Welcome to the m6ABasecaller GitHub repo!!
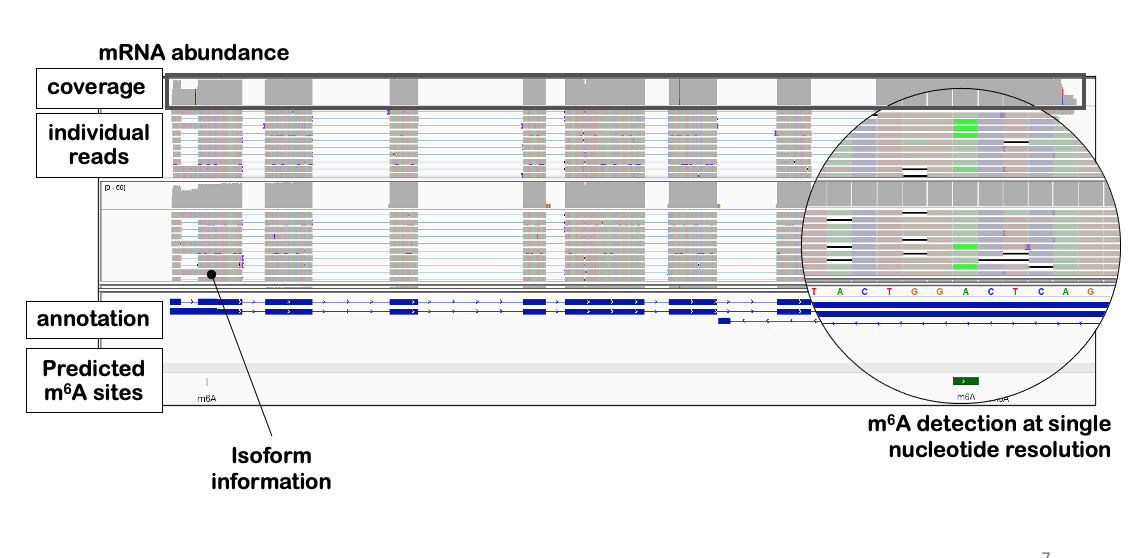
The m6ABasecaller allows to directly base-call m6A RNA modifications in individual reads, with single nucleotide resolution, from direct RNA sequencing nanopore raw FAST5 files, without the need of paired 'control' conditions (e.g. IVT, knockout, knockdown, etc).
The m6ABasecaller is an modification-aware RNA basecalling model that predicts 5 nucleosides (A,C,G,U,m6A) compared to canonical RNA basecalling models, which give as output 4 nuclesodies (A,C,G,U).
The RNA basecalling model can be used directly with Guppy. Alternatively, it can be fed to ModPhred, which facilitiates the storage and downstream analysis of RNA modification data from nanopore sequencing datasets.
This repo includes command line examples and scripts to:
-
- Use the m6A-modification-aware RNA basecalling model (which we refer to as m6ABasecaller for simplicity).
-
- Analyze the output generated by modPhred (ie. in this work, the RNA modification information was extracted by modPhred).
Please follow the instructions on how to install modPhred here.
Download the basecalling model rna_r9.4.1_70bps_m6A_hac.cfg and place it in your guppy folder at ont-guppy/data/. Then:
a) Option 1 -- All-in-one step solution: Base-call, store modification information and map with ModPhred (recommended option)
Here we use the tool ModPhred to base-call, encode m6A RNA modification and map the reads in a simple, and efficient manner, with a single command, making it very simple for the user to use alternative basecalling models. ModPhred performs the base-calling step using Guppy, and here we show how to run it with GPU. The data is stored both in the FASTQ and BAM files, in the QUALITY INFORMATION. Please note that with this option you are not going to save basecalled fast5 files!
For this option you need to download a singularity image with everything you need for ModPhred, we suggest to download it inside modPhred folder:
cd modPhred
singularity pull docker://lpryszcz/modphred-3.6.1
Usage:
-c: config for guppy, containing the m6A basecaller model. (for m6A basecaller: rna_r9.4.1_70bps_m6A_hac.cfg)
--host: path to your guppy_basecall_server
-f: your reference.fa file
-o: path to output folder
-i: path to input folders (containing the fast5 files). You can provide >=1 input folders
[--nv is to use singularity in a GPU node]
module load Singularity/3.2.1
singularity exec --nv modPhred/modphred-3.6.1.sif modPhred/run -c ont-guppy/data/rna_r9.4.1_70bps_m6A_hac.cfg --host soft/ont-guppy/bin/guppy_basecall_server -f reference.fa -o m6A_basecaller -i path/to/sample1 path/to/sample2 path/to/sample3
For more details on how to use ModPhred, please see the GitHub repository and the ReadTheDocs manual.
You may use this model standalone with Guppy, and then use megalodon or ModPhred to extract and process the RNA modification information. Please note that if you use megalodon, your RNA modification information will be encoded in the form of SAM tags. If you use ModPhred, your RNA modification information will be encoded in the quality of the FASTQ and BAM (future version of ModPhred will allow to encode modification information directly in SAM tags). In this work, all data was basecalled with Guppy 3.4.5, but other Guppy versions can work as well as the model provided is custom.
Usage:
guppy_basecaller –i path/to/sample/fast5 –s path/to/sample/output –c ont-guppy/data/rna_r9.4.1_70bps_m6A_hac.cfg
To use modPhred on previously m6A-basecalled fast5 files you can it as follows (no need for GPU at this point).
Usage:
-f: your reference.fa file
-o: path to output folder
-i: path to input folders (containing the fast5 files). You can provide >=1 input folders
module load Singularity/3.2.1
singularity exec modPhred/modphred-3.6.1.sif modPhred/run -f reference.fa -o m6A_basecaller -i path/to/sample1 path/to/sample2 path/to/sample3
modPhred will produce a mod.gz output file that contains all the sites that were found with at least 25 reads of coverage and at least 5% modification frequency in one sample, with information about coverage, modification probability, modification frequency and basecalling accuracy for each sample. For more information on the output see https://modphred.readthedocs.io/en/latest/output.html
| Software | Version |
|---|---|
| Singularity | 3.2.1 |
| ModPhred | 1.0b |
| Guppy | any between 3.4.5 and 6.0.6 |
If you find this work useful, please cite:
Cruciani S*, Delgado-Tejedor A*, Pryszcz LP*, Medina R, Llovera L and Novoa EM. De novo basecalling of m6A modifications at single-molecule and single-nucleotide resolution. BioRxiv 2023 (under review).
If you have any issues running this code, please go first over previous issues. If you still can't figure it out based on the prior responses/issues raised, please open a new issue. Thanks!