An algorithm for big integer multiplication, also described here.
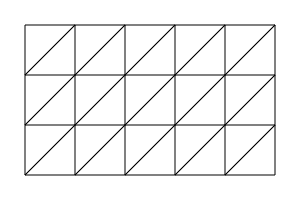
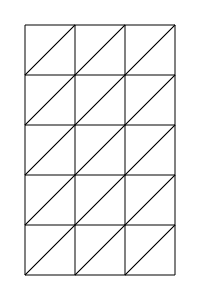
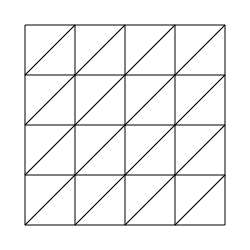
The lattice or gelosia method is an ancient multiplication method where numbers can be multiplied digit-by-digit and, as each digit only ranges from 0 to 9, the maximum multiplication performed per step is 9 x 9.
It works by walking cells of arbitrary shape (width x height) lattices (the grids shown above). Can compute 4999! (with 16322 digits) in 1m24s.
The basic procedure can be divided in the following kinds of steps:
-
Basic cell-to-cell walk
-
Line changes
-
Phase changes (including the end of the walk)
There are three phases.
In any phase, the basic cell walk routine is the same: if we are in an odd cell (the "uppermost" triangle in a square), we go to the left square to the even cell. Furthermore, if we are in an even cell (the "lowermost" triangle in the square), we go down one square and switch to the odd cell.
If we reach the lower cells in the first phase, in any shape lattices, or in the second phase in horizontal lattices, a line change occurs. If we reach the leftmost cells in the third phase of any shape lattice or in the second phase of vertical lattices, a line change also occurs.
The first and third phases are common to all shape lattices, and the second phase (only occurring in non-square lattices) is of different line-changing procedure with different orientation lattices.
In any phase, when changing lines, we look for when the phase changes. According to the orientation, the phase transition can jump an additional line, before changing phases, or not.
Pseudocode:
let d1 be the amount of digits in the multiplicator, and
d2 be the amount of digits in the multiplicand.
do:
multiply the digits at x and y.
add to the sum.
orientation undefined.
if end of line of any phase:
if carrying digit, add it to sum.
if one digit sum:
take the only digit.
if two digits sum:
take the second digit and carry the first.
result position less one.
reset the sum.
if end of line of phase 1:
if x is at d1 + 1 - d2 (the "square" position):
the lattice is horizontal.
if x is at 1:
the lattice is vertical.
if the lattice is both horizontal and vertical:
the lattice is square.
if orientation is defined and:
it's square:
phase is 3.
jump cell like the new phase, but
x is 1 and odd toggles to true.
it's horizontal:
phase is 2.
jump cell like the new phase.
it's vertical:
phase is 2.
jump cell normally.
if not:
jump cell normally.
if end of line phase 2 vertical:
if y is d1 + 1:
phase is 3.
jump cell like the new phase.
if not:
jump cell normally.
if end of line phase 2 horizontal:
if x is 1:
phase is 3.
jump cell normally.
if end of line phase 3:
if y is 1:
end of walk.
if not:
jump cell normally.
if no end of line:
if not odd:
y is increased 1.
if odd:
x is decreased 1.
toggle odd.