The management of data is one of the most important considerations to bear in mind while designing any application. The purpose of any application is to get some data as input, process or operate on in, and then provide suitable data as output.
This repo pretend understand and fun with datastructures and algorithms.
We will look at how we can use these data structures to create more sophisticated data structures, such as stacks, queues, and trees, which are needed to develop complex algorithms.
Algorithms need necessary in-memory data structures that can hold temporary data while executing. Choosing the right data structures is essential for their efficient implementation. Certain classes of algorithms are recursive or iterative in logic and need data structures that ase specially designed for them. For example, a recursive algorithm may be more easily implemented, exhibiting better performance, if nested data structures are used.
- Lists: Ordered mutable sequences of elements
- Tuples: Ordered inmmutable sequence of elements
- Sets: Unordered bags of elements
- Dictionary: Unordered bags of key-values pairs
- Data frames: Two-dimensional structures to store two dimensional data
Is a mathematical notation that describes the limiting behavior of a function and we can classify algorithms according to how their run time or space requirements grow as the input size grows.
The time complexity of various functions of a list can be summarized as follows using the Big O notation:
| Different methods | Time complexity |
|---|---|
| Insert an element | O(1) |
| Delete an elment | O(n)(as in the worst case may have to iterate the whole list) |
| Slicing a list | O(n) |
| Element retrieval | O(n) |
| Copy | O(n) |
Is a data structure used to store tabular data available in Python's pandas
package or in onther languages like R or Apache spark. It is one of the most
important data structures for algorithms and is used to process traditional structured data.
| id | name | age | decision |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | fares | 32 | True |
| 2 | Elena | 18 | False |
| 3 | Steven | 40 | False |
>>> import pandas as pd
>>> df = pd.DataFrame([
... ['1', 'Fares', 32, True],
... ['2', 'Elena', 23, False],
... ['3', 'Steven', 40, True]])
>>> df.columns = ['id', 'name', 'age', 'decision']
>>> dfLet's look into some of the terminologies that are used in the context of a DataFrame:
- Axis: In the pandas documentation, a single column or row of a DataFrame is called an axis.
- Axes: If there is more than one axis, they are called axes as a group
- Label: A DataFrame allows the naming of both columns and rows with what's called a label
Fundamentally, there are two main ways of creating the subset of a DataFrame:
- Column selection
- Row selection
In machine learning algorithms, selecting the right set of features is an important task. We can select through position or specifying a filter
>>> df[['name','age']]
# A column can be retrieved by its position as follows
>>> df.iloc[:,3]
>>> df.iloc[0:2,:]To create a subset using a filter, we need to use one or more colums to define the selection criterion.
>>> df[df.age>30]
>>> df[(df.age < 35)&(df.decision==True)]A stack is a linear data structure to store a one-dimensional list. And store
in Last-In, First-Out(LIFO). The time complexity in the 4 elements is: O(1)
implementation
The elements are added and removed in FIFO format.
implementation
A tree is one of the mos useful data structures due to its hierarchical data storage capabilities. While designing algorithms, we use trees wherever we need to represent hierarchical relationships among the data elements that we need to store or process.
Each tree has a finite set of nodes so that it has a starting data element called
root and a set of nodes joined together by links called branches.
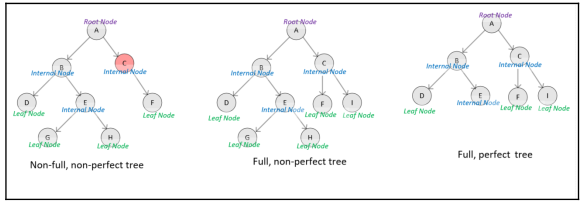
- Binary tree: If the degree of a tree is two, that tree is called binary tree.
- Full tree: Is the one in which all of the nodes are of the same degree, which will be equal to the degree of the tree.
- Perfect tree: Is a full tree in which all the leaf nodes are the same level.
- Ordered tree: If the children of a node are organized in some order according to particular criteria, the tree is called an ordered tree. For example can be ordered left to right in an ascending order in which the nodes at the same level will increase
This is an important class of algorithms and depending of many aspects as the amount of data there are some better approaches than others. The following are types of sorting algorithms:
- Bubble sort
- Merge sort
- Insertion sort
- Shell sort
- Selection sort
Is the simplest and slowest algorithm used for sorting. It is designed in a way that the highest value in its list bubbles its way to the top as the algorithm loops through iterations. As it worst-case performance is O(N^2), it should be used for smaller datasets.
in this example we will