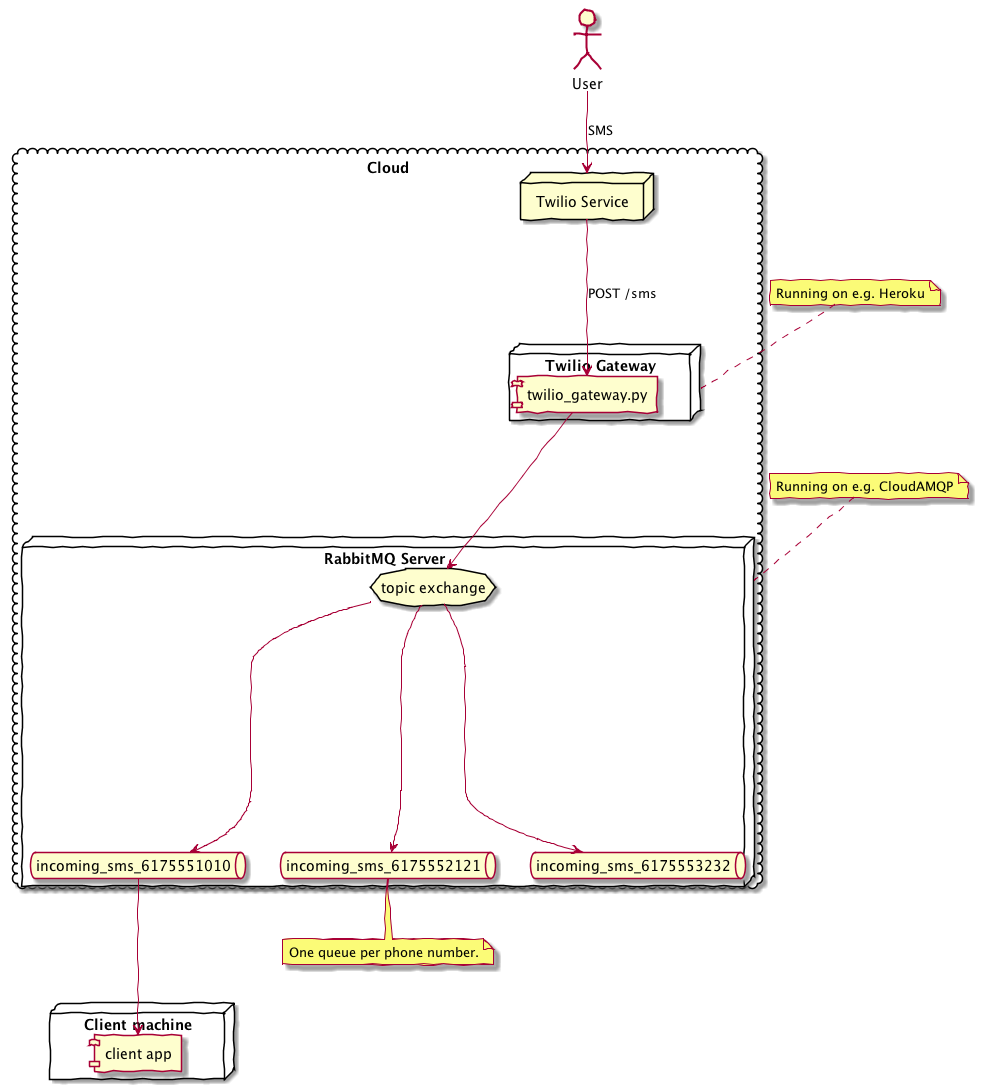
Twilio ⟶ MQTT Gateway
A web application implementing a Twilio webhook handler, that relays incoming SMS messages to an MQTT server.
This allows a number of clients to subscribe to incoming SMS messages, without each requiring a web presence.
For the original motivation, see the Olin Library Bear-as-a-Service project.
Each number +16175551212 is published with topic incoming-sms-16175551212,
and with a payload of the JSON-encoded HTTP request form fields.
Deploy
Provision a RabbitMQ server. (I'm using CloudAMQP.) Note your server's URL.
For each provisioned phone number:
rabbitmqadmin declare queue name=incoming-sms-16175551010
rabbitmqadmin declare binding source=amq.topic destination_type=queue \
destination=incoming-sms-16175551010 routing_key=incoming-sms-16175551010Execute the following. Replace the value of MQTT_URL by the URL of your RabbitMQ server.
$ heroku create
$ heroku config:set
$ MQTT_URL='mqtt://username:password@termite.rmq.cloudamqp.com:1883/vhost'
$ git push heroku masterOptionally set the RESPONSE_TEXT envrionment variable. (On Heroku, config:set RESPONSE_TEXT.) if set, the gateway responds with this
text to incoming messages.
Provision a Twilio phone number. Set its messaging webhook to https://sharp-rain-871.herokuapp.com/sms_webhook, where sharp-rain-871
is the name of your Heroku app.
In RabbitMQ, for each phone number +16175551010, create a queue named
incoming-sms-16175551010, and bind it with that same name to the topic
exchange.
You can also do this programmatically. See the server management notebook.
Manage
See the wiki and the server management notebook.
Develop
Setup
Either install a local RabbitMQ server, or set MQTT_URL to a remote
server.
Run pip install -r dev-requirements.txt
Run python twilio_gateway.py.
Install ngrok. In another terminal, run
ngrok http 5000. This gives your local webserver a public hostname that Twilio can to connect to.
- Navigate to the Twilio phone number configuration page.
- Under "Messaging: A Message Comes In", set the webhook to the server URL
followed by the
/sms_webhookpath, e.g.https://c115d7a2.ngrok.io/sms_webhook.
Test
pytest runs the unit tests (currently just of the mqtt_json package).
pytest-watch runs the tests in watch mode.
flake8 . lints the code.
tox runs the tests and linter in their own Python virtual environment.
Use a local RabbitMQ server
For local development, you may find it useful to run a local RabbitMQ server.
macOS: brew install rabbitmq (and then follow the instructions to launch the
daemon, now and on restart).
Add rabbitmqadmin to your path. (On macOS: export PATH=/usr/local/Cellar/rabbitmq/3.7.2/sbin/:PATH.) Alternatively, you can
replace rabbitmqadmin by /path/to/rabbitmqadmin in the instructions below.
Create a queue for your phone number:
rabbitmqadmin declare queue name=incoming-sms-16175551010
rabbitmqadmin declare binding source=amq.topic destination_type=queue \
destination=incoming-sms-16175551010 routing_key=incoming-sms-16175551010License
MIT