For this project, we will use a Docker container to containerize our code.
This document assumes that you already have Docker and NVIDIA-Docker installed on your machine.
Download the docker container for this project as follows:
docker pull alikhalid3110/ros_essentials:latest
To check if you have pulled the docker, run the following:
docker images
This should output all the dockers you have on your machine and it should contain alikhalid3110/ros_essentials:latest. Now, that you have the docker, you can run it on your machine. We have a script for this which will let you mount folders (volumes) to the docker as well. It also sets up different parameters so that you can use GUI programs from within the docker. To use this script, you need to do the following. Open the run_vrf_docker.bash file and change lines 4 and 5 to reflect paths to where you keep your datasets and codebases. As you can see, I keep datasets in /home/ali/dataset/ and my VRF code in ```/home/ali/workspace/VRF``. After you have made these changes, simply run the script to fire up the docker.
bash run_edge_assist_docker.bash
This will fire up the docker and you can interact with it using the current terminal window. If you want to attach another terminal to it, open a new terminal and type the following
docker exec -it vrf bash
This will open another terminal within the same docker.
If you are curious about the docker, it contains ROS (Robot Operating System), PCL (Point Cloud Library), ColMap and some of their dependencies.
This section explains how you can build the code that this repository contains. Again, the assumption is that you are running the alikhalid3110/ros_essentials:latest docker when you run the following commands. This repository uses the ROS build system (catkin_make). To build all the above modules, simply do the following.
- First, run the ROS master. To do this, run the following:
roscore &
- After the output stops, press enter and you'll be back to the terminal. With that, we can now build all the tools mentioned above as.
cd /workspace/catkin_ws/
catkin_make
catkin_make is the ROS build tool. It will build all tools in catkin_ws/src.
Download the three datasets (carla, usc_data_accuracy, rit_data_accuracy) from this link, unzip them, and place in the dataset directory that you have mounted with docker container. The dataset consists of 26 sub-datasets which are grouped into 3 main datasets. A brief descriptoin of datasets is provided below:
- carla:
This dataset consist of three different datasets (Dataset_1, Dataset_2,Dataset_3), collected in varying traffic conditions. Each dataset further consists of five datasets (D1-D5). - usc_data_accuracy
This dataset is refered in the paper as off-campus dataset and is a collection of five datasets (D1-D5). - rit_data_accurcay
This dataset is refered in the paper as on-campus dataset and is a collection of six datasets (D1-D6).
This section explains how to run the code and reproduce accuracy results mentioned in Table#3 and Table#9 in the paper.
- Download the datasets as explained here.
- Open five teminals and run docker in all of them as explained in docker setup. After that run the following command in all the terminals:
cd workspace/carkin_ws
- Run the ROS master. To do this, run the following command in any of the terminal:
roscore &
After the output stops, press enter and you'll be back to the terminal.
4. Modify setup_env.bash as explained here for each dataset and then run the following command in all the five terminals:
source setup_env.bash
- After sourcing the ```setup_env.bash``, run following commands in the specified terminals:
Terminal#1
rosrun fast_gicp infra_3
After runing the above command wait until you say Going into ros::spin() ...
Terminal#2
rosrun fast_gicp vehicle_ndt_5
After runing the above command wait until you say Going into ros::spin() ...
Terminal#3
rosrun fast_gicp vehicle_fusion_5
After runing the above command wait until you say Going into ros::spin() ...
Terminal#4
rosrun ./vehicle
Terminal#5
rosrun ./infra
- Now press space to play vehicle bag in terminal#4 and then in terminal#5 to play infrastructure(rsu) bag.
- After the bags are stoped, kill process in the first 3 terminals using 'Ctrl+C'.
- Update setup_env.bash and repeat the process for other dataset.
- After you are finished executing the code for all the datasets, run the python scripts (as shown below) to calculate and print the results. These python scripts are present in the root directory. The output of each python script is also shown below:
python3 carla_results.py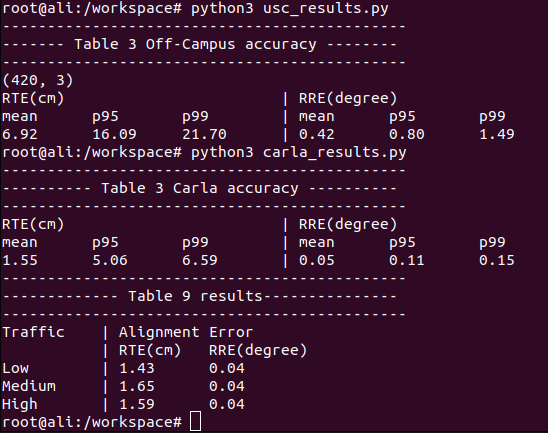
python3 usc_results.py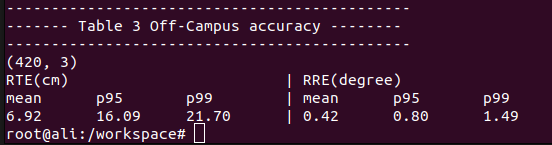
python3 rit_results.py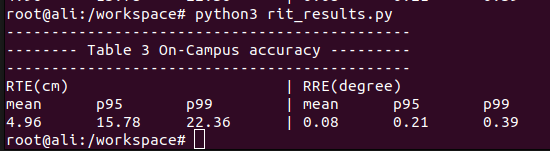
In this section, we will explain how to configure setup_env.bash for different datasets. You have to modify lines 12-17 for each dataset before running VRF.
-
Modify the file as follow
-
line # 12:
rosparam set /data_mode carla -
line # 15-16:
Modifydataset_pathanddataset_namelines according to the name of dataset. For Dataset_1(D1) it will look like this:dataset_path="/dataset/Dataset_1" dataset_name="D1" -
line # 17:
Modify this line according to dataset_name value.- For D1:
append="f" # true(t) or false(f) - For D2-D5:
append="t" # true(t) or false(f)
- For D1:
The Carla dataset consists of three sub-datasets: Dataset 1, Dataset 2, and Dataset 3. Each of these sub-datasets comprises five different datasets (D1 to D5). The results of these smaller datasets (D1 to D5) are concatenated into one file. It is necessary to run the code for these datasets in order (starting with D1, followed by D2, and so on to D5) because the ground truth for these datasets is also concatenated in the same order.
-
-
The setup_env.bash file for rit data will look like this:
rosparam set /data_mode rit dataset_path="/dataset/rit_data_accuracy" dataset_name="D1" append="f" # true(t) or false(f)Change
dataset_name(D1-D6) to reflect the dataset for which you are running VRF. -
The setup_env.bash file for rit data will look like this:
rosparam set /data_mode usc dataset_path="/dataset/usc_data_accuracy" dataset_name="D1" append="f" # true(t) or false(f)Change
dataset_name(D1-D5) to reflect the dataset for which you are running VRF.
@inproceedings{khan2024vrf,
title={VRF: Vehicle Road-side Point Cloud Fusion},
author={Khan, Kaleem Nawaz and Khalid, Ali and Turkar, Yash and Dantu, Karthik and Ahmad, Fawad},
booktitle={Proceedings of the 22nd Annual International Conference on Mobile Systems, Applications and Services},
pages={547--560},
year={2024}
}