Modified from https://github.com/JialianW/GRiT/.
- Download images from official website
- Download grit pre-processed annotations: test.json
mkdir models && cd models
wget https://datarelease.blob.core.windows.net/grit/models/grit_b_densecap_objectdet.pth
cd ..
python eval_grit.py
| Method | CIDEr | METEOR | SPICE | BLEU@1 | BLEU@2 | BLEU@3 | BLEU@4 | ROUGE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GRiT | 145.0 | 17.3 | 30.9 | 36.4 | 22.5 | 15.6 | 11.5 | 34.8 |
GRiT is a general and open-set object understanding framework that localizes objects and describes them with any style of free-form texts it was trained with, e.g., class names, descriptive sentences (including object attributes, actions, counts and many more).
GRiT: A Generative Region-to-text Transformer for Object Understanding
Jialian Wu, Jianfeng Wang, Zhengyuan Yang, Zhe Gan, Zicheng Liu, Junsong Yuan, Lijuan Wang
1State University of New York at Buffalo, 2Microsoft
arXiv technical report (PDF)
Please follow Installation instructions.
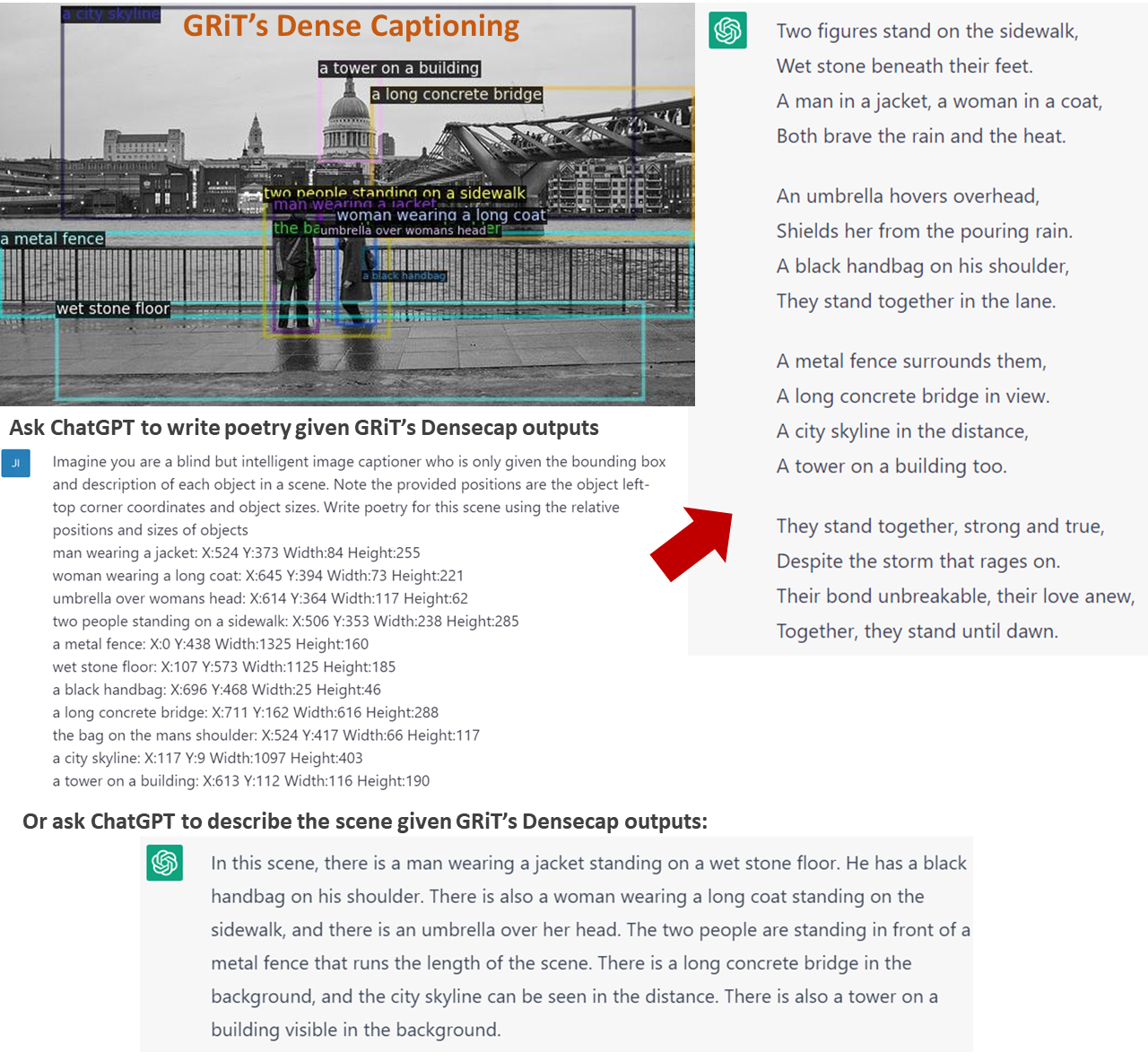
We give ChatGPT GRiT's dense captioning outputs (object location and description) to have it describe the scene and even write poetry. ChatGPT can generate amazing scene descriptions given our dense captioning outputs. An example is shown below: 🤩🤩🤩
Download the GRiT model or use the following commend to download:
mkdir models && cd models
wget https://datarelease.blob.core.windows.net/grit/models/grit_b_densecap_objectdet.pth && cd ..
The downloaded GRiT model was jointly trained on dense captioning
task and object detection task. With the same trained model, it can
output both rich descriptive sentences and short class names by varying
the flag --test-task. Play it as follows! 🤩
python demo.py --test-task DenseCap --config-file configs/GRiT_B_DenseCap_ObjectDet.yaml --input demo_images --output visualization --opts MODEL.WEIGHTS models/grit_b_densecap_objectdet.pth
python demo.py --test-task ObjectDet --config-file configs/GRiT_B_DenseCap_ObjectDet.yaml --input demo_images --output visualization --opts MODEL.WEIGHTS models/grit_b_densecap_objectdet.pth
Output images will be saved under the visualization folder, which looks like:
You can also try the Colab demo provided by the TWC team:
Please follow dataset preparation instructions to download datasets.
Download our trained models and put them to models/ for evaluation.
| Model | val AP | test-dev AP | Download |
|---|---|---|---|
| GRiT (ViT-B) | 53.7 | 53.8 | model |
| GRiT (ViT-L) | 56.4 | 56.6 | model |
| GRiT (ViT-H) | 60.4 | 60.4 | model |
To evaluate the trained GRiT on coco 2017 val, run:
# GRiT (ViT-B)
python train_net.py --num-gpus-per-machine 8 --config-file configs/GRiT_B_ObjectDet.yaml --output-dir-name ./output/grit_b_objectdet --eval-only MODEL.WEIGHTS models/grit_b_objectdet.pth
# GRiT (ViT-L)
python train_net.py --num-gpus-per-machine 8 --config-file configs/GRiT_L_ObjectDet.yaml --output-dir-name ./output/grit_l_objectdet --eval-only MODEL.WEIGHTS models/grit_l_objectdet.pth
# GRiT (ViT-H)
python train_net.py --num-gpus-per-machine 8 --config-file configs/GRiT_H_ObjectDet.yaml --output-dir-name ./output/grit_h_objectdet --eval-only MODEL.WEIGHTS models/grit_h_objectdet.pth
| Model | mAP | Download |
|---|---|---|
| GRiT (ViT-B) | 15.5 | model |
To test on VG test set, run:
python train_net.py --num-gpus-per-machine 8 --config-file configs/GRiT_B_DenseCap.yaml --output-dir-name ./output/grit_b_densecap --eval-only MODEL.WEIGHTS models/grit_b_densecap.pth
It will save the inference results to output/grit_b_densecap/vg_instances_results.json.
We use the VG dense captioning official evaluation codebase
to report the results. We didn't integrate the evaluation code into our project as it was written in Lua.
To evaluate on VG, please follow the original codebase's instructions and test based upon it. We're happy to discuss
in our issue section about the issues you may encounter when using their code.
To save training memory, we use DeepSpeed for training which can work well for activation checkpointing in distributed training.
To train on single machine node, run:
python train_deepspeed.py --num-gpus-per-machine 8 --config-file configs/GRiT_B_ObjectDet.yaml --output-dir-name ./output/grit_b_objectdet
To train on multiple machine nodes, run:
python train_deepspeed.py --num-machines 4 --num-gpus-per-machine 8 --config-file configs/GRiT_B_ObjectDet.yaml --output-dir-name ./output/grit_b_objectdet
Fix the problem of "AttributeError: module 'distutils' has no attribute 'version'" in torch.utils.tensorboard by pip install setuptools==59.5.0
python train_net.py --num-gpus-per-machine 1 --config-file configs/GRiT_B_DenseCap.yaml --output-dir-name ./output/reimp-grit_b_densecap \
DATALOADER.DATASET_BS 1 \
DATALOADER.NUM_WORKERS 0
# Original DATALOADER.DATASET_BS 2, the GPU memory takes 24G
# from PIL import Image
# Image.fromarray(data[0]["image"].permute(1,2,0).numpy()).save("haha.jpg")
# [batched_inputs[0]["image"].shape] + [i.shape for i in features.values()]
# instances.gt_boxes.nonempty()
Our code is in part based on Detic, CenterNet2, detectron2, GIT, and transformers. We thank the authors and appreciate their great works!
If you find our work interesting and would like to cite it, please use the following BibTeX entry.
@article{wu2022grit,
title={GRiT: A Generative Region-to-text Transformer for Object Understanding},
author={Wu, Jialian and Wang, Jianfeng and Yang, Zhengyuan and Gan, Zhe and Liu, Zicheng and Yuan, Junsong and Wang, Lijuan},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2212.00280},
year={2022}
}