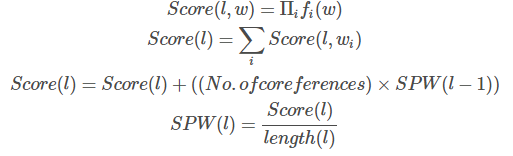The guide to tackle with the Text Summarization.
We want to catch up up-to-date information to take a suitable action. But on the contrary, the amount of the information is more and more growing. There are many categories of information (economy, sports, health, technology...) and also there are many sources (news site, blog, SNS...).
from THE HISTORICAL GROWTH OF DATA: WHY WE NEED A FASTER TRANSFER SOLUTION FOR LARGE DATA SETS
So to make an automatically & accurate summaries feature will helps us to understand the topics and shorten the time to do it.
Summarization is the function that takes some documents and outputs the summary.
- Single document summarization
- summary = summarize(document)
- Multi-document summarization
- summary = summarize(document_1, document_2, ...)
- Sometimes user provides the multiple documents by query
This basic task is so-called "Generic summarization". It produces the summary for everybody. In contrast, to specify the topic or some keywords is called "Query focused summarization".
- Query focused summarization
- summary = summarize(document, query)
As like our minutes of the meeting, there is a scene that we want to focus on the difference between the previous time and this time. It is called "Update summarization".
- Update summarization
- summary = summarize(document, previous_document_or_summary)
The "summary" itself has some variety.
- Indicative summary
- It likes a summary of the book. It describes what kinds of the story, but not tell all of the story especially its ends (so indicative summary has only partial information).
- Informative summary
- The summary that summarizes fully information of the document.
- Keyword summary
- A set of indicative words or phrases mentioned in the input document.
- Headline summary
- Only one line summary.
Discussion
Generic summarization is really useful? Sparck Jones argued that summarization should not be done in a vacuum, but rather done according to the purpose of summarization ([2]). She argued that generic summarization is not necessary and in fact, wrong-headed. On the other hand, the headlines and 3-line summaries in the newspaper helps us.
There are mainly two ways. Extractive and Abstractive.
- Select relevant phrases of the input document and concatenate them to form a summary (like "copy-and-paste").
- Pros: They are quite robust since they use existing natural-language phrases that are taken straight from the input.
- Cons: But they lack in flexibility since they cannot use novel words or connectors. They also cannot paraphrase like people sometimes do.
Now I show the some categories of extractive summarization.
Make the graph from the document, then summarize it by considering the relation between the nodes (text-unit). TextRank is the typical graph based method.
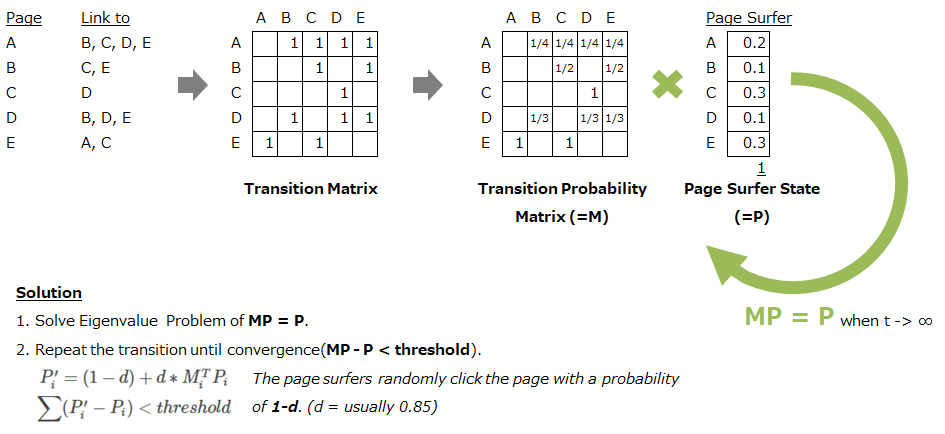
TextRank is based on PageRank algorithm that is used on Google Search Engine. Its base concept is "The linked page is good, much more if it from many linked page". The links between the pages are expressed by matrix (like Round-robin table). We can convert this matrix to transition probability matrix by dividing the sum of links in each page. And the page surfer moves the page according to this matrix.
TextRank regards words or sentences as pages on the PageRank. So when you use the TextRank, following points are important.
- Define the "text units" and add them as the nodes in the graph.
- Define the "relation" between the text units and add them as the edges in the graph.
- You can set the weight of the edge also.
Then, solve the graph by PageRank algorithm. LexRank uses the sentence as node and the similarity as relation/weight (similarity is calculated by IDF-modified Cosine similarity).
If you want to use TextRank, following tools support TextRank.
Extract the features of sentence, then evaluate its importance. Here is the representative research.
Sentence Extraction Based Single Document Summarization
In this paper, following features are used.
- Position of the sentence in input document
- Presence of the verb in the sentence
- Length of the sentence
- Term frequency
- Named entity tag NE
- Font style
...etc. All the features are accumulated as the score.
The No.of coreferences are the number of pronouns to previous sentence. It is simply calculated by counting the pronouns occurred in the first half of the sentence. So the Score represents the reference to the previous sentence.
Now we can evaluate each sentences. Next is selecting the sentence to avoid the duplicate of the information. In this paper, the same word between the new and selected sentence is considered. And the refinement to connect the selected sentences are executed.
Luhn’s Algorithm is also feature base. It evaluates the "significance" of the word that is calculated from the frequency.
You can try feature base text summarization by TextTeaser (PyTeaser is available for Python user).
Calculate the topic of the document and evaluate each sentences by what kinds of topics are included (the "main" topic is highly evaluated when scoring the sentence).
Latent Semantic Analysis (LSA) is usually used to detect the topic. It's based on SVD (Singular Value Decomposition).
The following paper is good starting point to overview the LSA(Topic) base summarization.
Text summarization using Latent Semantic Analysis
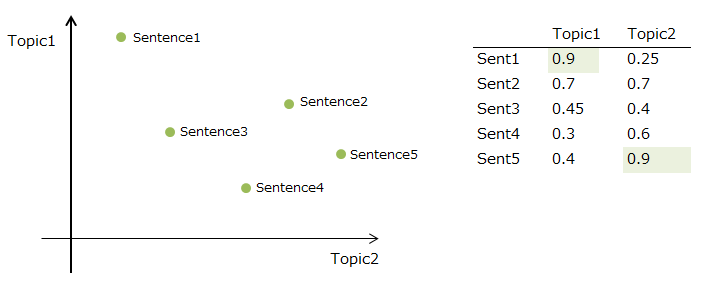
The simple LSA base sentence selection
There are many variations the way to calculate & select the sentence according to the SVD value. To select the sentence by the topic(=V, eigenvectors/principal axes) and its score is most simple method.
If you want to use LSA, gensim supports it.
- Generate a summary that keeps original intent. It's just like humans do.
- Pros: They can use words that were not in the original input. It enables to make more fluent and natural summaries.
- Cons: But it is also a much harder problem as you now require the model to generate coherent phrases and connectors.
Extractive & Abstractive is not conflicting ways. You can use both to generate the summary. And there are a way collaborate with human.
- Aided Summarization
- Combines automatic methods with human input.
- Computer suggests important information from the document, and the human decide to use it or not. It uses information retrieval, and text mining way.
The end-to-end approach tries to learn the process to convert the input document to the summary directly. The encoder-decoder model is most simple but powerful model, that from machine translation. The encoder encodes the input document, and decoder generates the summary from the encoded representation.
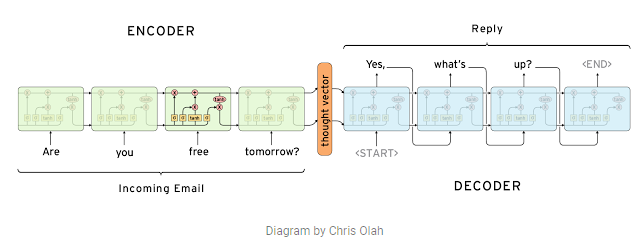
Computer, respond to this email
If you want to try the encoder-decoder summarization model, tensorflow offers basic model.
Rouge-N is a word N-gram count that matche between the model and the gold summary. It is similart to the "recall" because it evaluates the covering rate of gold summary, and not consider the not included n-gram in it.
ROUGE-1 and ROUGE-2 is usually used. The ROUGE-1 means word base, so its order is not regarded. So "apple pen" and "pen apple" is same ROUGE-1 score. But if ROUGE-2, "apple pen" becomes single entity so "apple pen" and "pen apple" does not match. If you increase the ROUGE-"N" count, finally evaluates completely match or not.
BLEU is a modified form of "precision", that used in machine translation evaluation usually. BLEU is basically calculated on the n-gram co-occerance between the generated summary and the gold (You don't need to specify the "n" unlike ROUGE).
- TensorFlow summarization
- Dataset: Annotated English Gigaword
- gensim
gensim.summarizationoffers TextRank summarization
- Wikipedia
- Blogs
- Papers
- A. Nenkova and K. McKeown, "Automatic summarization,". Foundations and Trends in Information Retrieval, 5(2-3):103–233, 2011.
- K. Sparck Jones, “Automatic summarizing: factors and directions,”. Advances in Automatic Text Summarization, pp. 1–12, MIT Press, 1998.