Jettison is a high performance, reflection-less, and configurable JSON encoder for the Go programming language, inspired by bet365/jingo, with a richer features set, aiming at 100% compatibility with the standard library.
Jettison uses the new Go modules. Releases are tagged according to the SemVer format, prefixed with a v, starting from 0.2.0. You can get the latest release using the following command.
$ go get github.com/wI2L/jettison❗ Requires Go1.12+, due to the usage of the io.StringWriter interface.
- Fast, see benchmarks
- Efficient, zero allocations on average
- Behavior identical to the standard library by default
- No code generation required
- Clear and concise API
- Configurable with opt-in functional options
- Native support for
time.Timeandtime.Durationtypes - Custom
Marshalerinterface to work with aWriter - Extensive testsuite that compares its output against
encoding/json
The goal of Jettision is to take up the idea introduced by the bet365/jingo package and build a fully-featured JSON encoder around it, that comply with the behavior of the encoding/json package. Unlike the latter, Jettison does not use reflection during marshaling, but only once to create the instruction set for a given type ahead of time. The drawback to this approach requires to instantiate an encoder once for each type that needs to be marshaled, but that is overcomed with a package cache.
The package aims to have a behavior similar to that of the standard library for all types encoding and struct tags, meaning that the documentation of the json.Marshal function is applicable for Jettison, with a few exceptions described in this section. As such, most of the tests compare their output against it to guarantee that.
The main concept of Jettison consists of using pre-build encoders to reduce the cost of using the reflect package at runtime. When a new instance of an encoder is created for a specific type, a set of instructions is recursively generated, which defines how to iteratively encode a value. An instruction is a function or a closure, that have all the information required to read the data from memory using unsafe operations during the instruction set execution.
All notable differences with the standard library behavior are listed below. Please note that these might evolve with future versions of the package.
- The JSON returned by the
MarshalJSONmethod of types implementing thejson.Marshalerinterface is neither validated nor compacted.
- The
time.Timeandtime.Durationtypes are handled natively. For time values, the encoder doesn't invokeMarshalJSONorMarshalText, but use thetime.AppendFormatfunction instead, and write the result to the stream. Similarly, for durations, it isn't necessary to implements thejson.Marshalerorencoding.TextMarshalerinterfaces on a custom wrapper type, the encoder uses the result of one of the methodsMinutes,Seconds,NanosecondsorString, based on the duration format configured.
-
Nil map keys values implementing the
encoding.TextMarshalerinterface are encoded as empty strings, while theencoding/jsonpackage currently panic because of that. See this issue for more details.[1] -
Nil struct fields implementing the
encoding.TextMarshalerinterface are encoded asnull, while theencoding/jsonpackage currently panic because of that. See this issue for more details.[1]
1: The issues mentioned above have had their associated CL merged, and should be shipped with Go 1.14.
Starting from version 0.3.0, the Marshal and MarshalTo functions are available. The first will allocate a new bytes slice to store the encoding of the given value, similar to json.Marshal, while the latter will write to the Writer. These functions use a package's cache to fetch the appropriate encoder for the given value type. If an encoder does not exist, a new one is created on the fly and stored in the cache for future reuse.
type X struct {
A string `json:"a"`
B int64 `json:"b"`
}
b, err := jettison.Marshal(X{
A: "Loreum",
B: 42,
})
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
os.Stdout.Write(b){"a":"Loreum","b":42}If more control over the encoding behavior is required, or to avoid the latency of creating a new encoder when encoding a type for the first time, an encoder can be created ahead of time, during initialization. Note that if you don't invoke the Compile method, the instruction set will be generated once, on the first call to the Encode method.
The second parameter of the Encode method is an interface that groups the io.Writer, io.StringWriter and io.ByteWriter interfaces. In the following example, we use a new bytes.Buffer instance, which implements the three interfaces previously mentioned.
type X struct {
A string `json:"a,omitempty"`
B int `json:"b"`
}
enc, err := jettison.NewEncoder(reflect.TypeOf(X{}))
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
err = enc.Compile()
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
xx := X{
A: "Loreum",
B: 42,
}
var buf bytes.Buffer
if err := enc.Encode(&xx, &buf); err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
os.Stdout.Write(b){"a":"Loreum","b":42}Several opt-in options are available to customize the behavior of an encoder during marshaling. The third parameter of the Encode method is variadic and accept a list of functional options described below.
- TimeLayout • Defines the layout used to encode
time.Timevalues. The layout must be compatible with the AppendFormat method. The default layout istime.RFC3339Nano. - DurationFormat • Defines the format used to encode
time.Durationvalues. The default format isDurationString. See the documentation of theDurationFmttype for the complete list of formats available. - UnixTimestamp • Encode
time.Timevalues as JSON numbers representing Unix timestamps, the number of seconds elapsed since Januaray 1, 1970 UTC. It uses thetime.Unixmethod. This option has precedence overTimeLayout. - UnsortedMap • Disables map keys sort. See Map benchmark for performance difference.
- ByteArrayAsString • Encodes byte arrays as JSON strings rather than JSON arrays. The output is subject to the same escaping rules used for the
stringtype, unless the optionNoStringEscapingis also used. - RawByteSlice • Disables the base64 default encoding used for byte slices.
- NilMapEmpty • Encodes nil Go maps as empty JSON objects rather than
null. - NilSliceEmpty • Encodes nil Go slices as empty JSON arrays rather than
null. - NoStringEscaping • Disables string escaping.
NoHTMLEscapingandNoUTF8Coercionare ignored when this option is used. - NoHTMLEscaping • Disables the escaping of special HTML characters such as
&,<and>in JSON strings. This is similar tojson.Encoder.SetEscapeHTML(false). - NoUTF8Coercion • Disables the replacement of invalid bytes with the Unicode replacement rune in JSON strings.
- WithFields • Sets a whitelist that represents which fields are to be encoded when marshaling a Go struct.
If you'd like to run the benchmarks yourself, use the following command.
go get github.com/cespare/prettybench
go test -bench=. | prettybenchThe benchmarks has been run 10x (statistics computed with benchstat) on a machine with the following specs:
OS: Ubuntu 16.04.6 LTS
CPU: Intel(R) Core(TM) i5-6600 CPU @ 3.30GHz
Mem: 16GB
Go: go version go1.13 linux/amd64
Tag: v0.4.1
Stats
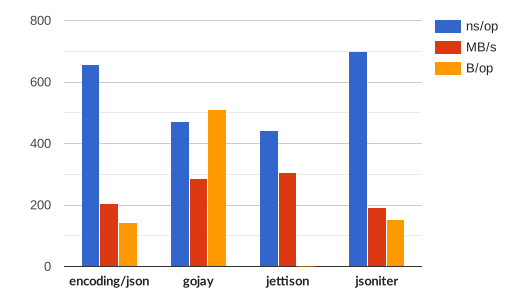
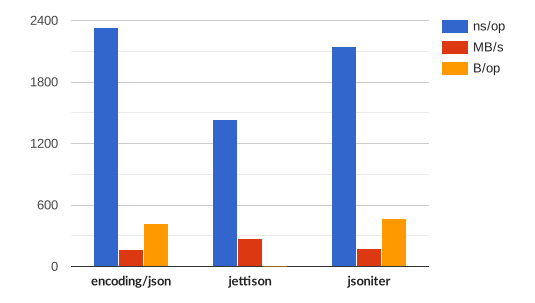
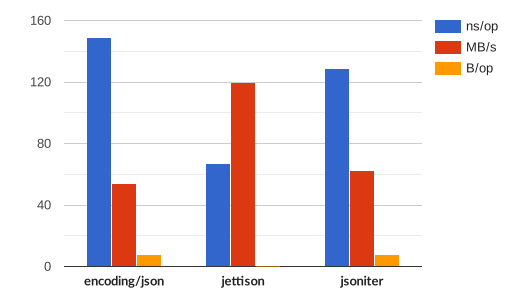
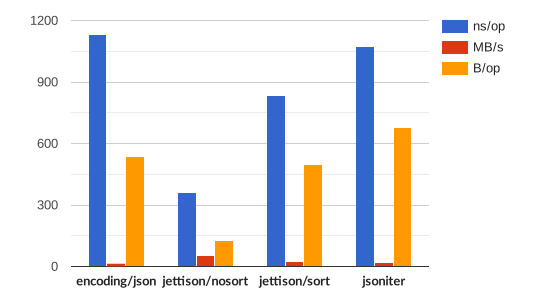
name time/op SimplePayload/encoding/json-4 656ns ± 1% SimplePayload/jsoniter-4 698ns ± 1% SimplePayload/gojay-4 473ns ± 2% SimplePayload/jettison-4 443ns ± 2% ComplexPayload/encoding/json-4 2.59µs ± 1% ComplexPayload/jsoniter-4 2.37µs ± 0% ComplexPayload/jettison-4 1.56µs ± 1% Interface/encoding/json-4 162ns ± 5% Interface/jsoniter-4 140ns ± 3% Interface/jettison-4 69.3ns ± 3% Map/encoding/json-4 1.20µs ± 1% Map/jsoniter-4 1.09µs ± 0% Map/jettison/sort-4 866ns ± 0% Map/jettison/nosort-4 381ns ± 1%name speed SimplePayload/encoding/json-4 206MB/s ± 1% SimplePayload/jsoniter-4 193MB/s ± 1% SimplePayload/gojay-4 286MB/s ± 2% SimplePayload/jettison-4 305MB/s ± 1% ComplexPayload/encoding/json-4 150MB/s ± 1% ComplexPayload/jsoniter-4 163MB/s ± 0% ComplexPayload/jettison-4 248MB/s ± 1% Interface/encoding/json-4 49.4MB/s ± 5% Interface/jsoniter-4 57.3MB/s ± 3% Interface/jettison-4 115MB/s ± 3% Map/encoding/json-4 15.9MB/s ± 1% Map/jsoniter-4 17.5MB/s ± 0% Map/jettison/sort-4 21.9MB/s ± 0% Map/jettison/nosort-4 49.9MB/s ± 1%
name alloc/op SimplePayload/encoding/json-4 144B ± 0% SimplePayload/jsoniter-4 152B ± 0% SimplePayload/gojay-4 512B ± 0% SimplePayload/jettison-4 0.00B ComplexPayload/encoding/json-4 416B ± 0% ComplexPayload/jsoniter-4 472B ± 0% ComplexPayload/jettison-4 0.00B Interface/encoding/json-4 8.00B ± 0% Interface/jsoniter-4 8.00B ± 0% Interface/jettison-4 0.00B Map/encoding/json-4 536B ± 0% Map/jsoniter-4 680B ± 0% Map/jettison/sort-4 496B ± 0% Map/jettison/nosort-4 128B ± 0%
name allocs/op SimplePayload/encoding/json-4 1.00 ± 0% SimplePayload/jsoniter-4 2.00 ± 0% SimplePayload/gojay-4 1.00 ± 0% SimplePayload/jettison-4 0.00 ComplexPayload/encoding/json-4 1.00 ± 0% ComplexPayload/jsoniter-4 3.00 ± 0% ComplexPayload/jettison-4 0.00 Interface/encoding/json-4 1.00 ± 0% Interface/jsoniter-4 1.00 ± 0% Interface/jettison-4 0.00 Map/encoding/json-4 13.0 ± 0% Map/jsoniter-4 11.0 ± 0% Map/jettison/sort-4 6.00 ± 0% Map/jettison/nosort-4 2.00 ± 0%
Simple [source]
Basic payload with fields of type string, int and bool.
Complex [source]
Large payload with a variety of composite Go types, such as struct, multi-dimensions array, and slice, with pointer and non-pointer value types.
Interface [source]
Map [source]
Compares Go map marshaling performances, with and without keys sort.
Jettison is licensed under the MIT license. See the LICENSE file.
This package also uses some portions of code from the Go encoding/json package. The associated license can be found in LICENSE.golang.