Software for the identification of RNA modifications that affect the Watson-Crick base pairing (e.g. m3C, m1A, m22G) from RNAseq datasets.
This code takes samtools mpileup format (generated from a BAM) and extracts per-site information, specifically:
- mismatches (with proportion of bases: A,C,G,T), in addition to the mismatch frequency
- insertions
- deletions
- coverage
- reference base (A,C,G,T)
- position in transcript
- RT drop-off.
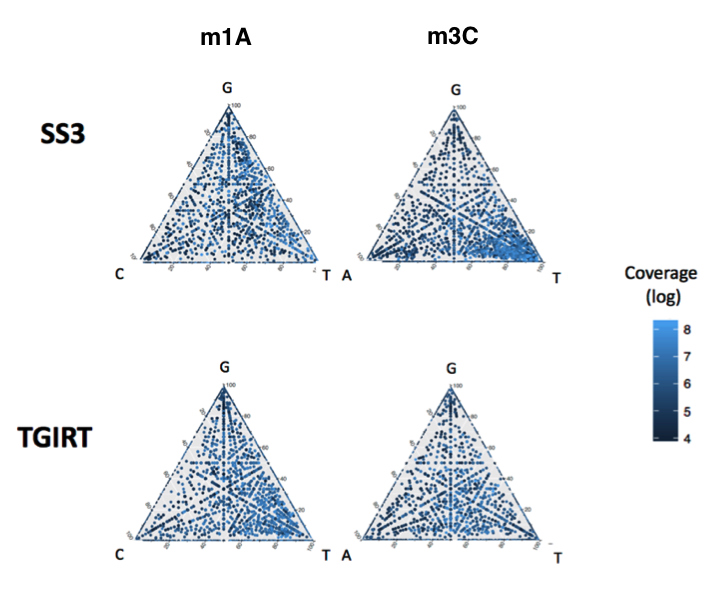
Please note that the "footprints" of RNA modifications in RNAseq datasets will vary depending on the reverse transcriptase enzyme used in your analysis. (see for example: Novoa*; Beaudoin* et al., bioRxiv 2020 for comparative analysis of mismatch signatures using SS3 vs TGIRT). Thus, you should only compare in a pairwise manner those datasets that have been reverse transcribed under the same conditions.
- It was written for the RNA modifications in cDNA sequencing data coming from Illumina RNAseq
- It can be used also for the analysis of nanopore cDNA sequencing data, and will be specially useful if using the CUSTOM protocol (first-strand only), because RT drop-offs will appear
- It can also be used for the analysis of direct RNA sequencing data, however please consider checking EpiNano (https://github.com/enovoa/EpiNano) in that case, as 5mer information is not given as output here, whereas EpiNano will give you that.
- You might find this code useful to use the RT drop-off to predict isoforms from dRNAseq data, based on where you observe a big drop of coverage along your transcripts (not tested)
Uses third-party code (e.g. pileup2base) to extract some of its features
It does pretty much what HAMR does, but with the following differences:
- mpileup2stats includes some additional information, e.g. RT drop off and indels.
- mpileup2stats does not compute pvalues, whereas HAMR does.
- mpileup2stats requires less time to compute than HAMR
- mpileup2stats requires requires fewer resources (CPU time and memory) than HAMR
- EpiNano computes per-read statistics and then per-site, using the per-read files.
- This software computes per-site stats directly from samtools mpileup.
- This software will not provide output per 5mer, whereas EpiNano reports both 1mer (per-site) and 5mer
- This code gives info about RT stops whereas EpiNano doesn't
- This code will tell you the relative frequency of A:C:G:T at each site (not just the global mismatch frequency),which is important to identify the underlying RNA modification identity, as these seem to cause different "error signatures". EpiNano doesn't give this info.
- This feature is also important for comparing different RT enzymes, they tend to change their relative misincorporation rates, in an RNA modification-dependent manner.
- Update 2021: EpiNano_RMS.py version now does give you this info - please see NanoRMS Github Repo.
This code is better suited for the analysis of RNA modifications in cDNA datasets, where the per-read information is more irrelevant. Also, this code provides information both on mismatches as well as on RT drop-offs.
If you are analyzing direct RNA nanopore sequencing data, EpiNano typically be a better choice.
Please open a GitHub issue if you have any doubts/questions/concerns. Thanks!
Written by Eva Novoa (2017). Last updated: April 2020.