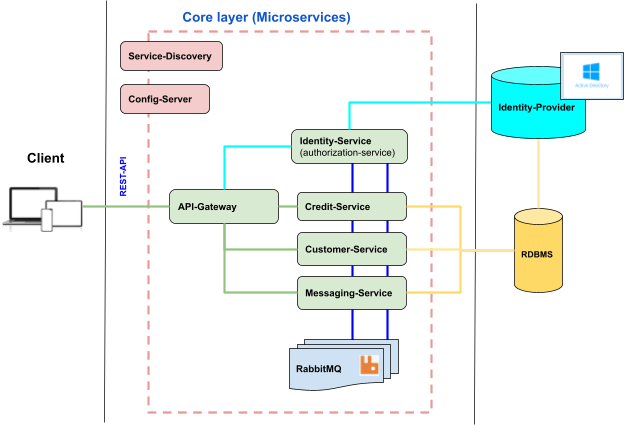
General structure is more based on Event-Driven Microservices architecture, leveraging Spring Cloud Framework and RabbitMQ message-broker.
Technical stack information :
| No | Name | Version | Details |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | JDK | 17 | |
| 2 | PostgreSQL | 15.x | |
| 3 | Spring Boot | 3.x.x | Spring Framework v6, Spring Cloud v2022.x |
| 4 | RabbitMQ | 3.8 |
| No | Component | Details |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | service-discovery | Used as service discovery and load-balancing |
| 2 | config-server | Externalize configuration |
| 3 | api-gateway | Rest-API security, Load Balancing, API Traffic Management |
Microservice intercommunication is handled by RabbitMQ. Considering specific requirements of the Banking System, the choice was made to RabbitMQ over Kafka.
Main features of RabbitMQ:
-
Flexible/Extended/Advanced message routing (RabbitMQ supports 4 methods of message routing, whereas Kafka only has a pub/sub model).
-
Support for message priorities
-
Reliable message delivery
-
Support of several legacy protocols (MQTT, STOMP, AMQP) (that facilitate integration and communication between different systems).
-
Wide range of plugins support
Recently, I did research on alternatives and enhancements for microservice communication. And has concluded that infrastructure can be enhanced by leveraging Service-Mesh patterns. They can be used as a complementary to an existing components (Spring Cloud). Service-mesh platforms Istio, "Linkerd" seem to be better option that best integrate with Spring Environment.
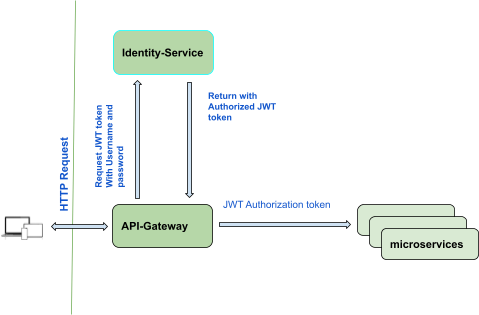
REST-API endpoints are secured by API-Gateway. API-Gateway intercepts (gateway filter) all HTTP requests and based on Authorization header forwards requests either to Identity or other microservices. Identity-Service authorizes requests and generates access tokens.
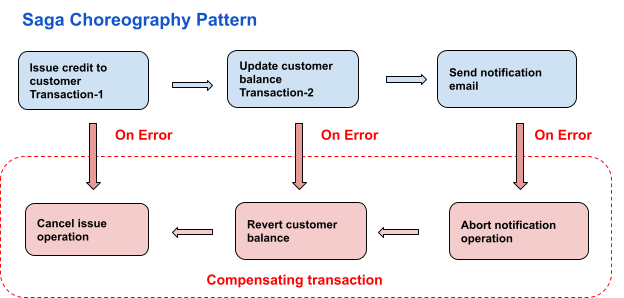
There isn’t a concrete solution to achieve data consistency (distributed transaction) in microservices systems. I found the SAGA pattern and XA transaction approaches are more convenient. As XA transactions have some drawbacks compared to the Saga pattern, like management complexity, performance overhead etc, SAGA pattern better fits for specific requirements. In a template application a simple SAGA flow was implemented. To hide some complexities AXON or Apache Camel EIP frameworks can bi used to implement SAGA pattern.
To improve performance and security, CQRS (Command Query Responsibility Segregation) pattern can be implemented by separating Read and Write database operations. Especially, when CQRS pattern is used by specific separate microservices, optimizing connection performance and scalability. Complex read logic can be scaled independently from write logic. Additionally, components like Zuul (Gateway + Loadbalancing), Ribbon (Load Balancing) and Resilience4J (Circuit Breaker) can be used to add extra performance optimizations.
1.Build project
mvn clean install
2.Deploy with docker-compose (this will setup and start postgreSQL, RabbitMq and all microservices)
docker-compose -p bmt up -d
-
Service-discovery UI: http://localhost:9000/
-
Identity-service:
a. Rest-API documentation: http://localhost:8180/swagger-ui/index.html
b. Authenticate user:
curl -X POST -H 'Content-Type: application/json' --data '{"username":"admin","password":"admin"}' http://localhost:8080/api/identity/login -
Customer-service:
a. Rest-API documentation: http://localhost:8184/swagger-ui/index.html
-
Credit-service:
a. Rest-API documentation: http://localhost:8183/swagger-ui/index.html