this mode provides simple utilities for editing and viewing CoNLL-U files.
you can watch the following demo for an idea of what it can do:
| command | key binding | description |
|---|---|---|
conllu-edit-hydra/body | C-c C-e | edit token line at point interactively using a hydra |
conllu-align-fields | C-c C-a | align columns (inserts no real whitespace) in the selected region (defaults to the current sentence) |
conllu-unalign-fields | C-c C-u | unalign columns in the selected region (defaults to current sentence) |
conllu-move-to-head | C-c C-h | move point to head token of present token |
conllu-clear-field | C-c C-c | clear field at point, placing _ as its value |
conllu-command | C-c C-! | run shell command on region (or sentence at point if no region is active) |
conllu-insert-token-line | C-c C-l | insert empty token line at point or at next line (can be called with prefix argument for more lines) |
conllu-previous-sentence | M-a | jump to the next sentence keeping current alignment |
conllu-next-sentence | M-e | jump to the previous sentence, keeping current alignment |
conllu-move-to-field-number-[N] | C-c [N] | move to field number [N] in a token line (C-c 0 moves to field number 10, i.e. MISC) |
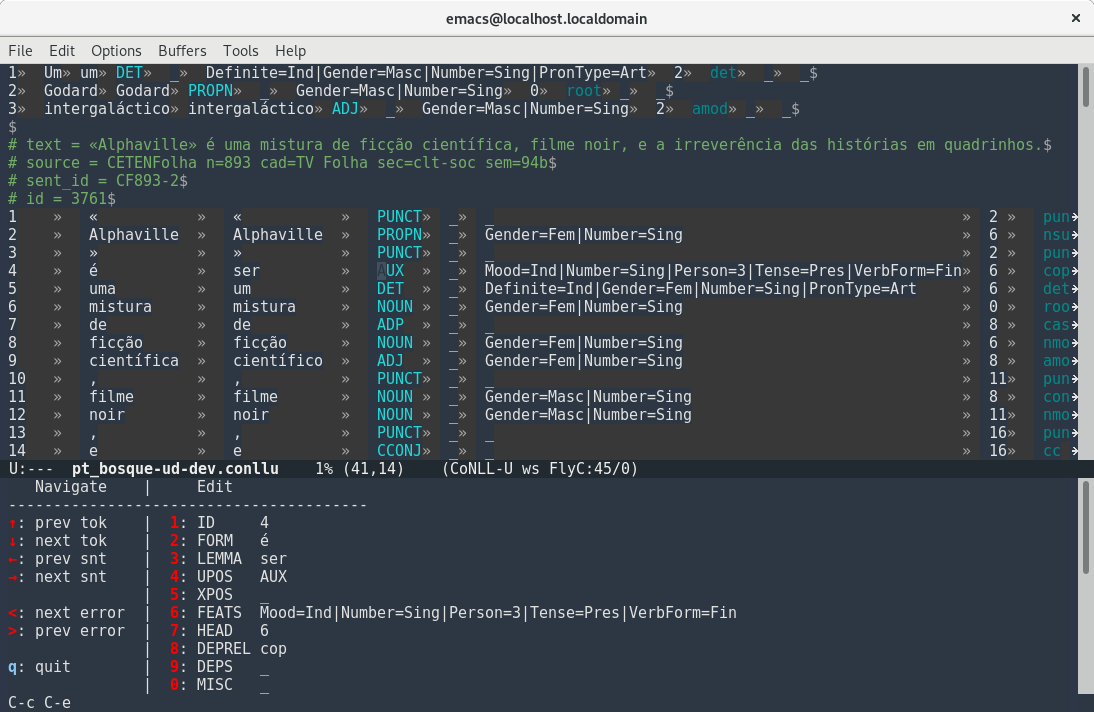
the default keybing C-c C-e calls a hydra for interactive
editing. this enters an editing loop where you can navigate through
the file or choose a field, edit it in a minibuffer, and press RET
to confirm the edit; you can quit by pressing any unbound key or by
pressing q. if you delete the field’s contents the empty field will
be inserted automatically.
- obtain the
validate.pyscript from the UD-tools repository (make sure you clone/download the whole repo, because the script depends on data and configuration files in there). - make
validate.pyavailable somewhere in yourPATH. the best way to do it is to symlink it to a suitable directory.ln -st /home/user/.local/bin/ /home/user/tools/validate.py - do
M-x customize-variable RET conllu-flycheck-checkersand select the checkers you want Flycheck to use. (or simply do(setq conllu-flycheck-checkers '(conllu-validate-python3))on your init file.)
if you have any problems open a conllu-mode buffer and run:
M-x flycheck-verify-setup
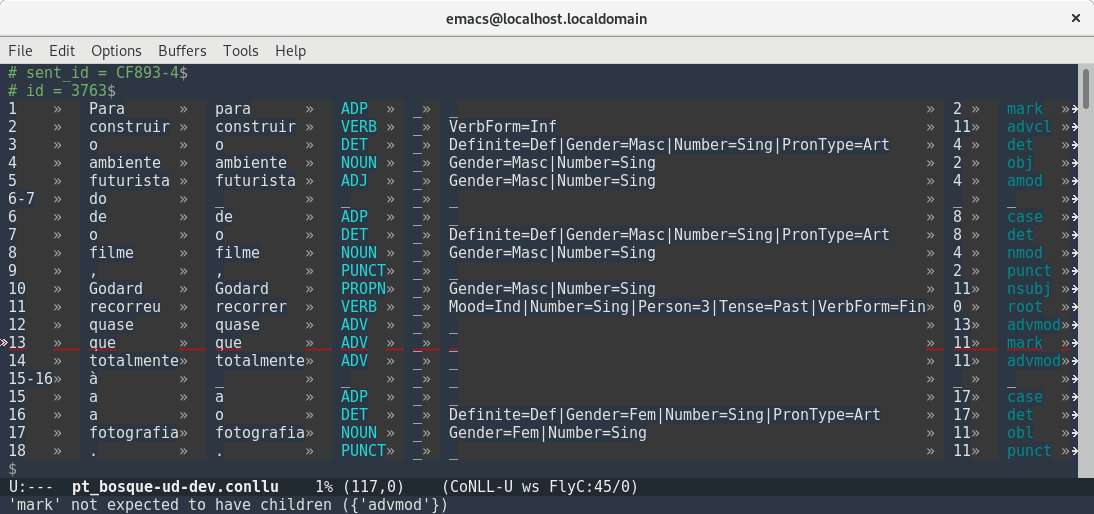
you can use the normal flycheck keybindings (here’s a nice summary),
or you can enter interactive editing mode and use < and > to
navigate between errors.
- By default
conllu-modewill ask if you would like to check every CoNLL-U buffer you open; you can change this behavior withM-x customize-variable RET conllu-flycheck-on?. You can also callconllu-flycheckto invoke Flycheck manually. - note that the
validate.pydemands a two-letter language code to do its validation;conllu-modetries to infer this from the file name, assuming it follows UD filename convention of starting with such a language code (as inpt_bosque-ud-test.conllu). if your file doesn’t start with a language code,conllu-modewill ask you for a language code; if you don’t supply anything, Flycheck will invoke the validate script with the default value ofud. - you can customize validation level and the maximum number of errors
shown by customizing other variables. See
M-x customize-group conllu.
it’s sometimes useful to customize these variables per directory: if you have a directory of CoNLL-U files that you always want to validate as part of certain language, you can issue:
M-x add-dir-local-variable RET conllu-mode RET conllu-flycheck-on? RET yes M-x add-dir-local-variable RET conllu-mode RET conllu-flycheck-lang RET "pt"
while flycheck takes care of running a validator interactively, you
may still have uses for running other interactive commands in a
CoNLL-U sentence or region. for this you can use conllu-command
(bound by default to C-c C-!).
As an example, let’s say you have a program called conllu2tree in
your PATH that takes a CoNLL-U sentence as standard input and outputs
a textual tree representation of the input sentence. To see the tree
representation of the sentence you are editing, you’d simply call the
conllu-command and specify conllu2tree as an argument. If you
dislike specifying the same shell program argument over and over, you
can set the variable conllu-default-command to something else. If
you have more than one command that you run often, you can define your
own function like so (and optionally bind it to whatever you like),
changing only the =”command-to-run”=:
(defun my-conllu-command ()
(interactive)
(let ((conllu-default-command "my-default-command"))
(call-interactively #'conllu-command)))another example would be a function to run the UD validation script (see #validation-setup) on a sentence or a selection of sentences:
(defun conllu-validate-sentence ()
(interactive)
(let ((conllu-default-command (format "validate.py --lang %s --max-err %s --level %s -"
conllu-flycheck-lang
conllu-flycheck-error-threshold
conllu-flycheck-validation-level)))
(call-interactively #'conllu-command)))if you want to bind this command to a key, see an example at #use-package-declaration.
- highlighting comments, and
upostaganddeprelfields - truncate lines by default
- show newline and tab characters using
whitespace.el - aligning and unaligning column fields
- jumping to next or previous sentence
- jump to the token at point’s
head
if you’d like to have a feature implemented, you should file at ticket at the issue tracker. here is our wishlist of what we would like to implement in the future:
- hiding columns
- call a parser to create CoNLL-U output from a sentence
- call external visualization tool
- …
you may install the latest versions from MELPA, or proceed to a manual installation:
set MELPA up if you haven’t already and then do:
M-x package-install RET conllu-mode
(use-package conllu-mode
:mode "\\.conllu\\'"
;;; ;; if you want to bind a command to a key, uncomment this:
;; :bind (("C-c C-t" . my-conllu-command))
;;; ;; if you want to have flycheck validation, uncomment these:
;; :custom
;; ((conllu-flycheck-on? 'ask)
;; (conllu-flycheck-checkers (quote (conllu-validate-python3))))
)first you must install the dependencies: assuming you have a standard Emacs distribution, you need to install s and flycheck.
after having installed the dependencies, clone the repo, as in:
$ cd ~/some/path/
$ git clone https://github.com/odanoburu/conllu-modemake sure that the repository is in the emacs load path and that the autoloads are properly set with
(add-to-list 'load-path "~/some/path/conllu-mode")
(require 'conllu-mode)in your .emacs.
yes, please! even comments from experienced elispers are welcome. just send an email or open an issue – if you’d like a suggestion on what to work on, take a look at the open issues or at the missing features (above).