Octrees are used in color quantization to divide the image color space into nested clusters. The deepest clusters are the leaves and they represent only one color. Upper nodes represent the average color of their children, taking into account the pixel count of each color. The octree is pruned until the desired number of color is reached, the remaining leaves forming the palette colors.
The method used to decide where to reduce the octree is roughly the one described in this imagemagick document. An error value is assigned to each node, and using heap sort, nodes with higher error values are folded in priority. The error value of a node is the sum of the differences between its average color and the color of its children (themselves also being average colors unless they are leaves). The difference between two colors is evaluated as the sum of squared differences between each channel, weighted by rough YUV-ish coefficients.
Dithering uses an error-diffusion Floyd Steinberg matrix. When applied, instead of browsing the pruned octree to find the palette color matching an original color, the original color must be compared to each color in the palette in order to find the closest match, using the same color difference formula described previously. This is because error diffusion will create new pixel values not included in the original image, therefore new colors that may not belong to any of the clusters in the octree.
Note that even without using dither, looking for the closest palette color yields better results than browsing the octree. The downside of this method is a major slowdown, as what was before a 8-step operation (the maximum depth of the octree) performed on each pixel becomes a 256-step operation.
Click for full-scale image
| Original | 256 colors | 256 colors dithered | ImageMagick |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
 |
| 859 kB | 231 kB | 287 kB | 336 kB |
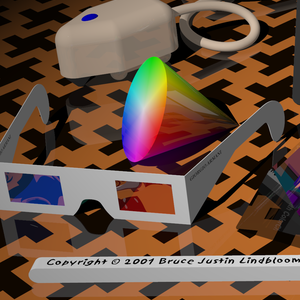
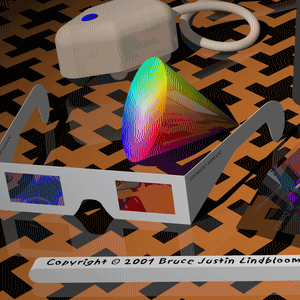
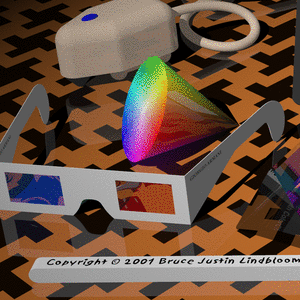
| Original | 256 colors | 256 colors dithered | ImageMagick |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
 |
| 454 kB | 89 kB | 130 kB | 195 kB |
ImageMagick command: convert in.png -colors 256 png8:out.png
Sample images from imagecompression.info
Reducing an octree node means folding all its leaves onto itself. It is not possible to "partially" fold a node and preserve some of its leaves. As a consequence, it may not be possible to fill the palette with the exact number of colors desired. This becomes obvious when setting a maximum number of colors lower than 8, which will always yield a palette of only 1 color: the average color of the image.
Limiting the octree depth can provide a speed gain (negligible when using dither), but also impact the chosen palette color. On some images (such as the second sample image), setting a lower depth may give results that are more visually convincing.