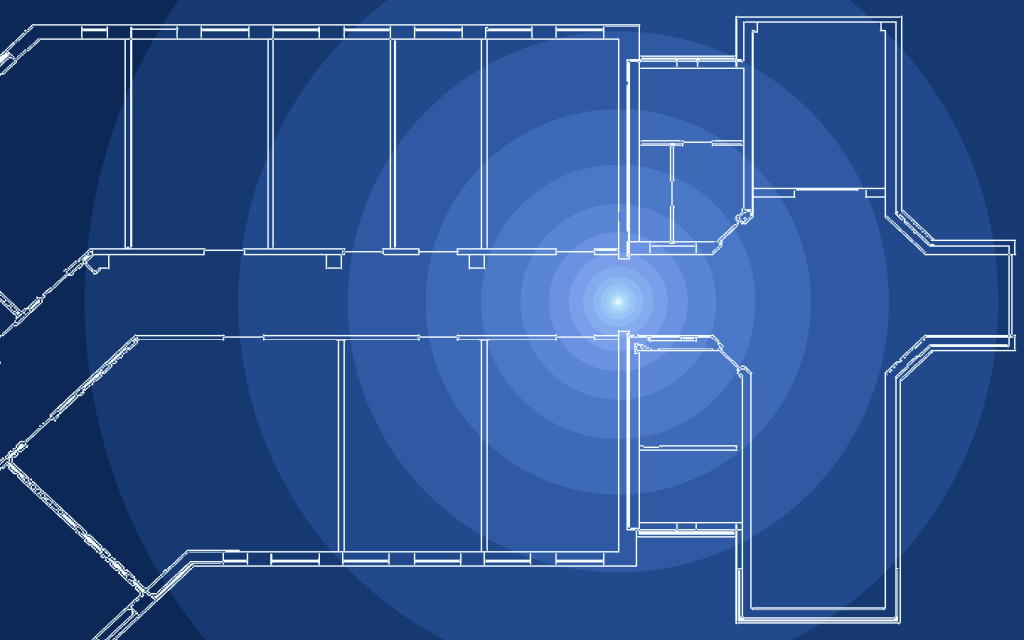
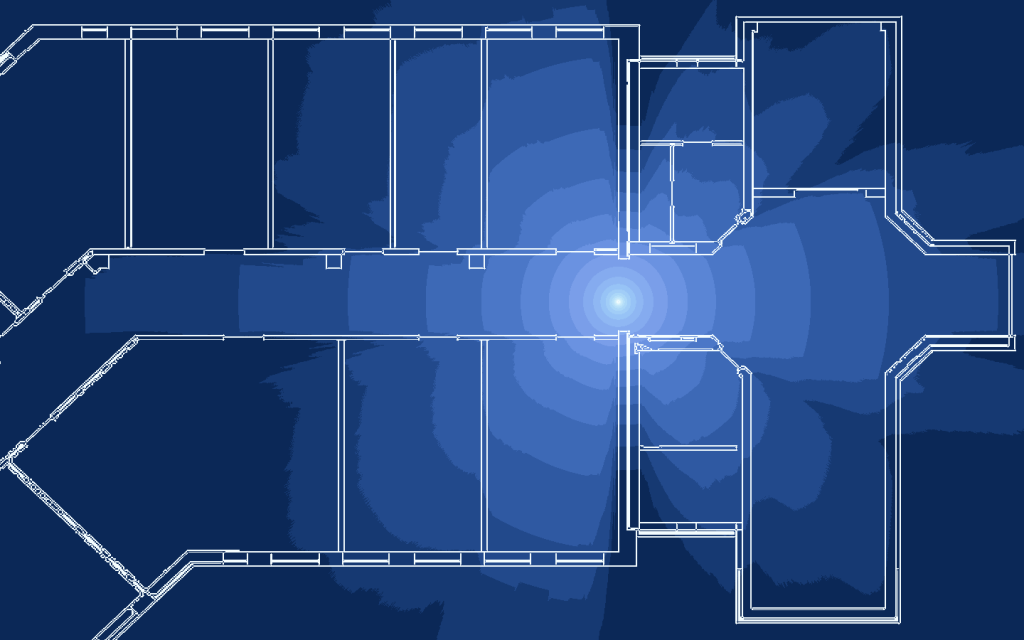
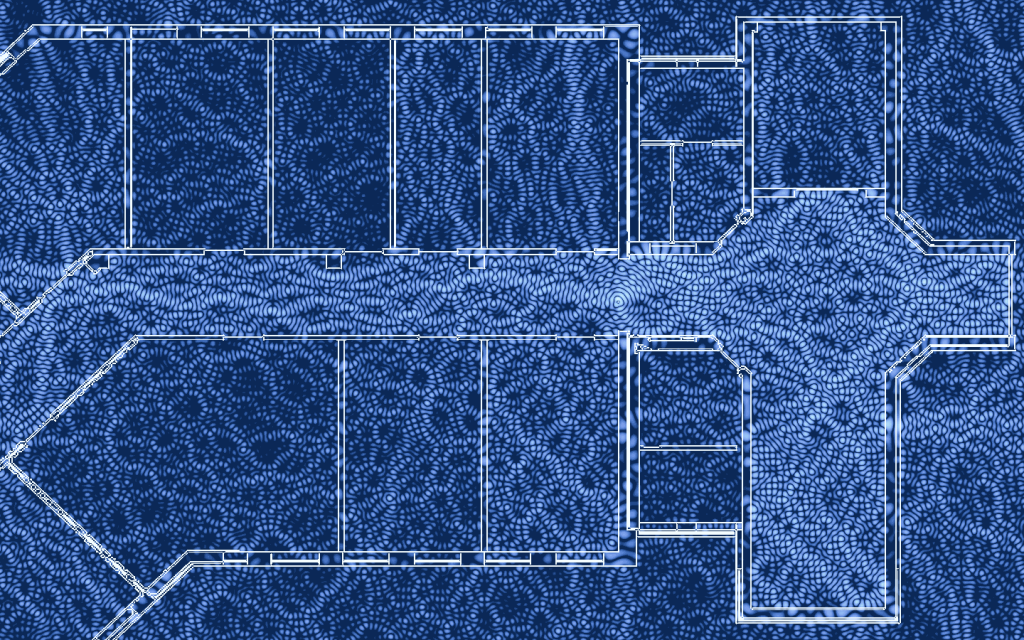
This code can be used to produce figures of wireless propagation effects in indoor scenarios, especially using the Helmholtz equation to model the amplitude field of wireless propagation. Additionally, simple path loss and shadowing can be applied to PNG images showing a simplified black-and-white floorplan.
The code can be extended to support different materials to see even more interesting effects, for example by interpreting different grayscale values as different materials. However, the ability to make accurate predictions on actual wireless behavior should be assumed to be non-existent for any practical purpose.
This code is inspired by the blog entry of Jason Cole that explains the idea and basically solves everything already.
I initially started by using code from Frédéric Testard (fredo-dedup, code preview using nbviewer).
The code iterates naively over each and every pixel of a floorplan to count wall pixels for shadowing or inverts a giant matrix, so try to use a PNG floorplan with less pixels if you run into problems.
From http://julialang.org/ or from repository. The currently targeted Julia version is 1.0, expect some issues due to Julia API changes. They really like to do that.
$ julia -e 'Pkg.add("Colors")'
$ julia -e 'Pkg.add("Images")'$ mkdir figs
$ julia src/helmhurts.jlBe aware that this operation needs a lot of RAM. For the demo example about 10 GB due to the resolution of the provided image.
Some example figures produced by the current implementation.