Fav Quotes is a sample baseline project based a Clean Architecture implementation using some of the latest Android features.
Clone this repository and import into Android Studio
> git clone git@github.com:pablodeafsapps/fav-quotes.git> git clone https://github.com/pablodeafsapps/fav-quotes.git In order to compile or execute the application, it is required to create a keystore.properties file at the project directory, with the following format:
storeFile = ""
storePassword = ""
keyAlias = ""
keyPassword = ""
This file can contain random or fake data when building as debug, but a real keystore is required to generate a signed APK.
Regarding the FavQs API, a user key is required. For this particular sample app, a default key has been automatically configured. This sensitive information should be placed in a separate file, and excluded from any VCS scheme.
From Android Studio:
- Build menu
- Generate Signed APK...
- Fill in the keystore information (you only need to do this once manually and then let Android Studio remember it)
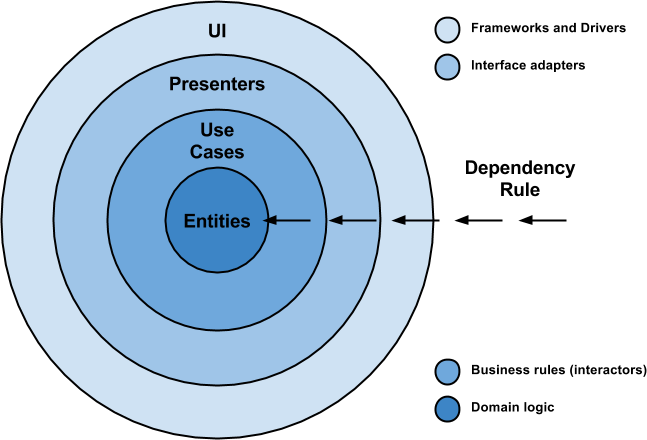
To address this sample app development, the team has decided to employ a class hierarchy based on the Clean Architecture paradigm, a concept with an increasing popularity thanks to Robert C. Martin (Uncle Bob).
Among the different implementations for Android applications of the aforementioned paradigm, there are remarkable contributions such as the ones from Antonio Leiva and Fernando Cejas. Precisely, this latter work has served as the main inspiration for this application architecture.
Therefore, the prior idea behind Fav Quotes is concern-layers separation. Each of this entities is in charge of certain responsibilities, which are handled in isolation. These layers get interconnected thanks through interfaces, which allow to achieve the necessary abstraction between them.
-
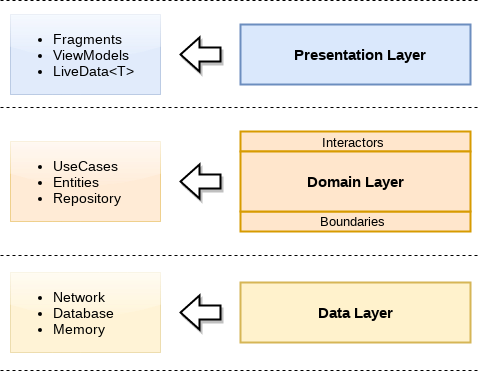
Presentation This layer's duties consist of managing the events caused by the user interactions, and rendering the information coming from the domain layer. In this particular case, the team has opted for using the Model-View-ViewModel (MVVM) architecture pattern. This entity "sees" the domain layer.
-
Domain This layer is in charge of the application business logic. It is built upon use-cases and repositories (repository pattern). The domain layer obtains data from the data module, use them to perform all the required operations, and format the outcomes to later deliver them to the presentation layer. This entity only contains Kotlin code, and thus testing should only consist of Unit Tests. This layer represents the most inner entity, and thus it does not "see" anyone but itself.
-
Data This layer simply contains libraries and frameworks which provide data to the application (data sources). Among them, stand out service-query frameworks (Retrofit), local databases (Room), events tracking (Omniture), etc. This layer "sees" the domain layer.
The usage of this class hierarchy and package organization pursues grasping the SOLID principles, getting more flexible when implementing new functionality, and easing code testing.
In order to facilitate the interaction between the above described layers, Fav Quotes uses a dependency injector. Dagger is a popuular framework which allows to abstract type injection in a neat and clear manner.
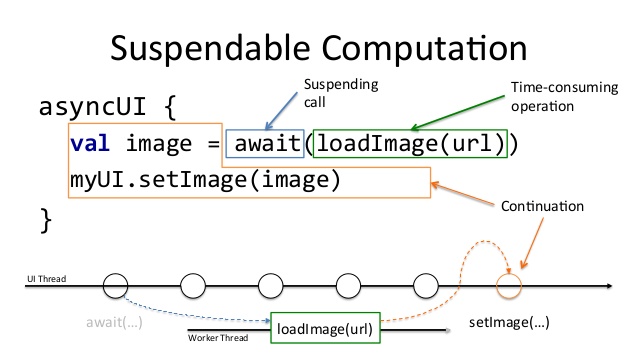
Since multithreading has historically been a challenge in Android Development, the team has decided to include Kotlin Coroutines. This is one of the most interesting and appealing features available in Kotlin.
The main advantage that supports the usage of coroutines is an easy and enhanced multithreading management. Coroutines allow to turn asynchronous operations in synchronous code, without affecting the application overall performance.
From the execution-flow perspective, every task is undertaken in the main thread (UI thread), until a use-case is invoked. From that moment onwards, operations are handled in worker threads, to later retrieve the computed results in the main thread again.
Furthermore, this sample project makes use of the Flow API, which is a cold stream lightweight implementation. This feature is specifically used when successively loading available public quotes. The ViewModel gets subscribed to the flow, whereas the data source gets updated asynchronously.
Functional Programming (FP) is a paradigm from the 1950s which is based upon the principals of declarative programming. It comprises certain prior foundations such as immutability, pure functions and no side effects/disciplined states, and referential transparency. Contrary to Object Oriented Programming (OOP), everything is meant to be a function (instead of an object). Bringing these concepts into an application allows to make it more flexible, understandable, and easily scalable.
Arrow is a functional programming suite written in Kotlin which aims to bring functional programming into Kotlin applications, such as Android ones. According to the official documentation, "Arrow is a modular set of libraries that build on top of each other to provide increasingly higher level features".
The aim when building this app is improve it adding more functional features. So far, only the Either data type is used, allowing to parametrize any data source query available.
Detekt is a static code analysis tool for the Kotlin programming language. It operates on the abstract syntax tree provided by the Kotlin compiler.
When integrated, it enables several Gradle tasks which allow to assess the code quality.
As one main aspect in the current state-of-the-art in software development, Fav Quotes does include Unit Tests, which cover the domain, presentation, and data layers. In a more complex project, some Integration Tests* would have been necessary to ensure a robust app performance.
It is recommended to advocate for an extensive usage of Unit Tests and Integration Tests. Instrumentation Tests are worth mentioning, since they cover testing on platform-dependent features, such as UI. None of these have been included here due to their slow execution and emulator/device dependency.
Continuous Integration (CI) is the practice of automating the integration of code changes from multiple contributors into a single software project. The CI process is comprised of automatic tools that assert the new code's correctness before integration. A source code version control system is the crux of the CI process.
Among the many options available when it comes to CI, Fav Quotes uses GitHub Actions, which is a recent platform which is increasing popularity thanks to its straightforward integration when using GitHub. There are 2 different workflows, for develop and feature branches.
This project is licensed under the MIT License - see the LICENSE.md file for details
The documentation is managed in two different ways:
- Using this README.md file to give a quick overview of the project.
- Using dokka, which is a framework for Kotlin projects, similar to Javadoc.
For the latter, the documentation can be find in the docs/dokka folder, organized in modules. To generate it, simply run the next command from a terminal:
> ./gradlew dokkaWhen finished, open up index.html using your favourite browser.
This project is mantained by:
If you happen to find any issue or suggestion, feel free to start a new thread on the Issues section of the repository. I will try to address it as soon as possible.
- Fork it
- Create your feature branch (git checkout -b my-new-feature)
- Commit your changes (git commit -m 'Add some feature')
- Push your branch (git push origin my-new-feature)
- Create a new Pull Request