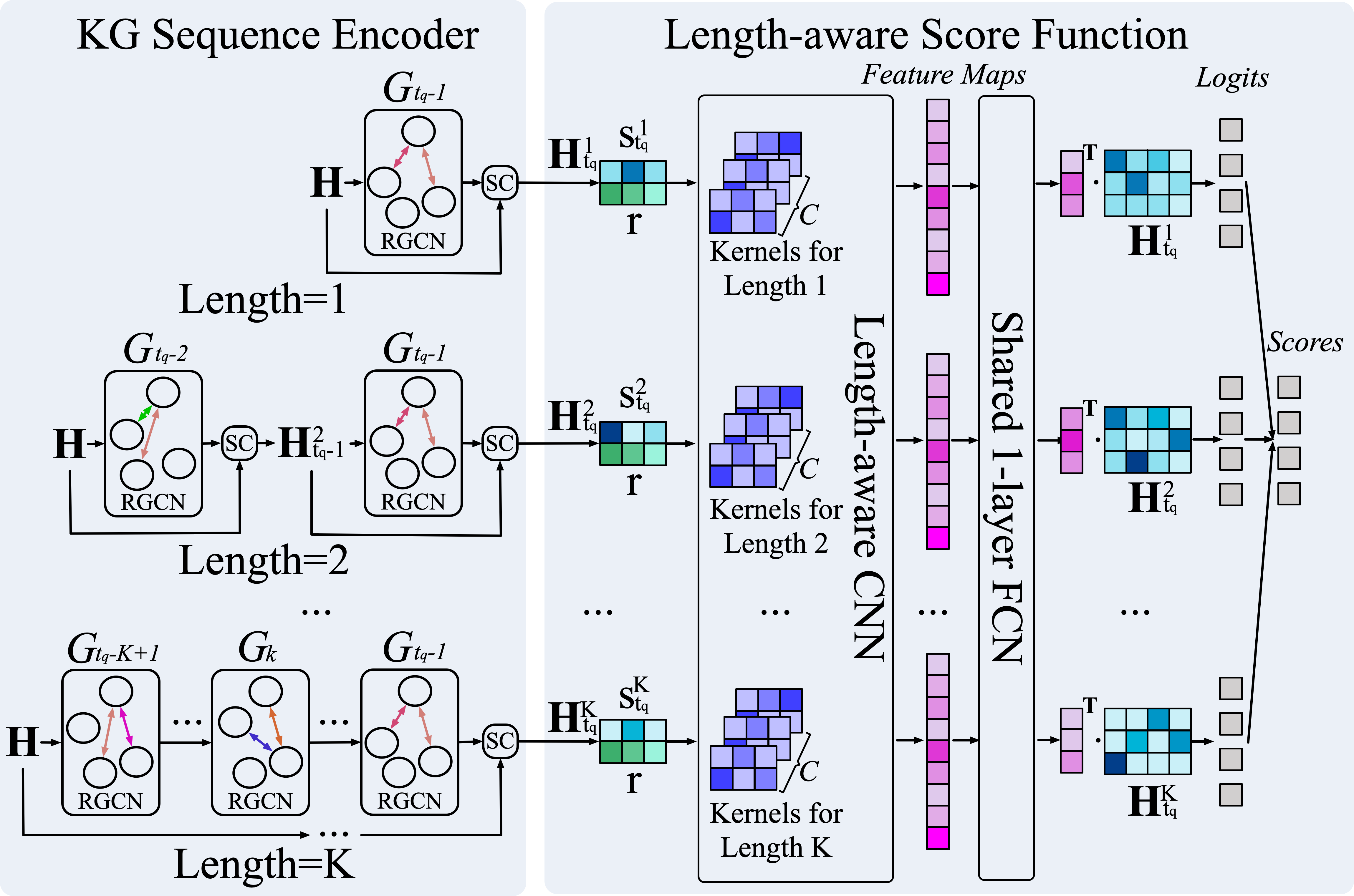
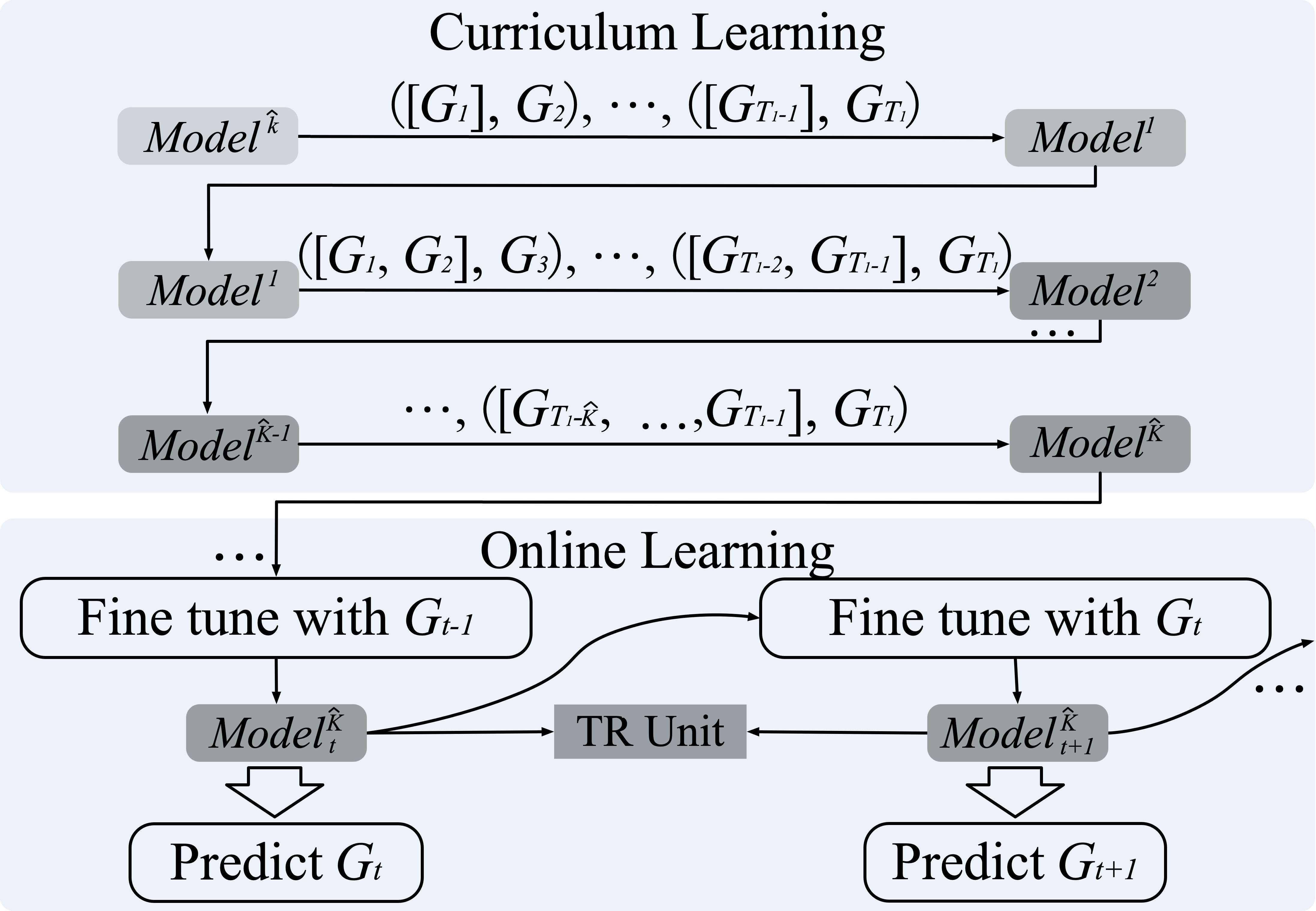
This is the official code release of the following paper:
Zixuan Li, Saiping Guan, Xiaolong Jin, Weihua Peng, Yajuan Lyu , Yong Zhu, Long Bai, Wei Li, Jiafeng Guo, Xueqi Cheng. Complex Evolutional Pattern Learning for Temporal Knowledge Graph Reasoning. ACL 2022.
conda create -n cen python=3.7
conda activate cen
pip install -r requirement.txt
The dataset files can be found in the project of our SIGIR 2021 paper "Temporal Knowledge Graph Reasoning Based on Evolutional Representation Learning"(RE-GCN).
First, unzip and unpack the data files,
tar -zxvf data-release.tar.gz
Then the following commands can be used to train the offline models.
- Pretrain models with the minimum length.
cd src
python main.py --dilate-len 1 --n-epochs 30 --lr 0.001 --n-layers 2 --evaluate-every 1 --n-hidden 200 --self-loop --decoder convtranse --encoder uvrgcn --layer-norm --entity-prediction --gpu 1 -d ICEWS14s --start-history-len 3 --train-history-len 10 --test-history-len 10 --test -1 --ft_lr=0.001 --norm_weight 1
- Curriculum Training.
python main.py --dilate-len 1 --n-epochs 30 --lr 0.001 --n-layers 2 --evaluate-every 1 --n-hidden 200 --self-loop --decoder convtranse --encoder uvrgcn --layer-norm --entity-prediction --gpu 1 -d ICEWS14s --start-history-len 3 --train-history-len 10 --test-history-len 10 --test 0 --ft_lr=0.001 --norm_weight 1
To generate the evaluation results of a offline model, set the --test to 1 (for valid set) or 2 (for test set) and the --test-history-len to k (k is the optimal length of history when the MRR metric decreases in the valid set or the length is up to maximum length K) in the commands above.
For example
python main.py --dilate-len 1 --n-epochs 30 --lr 0.001 --n-layers 2 --evaluate-every 1 --n-hidden 200 --self-loop --decoder convtranse --encoder uvrgcn --layer-norm --entity-prediction --gpu 1 -d ICEWS14s --start-history-len 3 --train-history-len 10 --test-history-len k --test 2 --ft_lr=0.001 --norm_weight 1
First, train the models with timestamps in the valid set
python main.py --dilate-len 1 --n-epochs 30 --lr 0.001 --n-layers 2 --evaluate-every 1 --n-hidden 200 --self-loop --decoder convtranse --encoder uvrgcn --layer-norm --entity-prediction --gpu 1 -d ICEWS14s --start-history-len 3 --train-history-len 10 --test-history-len k --test 3 --ft_lr=0.001 --norm_weight 1
Then, train the models with timestamps in the test set
python main.py --dilate-len 1 --n-epochs 30 --lr 0.001 --n-layers 2 --evaluate-every 1 --n-hidden 200 --self-loop --decoder convtranse --encoder uvrgcn --layer-norm --entity-prediction --gpu 1 -d ICEWS14s --start-history-len 3 --train-history-len 10 --test-history-len k --test 4 --ft_lr=0.001 --norm_weight 1
To get the optimal result reported in the paper, change the hyperparameters and other experiment set up according to Section 5 in the paper (https://arxiv.org/pdf/2203.07782.pdf).
If you find the resource in this repository helpful, please cite
@inproceedings{li-etal-2022-complex,
title = "Complex Evolutional Pattern Learning for Temporal Knowledge Graph Reasoning",
author = "Li, Zixuan and
Guan, Saiping and
Jin, Xiaolong and
Peng, Weihua and
Lyu, Yajuan and
Zhu, Yong and
Bai, Long and
Li, Wei and
Guo, Jiafeng and
Cheng, Xueqi",
booktitle = "Proceedings of the 60th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 2: Short Papers)",
month = may,
year = "2022",
address = "Dublin, Ireland",
publisher = "Association for Computational Linguistics",
url = "https://aclanthology.org/2022.acl-short.32",
doi = "10.18653/v1/2022.acl-short.32",
pages = "290--296"
}