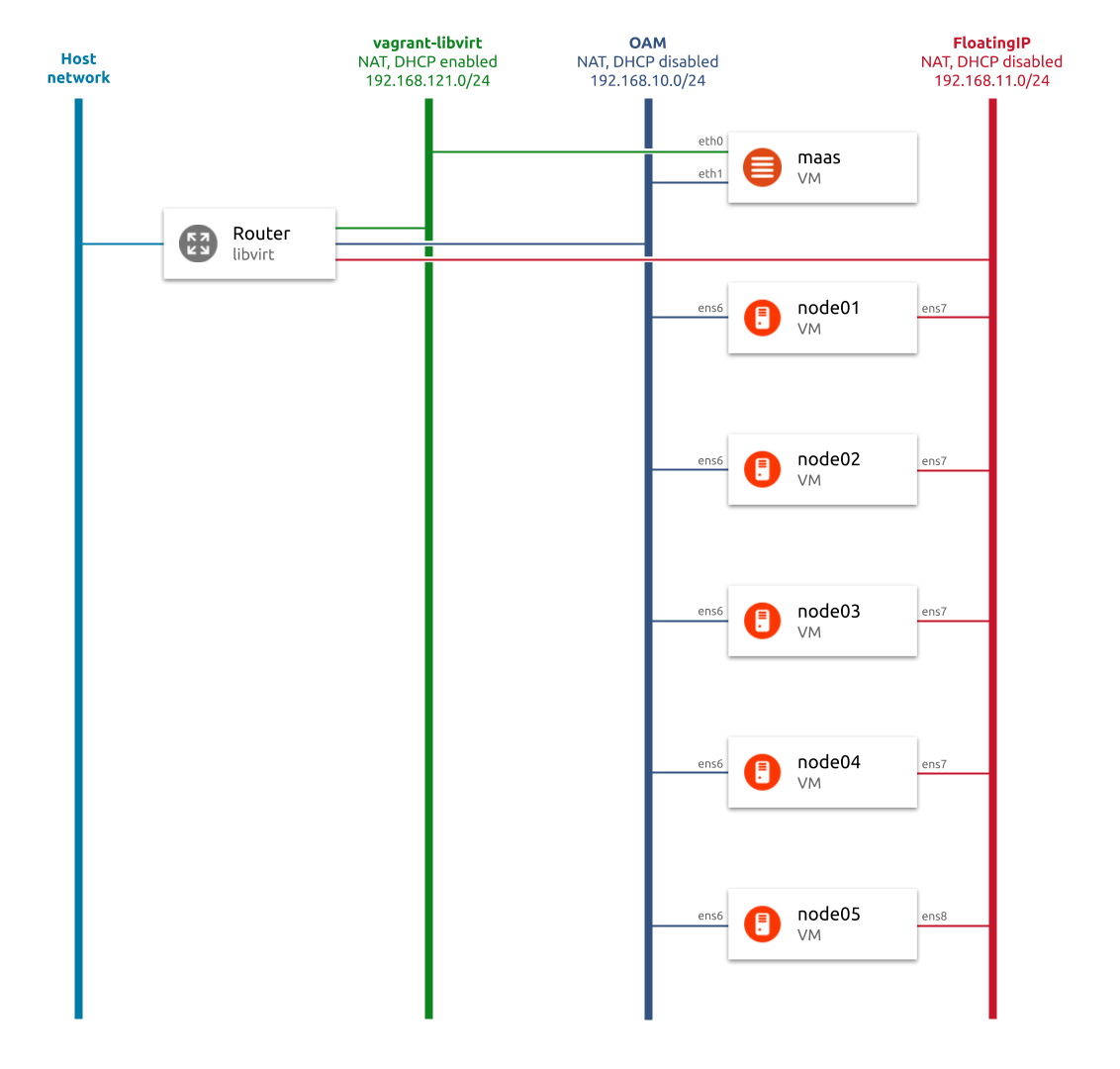
This set of scripts automates deployment of virtual MAAS sandbox. A virtual MAAS server and nodes managed by MAAS are deployed according to the following architecture diagram.
Make sure that you have installed Vagrant and vagrant-libvirt plugin. For example, on Ubuntu 18.04, you can run:
sudo apt install -y virt-manager vagrant vagrant-libvirt
sudo reboot
-
Update the 'Configuration section' at the top of
Vagrantfileso that it matches your environment. -
Add MAAS's public key to
authorized_hostson your host. This is necessary for MAAS to be able to control power of the Cloud Nodes.Vagrant will automatically provision MAAS with the key that you generate in this step.
(host)$ ssh-keygen -q -t rsa -f ./id_rsa -N "" (host)$ cat id_rsa.pub >> ~/.ssh/authorized_keys -
Deploy a virtual machine hosting MAAS server and virtual machines acting as Cloud Nodes. Wait until Vagrant finishes provisioning.
(host)$ vagrant up --provider libvirt -
Open web browser and login to MAAS using the following URL. Username:
root, password:root. -
Click "Go to dashboard" button.
-
Wait for machines to finish Commissioning.
Observe how machines are booting via PXE and commissioning in MAAS. When commissioning finishes, all nodes will report
Readystatus. -
(Optional) Deploy Ubuntu on a machine.
Select
Take action→Deployon selected machine to deploy Ubuntu. Once the machine is in stateDeployed, you can ssh to it frommaasnode. In order to learn the IP address assigned by MAAS to this machine, checkNetworktab for a specific machine.
Juju client has already been installed on maas machine. Juju configuration files
clouds.yaml and credentials.yaml have also been automatically provisioned
by Vagrant.
Now you can bootstrap a Juju Controller on one of the Cloud Nodes (typically
node01):
(host)$ vagrant ssh maas
(maas)$ juju bootstrap maas-cloud maas-cloud-controller
For OpenStack deployment, I have chosen OpenStack Stein on Ubuntu Bionic openstack-base #61 bundle from the official Juju charm store.
# Download the bundle
(maas)$ charm pull openstack-base-61 ~/openstack-base
# Customize bundle to fit the architecture
(maas)$ sed -i 's/eno2/ens7/g' openstack-base/bundle.yaml
(maas)$ sed -i 's/\/dev\/sdb //g' openstack-base/bundle.yaml
# Deploy OpenStack bundle
(maas)$ juju add-model openstack
(maas)$ juju deploy ./openstack-base/bundle.yaml
# Watch the deployment
(maas)$ watch -c juju machines --color
(maas)$ watch -c juju status --color
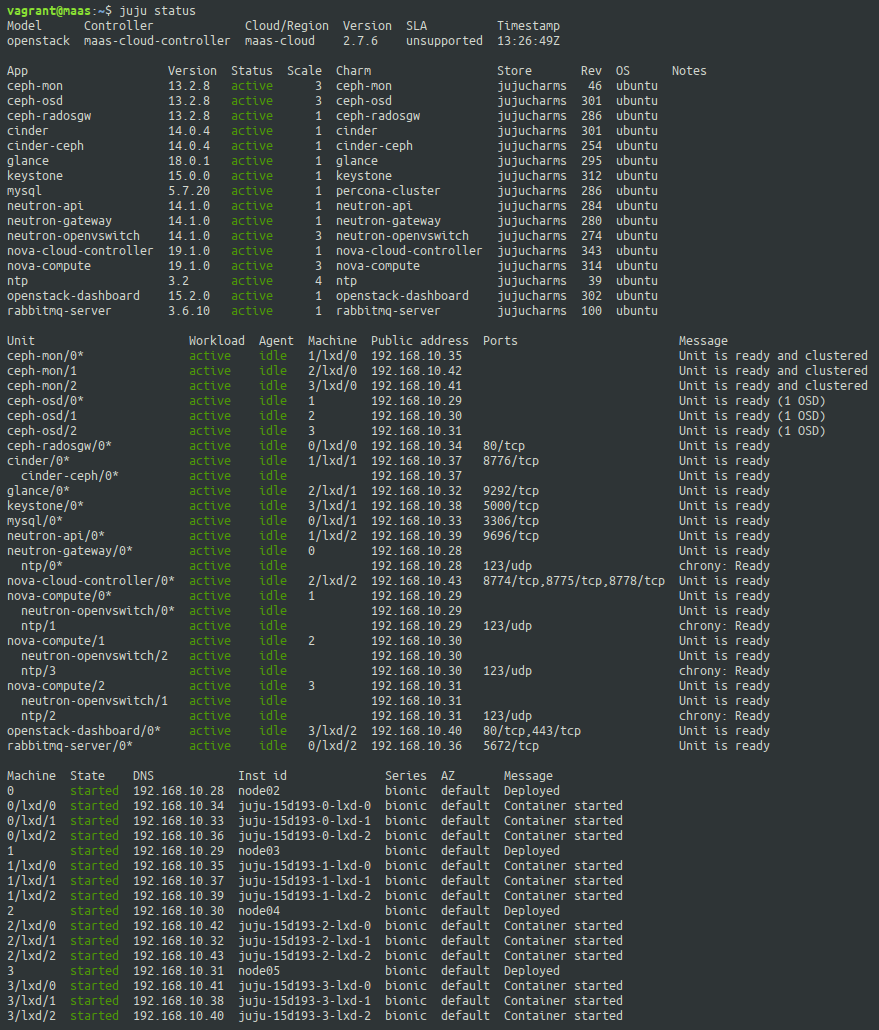
Once the deployment is finished, Juju will report all units in active state.
Get the IP address of OpenStack Dashboard and construct the URL to access it.
(maas)$ DASHBOARD_IP=$(juju run --unit openstack-dashboard/0 'unit-get public-address')
(maas)$ echo "http://${DASHBOARD_IP}/horizon/"
Run the following commands to find out what is the admin password for logging into OpenStack dashboard:
(maas)$ source openstack-base/openrc
(maas)$ env | grep OS_PASSWORD
Login with:
- Domain:
admin_domain, - User:
admin, - Password: as in
$OS_PASSWORDenvironment variable.
You can also interact with OpenStack using CLI, e.g.:
(maas)$ sudo snap install openstackclients --classic
(maas)$ openstack catalog list
Check out more examples on how to create networks, images and instances at https://jaas.ai/openstack-base.
If you haven't bootstrapped a Juju controller yet, go to the Bootstrap Juju Controller section above and run the commands.
Before deploying Kubernetes, destroy your openstack juju model, if you had
previously deployed OpenStack.
(maas)$ juju destroy-model openstack
For Kubernetes deployment, I have chosen kubernetes-core #1036 bundle from the official Juju charm store.
# Download the bundle
(maas)$ charm pull kubernetes-core-1036 ~/kubernetes-core
# Customize bundle to fit the machines you actually have
(maas)$ sed -i 's/cores=4/cores=2/g' kubernetes-core/bundle.yaml
# Deploy Kubernetes bundle
(maas)$ juju add-model kubernetes
(maas)$ juju deploy ./kubernetes-core/bundle.yaml
# Watch the deployment
(maas)$ watch -c juju status --color
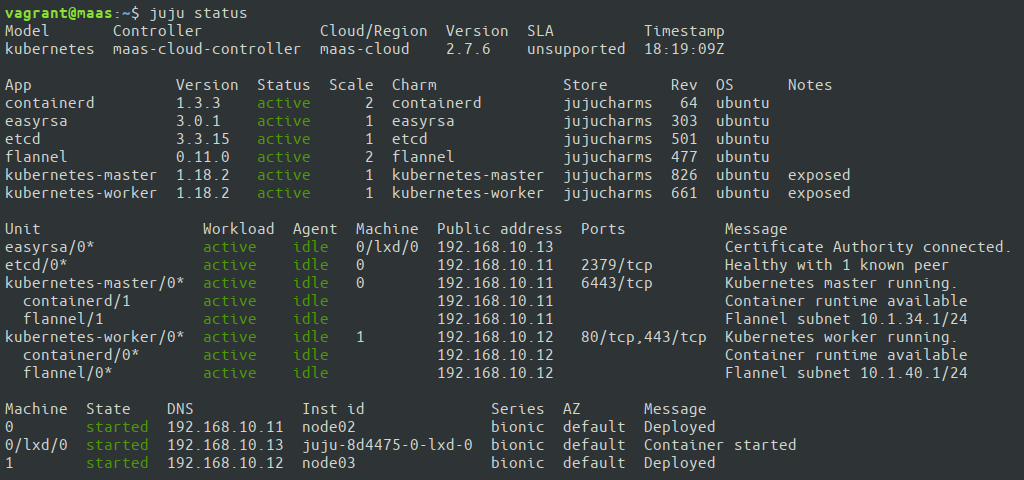
Once the deployment is finished, Juju will report all units in active state.
Check out more examples on how to deploy Kubernetes workloads at
https://jaas.ai/kubernetes-core.
If you haven't bootstrapped a Juju controller yet, go to the Bootstrap Juju Controller section above and run the commands.
Before deploying Kubernetes, destroy your openstack or kubernetes juju
model, if you had previously deployed OpenStack or Kubernetes with
juju destroy-model command.
Example Ceph bundle has been provisioned onto maas machine by Vagrant.
# Deploy Ceph bundle
(maas)$ juju add-model ceph
(maas)$ juju deploy ./ceph/bundle.yaml
# Watch the deployment
(maas)$ watch -c juju status --color
Once the deployment settles, you can interact with Ceph cluster from any
ceph-mon unit.
(maas)$ juju ssh ceph-mon/0
(ceph-mon/0)$ sudo ceph status