By Ngo Minh Tan
Video overview: https://youtu.be/IFfOULopmNA
The database simulate database of a task manager webapp, includes all entities necessary to facilitate the process of manage tasks's progress and leaving feedback on users work. The DBMS in use is MySQL .As such, included in the database's scope is:
- Users, including basic identifying information
- Tasks, including basic identifying information, the time at which the task will due, its priority (Low, Medium, High), its status(Not Started, In Progress, Completed), the created date and updated date.
- Categories submissions, including the name of category. Tasks can be associated with multiple categories.
- Roles, which includes the id and role of a user and id of task which they are assigned, also the date which they are assigned the role.
- Comments on task, including the content of the comment, the comment's date and the task on which comment was left.
Out of scope are elements like attachments, subtasks, reminders, and other non-core attributes.
This database will support:
- CRUD operations for userss and instructors
- Tracking all versions of users submissions, including multiple submissions for the same problem
- Adding multiple comments to a users submission from instructors
Note that in this iteration, the system will not support users responding to comments.
Entities are captured in SQLite tables with the following schema.
The database includes the following entities:
The users table includes:
id, which specifies the unique ID for the users as anINT UNSIGNED.UNSIGNEDis used to make sure there are no negative ids This column thus has thePRIMARY KEYconstraint applied.first_name, which specifies the users's first name asVARCHAR(50)with the maximum number of characters is 50, givenVARCHAR(50)is appropriate for name fields. It has a CHECK constraint which check if the name isn't include number in them.last_name, which specifies the users's last name.VARCHAR(50)is used for the same reason asfirst_name. It also has the CHECK constraint likefirst_name.username, which specifies the users's username.VARCHAR(15)is used for the same reason asfirst_name. AUNIQUEconstraint ensures no two users have the same GitHub username.email, which specifies the user's email.VARCHAR(128)is used for the same reason asfirst_name.password, which specifies the user's password.VARCHAR(128)is used for the same reason asfirst_name.
The tasks table includes:
id, which specifies the unique ID for the task as anINT UNSIGNED. This column thus has thePRIMARY KEYconstraint applied.creator_id, which is the ID of the users who made the submission as anINT UNSIGNED. This column thus has theFOREIGN KEYconstraint applied, referencing theidcolumn in theuserstable to ensure data integrity.title, which specifies the title or name of the task asVARCHAR(255).description, which specifies the text's description asTEXT. It allows for longer text entriesdue_date, indicating the due date and time for the task asDATETIME.DATETIMEdate type includes both date and time, as the name suggested.priority, representing the priority level of the task asENUM. It can take one of three values: 'Low', 'Medium', or 'High'.status, indicating the current status of the task asENUM. It can take one of three values: 'Not Started', 'In Progress', or 'Completed'.created_date, representing the date and time when the task was created usingTIMESTAMP.TIMESTAMPincludes both date and time just likeDATETIMEbut is more percise for logging reasons. The default value for thecreated_dateattribute is the current timestamp, as denoted byDEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP.updated_date, representing the date and time when the task was last updated asTIMESTAMP.TIMESTAMPis used for the same reason ascreated_date. The default value is also the current timestamp, as denoted byDEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP. It also auto using the current timestamp each time the task is updated, hence the use ofON UPDATE CURRENT_TIMESTAMP
All columns in the tasks table are required and hence should have the NOT NULL constraint applied.
The categories table includes:
id, which specifies the unique ID for the instructor as anINT UNSIGNED. This column thus has thePRIMARY KEYconstraint applied.name, which is the name of the problem set asVARCHAR(30), 30 is the sufficient length for the category's name.
All columns in the categories table are required, and hence should have the NOT NULL constraint applied. No other constraints are necessary.
The task_category table includes:
id, which specifies the unique ID for the instructor as anINT UNSIGNED. This column thus has thePRIMARY KEYconstraint applied.task_id, which is the ID of the users who made the submission as anINT UNSIGNED. This column thus has theFOREIGN KEYconstraint applied, referencing theidcolumn in thetaskstable to ensure data integrity.category_id, which is the ID of the users who made the submission as anINT UNSIGNED. This column thus has theFOREIGN KEYconstraint applied, referencing theidcolumn in thecategoriestable to ensure data integrity.
The roles table includes:
id, which specifies the unique ID for the submission as anINTEGER. This column thus has thePRIMARY KEYconstraint applied.assigned_user_id, which is the ID of the users who made the submission as anINTEGER. This column thus has theFOREIGN KEYconstraint applied, referencing theidcolumn in theuserstable to ensure data integrity.task_id, which is the ID of the problem which the submission solves as anINTEGER. This column thus has theFOREIGN KEYconstraint applied, referencing theidcolumn in thetaskstable to ensure data integrity.assigned_date, indicating the due date and time for the task asDATETIME.DATETIMEdate type includes both date and time, as the name suggested.role, indicating the role of the collaborator in the task asENUM. It can take one of three values: Assignee - The person responsible for completing the task, Creator - The person created the task, Approver - The person who has the authority to approve or reject the completion of the task, Collaborator - A general role for someone actively participating in the task but without a specific assigned responsibility.
All columns are required and hence have the NOT NULL constraint applied where a PRIMARY KEY or FOREIGN KEY constraint is not.
The comments table includes:
id, which specifies the unique ID for the submission as anINTEGER. This column thus has thePRIMARY KEYconstraint applied.user_id, which specifies the ID of the instructor who wrote the comment as anINTEGER. This column thus has theFOREIGN KEYconstraint applied, referencing theidcolumn in theuserstable, which ensures that each comment be referenced back to a users.task_id, which specifies the ID of the submission on which the comment was written as anINTEGER. This column thus has theFOREIGN KEYconstraint applied, referencing theidcolumn in thetaskstable, which ensures each comment belongs to a particular task.comment, which contains the contents of the columns asTEXT, given thatTEXTcan still store long-form text.comment_date, representing the date and time when the task was created usingTIMESTAMP.TIMESTAMPincludes both date and time just likeDATETIMEbut is more percise for logging reasons. The default value for thecomment_dateattribute is the current timestamp, as denoted byDEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP.
All columns are required and hence have the NOT NULL constraint applied where a PRIMARY KEY or FOREIGN KEY constraint is not.
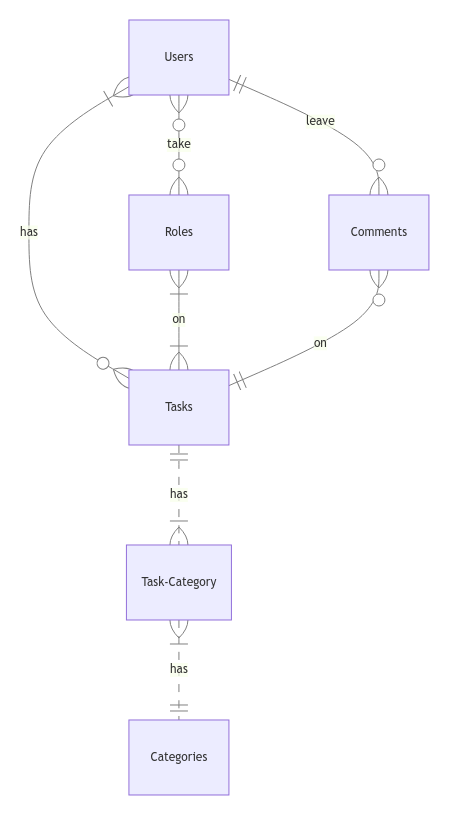
The below entity relationship diagram describes the relationships among the entities in the database.
As detailed by the diagram:
- One users is capable of having 0 to many tasks. 0, if they have yet just create their account, and many if they got assign to one or more tasks. A tasks can be assigned to one or more users.
- A role can be assign to 0 to many users. 0 if no users have yet got assigned to that role, and many because a role can be taken by many users. A role can work on one to many tasks. At them same time, a task have at least one role associated with (the creator) it or many roles.
- A comment is associated with one and only one user, whereas a task can have 0 to many comments: 0 if a user has yet to comment on the submission, and many if many users leave comments on the task.
- A task needed to have at least one or many categories. And on the other hands, a category have at least one task associated with it or many tasks can have the same category.
Per the typical queries in queries.sql, it is common for users of the database to access all tasks associated with any particular users. For that reason, indexes are created on the first_name, last_name, and username columns on users table to speed the identification of userss by those columns.
Similarly, it is also common practice for a user of the database to concerned with viewing all tasks associated with a user. As such, an index is created on the title column in the tasks table to speed the identification of problems by name.
Finally, users might want to see the categories associated with a task. Because of that, an index is created on the name column in the categories table to speed the identification of problems by name.