters sets are stored as xml files in the same folder, and can be copied and edited. For this reason, the file browse controls will automatically convert paths descendant from current working diretory to relative paths so they stay valid even if the precedding hierachy changes.
- Copy command line. Not only the this application is a interface, but it also can creates a command line for your script so you can run you script with the selected arguments even where you dont have a window server, such as ssh session or a already existing command line prompt session.
- Integrated help. You can distribute a PDF or CHM file with same name as the script, and the interface will open it when user clicks on the help button.
- Free. The only used library is WTL, which is header only (template) and licensed under the Microsoft Public License. This project is Apache 2.0.
- Supported file types:
- Perl (.pl, .lava)
- Python (.py)
- Windows Batch (.bat, .cmd)
- Unix C Shell (.csh)
- Windows Scripting Host (.vbs, .js)
- HTML application (.hta)
- Customized DLL with a
runfunction (.dll) - And with minor changes, anything that runs on the command line and can read argument parameters.
How to use
File name matters
The interface searches in the current working directory for all files that have the same base name, and are of a supported extension.
Ex.: "myscript.exe" will match a file named "myscript.py" if it exists.
If the interface cant locate a supported file, it will exit with the following error:
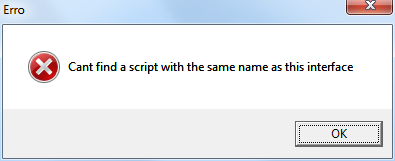
The usage: line
Once the interface finds a compatible script, it will do a text search on the contents of this file looking for a magic word: usage:
When it is found, its line is parsed into interface controls using the templates described below. This usage: can be a comment or, even better, can be the short help message describing its usage. Its common for a script to print their parameter syntax when called with a switch such as /? and -h or without any arguments. The origin of this interface was trying to "guess" a good control layout from existing usage lines. Conforming any already existing usage line to the templates should have no downsides and will even look informative.
Control templates
<name>=<default value>
text input control with a default value in the combo box<name>=<list of values seprated by ,>
choice combo box<name>*<extension>(,<extension>...)
file browse control, listing only files that match one of the given extensions<name>:<another control name>
derived control that gets its list values from the file pointed by another file browse control
different files will have differente associated lists
Ex.: csv files will be a list of column names<name>@
checkbox boolean control<name>#<control>(#<control>...)
grid of controls, allowing a the user to create a list of similar values
the resulting list is semicollon separated (;)
multiple controls can be used in a single line, and columns in each row will be comma (,) separated
Ex.: a,1;b,2;c,3
Example of a "usage:" line
usage: %0 input*csv selection=a,b,c numeric=123 boolean@ output*csv
Limitations
This interface was developped to catter to a already existing ecosystem of scripts and contain custom funcionalities and assumptions that may require adjusting.
It also relies on the Win32 API which is quirky and hard to understand.
License
Apache 2.0