CI (Continuous Integration) configuration for ROS (Robot Operating System).
Table of Contents
Other than the brief introduction in this page, you can also check the detailed doc here.
This package contains CI (Continuous Integration) configuration that any ROS-powered packages can commonly use. Some notable feature:
- Checks if your package builds, installs without issues. If unit/system tests are defined run them. ROS Prerelease Test can optionally be run.
- Proven to cover the general requirements of the ROS-based robotics repositories. Easily configurable.
- Users can add custom pre/post processes.
- Covers ROS Indigo, Jade, Kinetic distribution.
- As of January 2017, this repo provides configuration for Travis CI only, although it should be easily deployed from other CI services.
For a brief overall introduction, you could also check a presentation:
With a few steps, you can start in your client repository using CI confiurations stored in industrial_ci.
- Activate CI for your github repository on Travis CI). You may do so either at https://travis-ci.org/profile/YOUR_GITHUB_ORGANIZATION or at https://travis-ci.org/profile/YOUR_GITHUB_USER (depending on where your repository sits).
- In .travis.yml file in your client repo, add in "install" section a sentence git clone https://github.com/ros-industrial/industrial_ci.git .industrial_ci, like below:
install: - git clone https://github.com/ros-industrial/industrial_ci.git .industrial_ci script: - .industrial_ci/travis.sh
- Note: The name .industrial_ci is NO longer REQUIRED for the cloned folder starting version 0.3.2; you can pick any name (recommended practice to keep the folder hidden (by prepending ".").
- Enable CI for your repo. Please refer to official doc for the steps to do so. Note for Gitlab CI, necessary steps might be different between hosted version (i.e. the one on gitlab.com) v.s. the one on your own server, which Gitlab doesn't always clarify in its documentation.
- In .gitlab-ci.yml file in your client repo, add the following minimal configuration (this snippet can be the entire content of the file), replacing indigo for your chosen distro:
image: docker:git services: - docker:dind before_script: - apk add --update bash coreutils tar - git clone https://github.com/ros-industrial/industrial_ci .industrial_ci indigo: script: .industrial_ci/gitlab.sh ROS_DISTRO=indigo
- Enable CI for your repo. Please refer to official doc for the steps to do so.
- In the bitbucket-pipelines.yml file in your client repo, add the following minimal configuration (this snippet can be the entire content of the file), replacing indigo for your chosen distro:
image: docker:git
pipelines:
default:
- step:
services:
- docker
script:
- apk add --update bash coreutils tar
- git clone https://github.com/ros-industrial/industrial_ci .industrial_ci
- .industrial_ci/bitbucket.sh ROS_DISTRO=indigo
definitions:
services:
docker:
memory: 2048
- A template for Travis CI.
- For development branch intended for ROS Indigo: ros_canopen
- For development branch intended for ROS Indigo onward:
- example 1 (Indigo and Jade compatible).
- example 2 (Indigo, Jade, Kinetic compatible. Also runs ROS Prerelease Test).
- For development branch intended for ROS Kinetic: industrial_core
- For more complexed example: .travis.yml from the same repo. You can see how options are used.
- For Gitlab CI, a small sample config.
There might not an easy way to precisely count how many repositories out there are using industrial_ci. Counting that number isn't even our priority at all, but we're often simply curious. Here's some ways that give us some clues for the usage metrics:
Searching Github repos that contain string industrial_ci) (with some duplicates. Excluding industrial_ci repo):
- 675 (May 15, 2018)
- 457 (Dec 12, 2017)
- 142 (Jan 20, 2017)
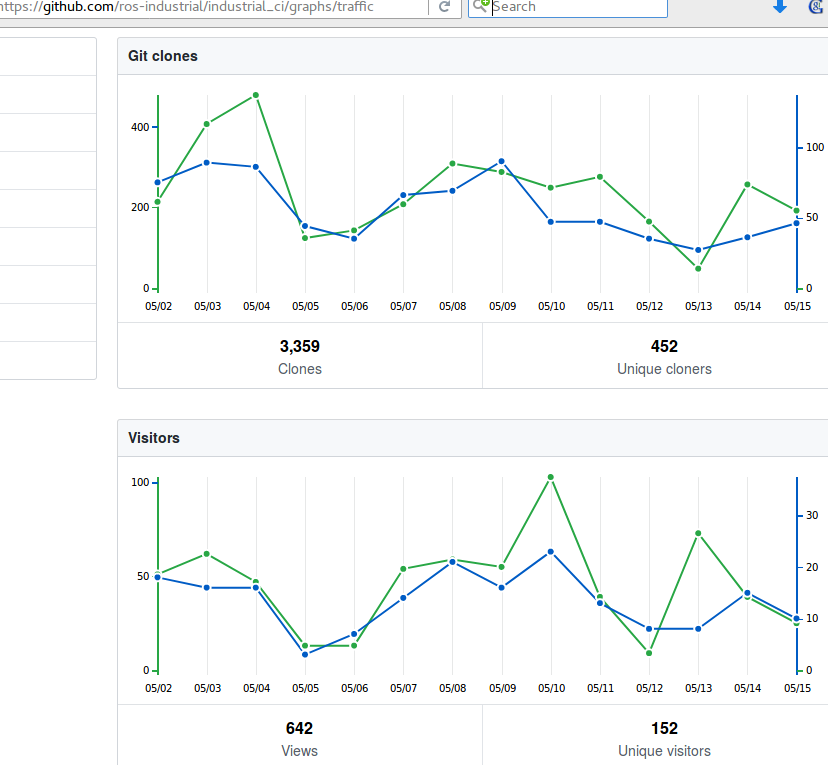
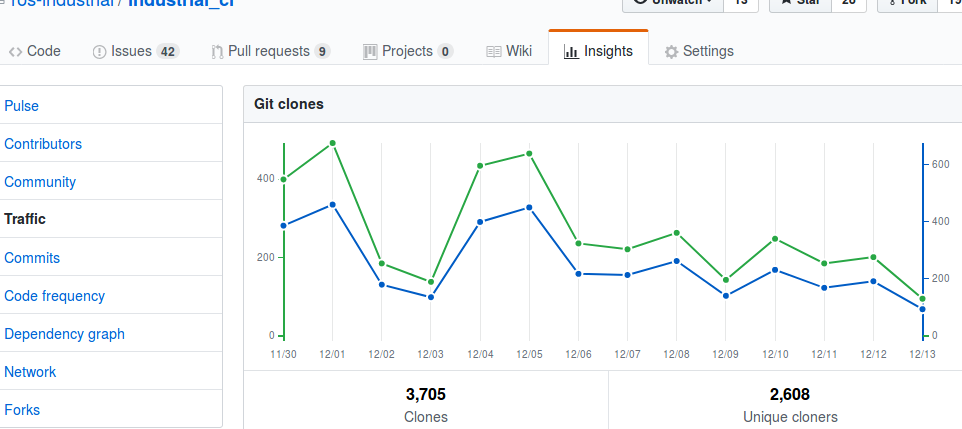
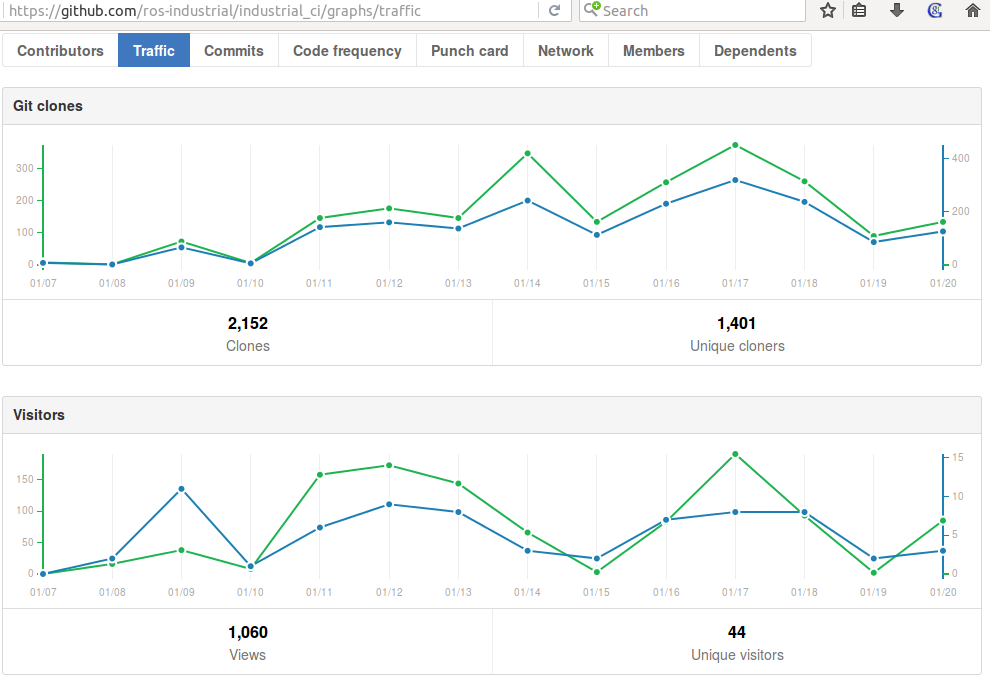
Github--> Graphs --> Traffic view (visible only to admins).
- May 15, 2018
- Dec 12, 2017
- Jan 20, 2017
EoF