COSE-PYTHON 
This project is a Python (>=3.4) implementation of the IETF CBOR Encoded Message Syntax (COSE). COSE has reached RFC status and is now available at RFC 8152.
In addition to the core document the following have also become RFCs:
- RFC 8230 How to use RSA algorithms with COSE. (Not currently supported)
The project is implemented using pyca/cryptography for the crypto libraries and additionally uses python-ecdsa (https://github.com/warner/python-ecdsa) for the deterministic ECDSA algorithm. The pyca/cryptography currently only supports the ECDSA version that requires strong random numbers for each signature.
What is COSE
CBOR Encoded Message Syntax (COSE) is a data format for concise representation of small messages. It is optimized for low power devices. COSE messages can be encrypted, MAC'ed and signed. There are 6 different types of COSE messages:
- Encrypt0: An encrypted COSE message that has one recipient.
- Encrypt: An encrypted COSE message that can have multiple recipients (the message can be encrypted under different keys for different receivers).
- MAC0: An authenticated COSE message that has one recipient.
- MAC: An authenticated COSE message that can have multiple recipients (the message can be authenticated under different keys for different receivers).
- Sign0: A signed COSE message with one signer.
- Sign: A COSE message that has been signed by multiple signers.
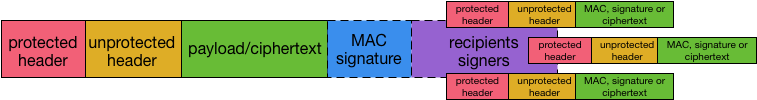
A basic COSE messages consists of 3 main parts:
- protected header: This message field contains information that needs to be protected. This information is taken into account during the encryption, calculation of the MAC or the signature.
- unprotected header: The information contained in the unprotected header is not protected by the cryptographic algorithms.
- payload: Contains the payload of the message (protected by the cryptographic algorithms).
Additionally, based on the message type, message fields can be added:
- mac/signature: This field contains a message authentication code or a signature.
- recipients/signers: This field either contains information for the individual recipients if the message has multiple receivers (e.g. key identifier information) or it contains information about the different signers of the message.
How to install
- Clone the repository
cd COSE-PYTHON- Run
git submodule init&&git submodule update - Install the python package (pycose) with pip:
pip3 install -e .
You should now be able to run the unit tests in the tests/ directory,
e.g.:
python3 test_crypto.py