中文 | English
- Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Illustrating RLHF
- RLHF Dataset preparation
- ☕ Quick Start ☕
- Examples
- Support Model
- Contributing
- License
Open-ChatGPT is a open-source library that allows you to train a hyper-personalized ChatGPT-like ai model using your own data and the least amount of compute possible.
Open-ChatGPT is a general system framework for enabling an end-to-end training experience for ChatGPT-like models. It can automatically take your favorite pre-trained large language models though an OpenAI InstructGPT style three stages to produce your very own high-quality ChatGPT-style model.
We have Impleamented RLHF (Reinforcement Learning with Human Feedback) powered by transformer library and DeepsSpeed. It supports distributed training and offloading, which can fit extremly large models.
If you like the project, please show your support by leaving a star ⭐.
ChatGPT continues the technical path of InstructGPT/GPT3.5 and adds RLHF (Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback) which enhances the adjustment of the model output by humans and sorts the results with greater understanding.
Reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF) is a challenging concept as it involves multiple model training processes and different deployment stages. We break down the training process into three core steps:
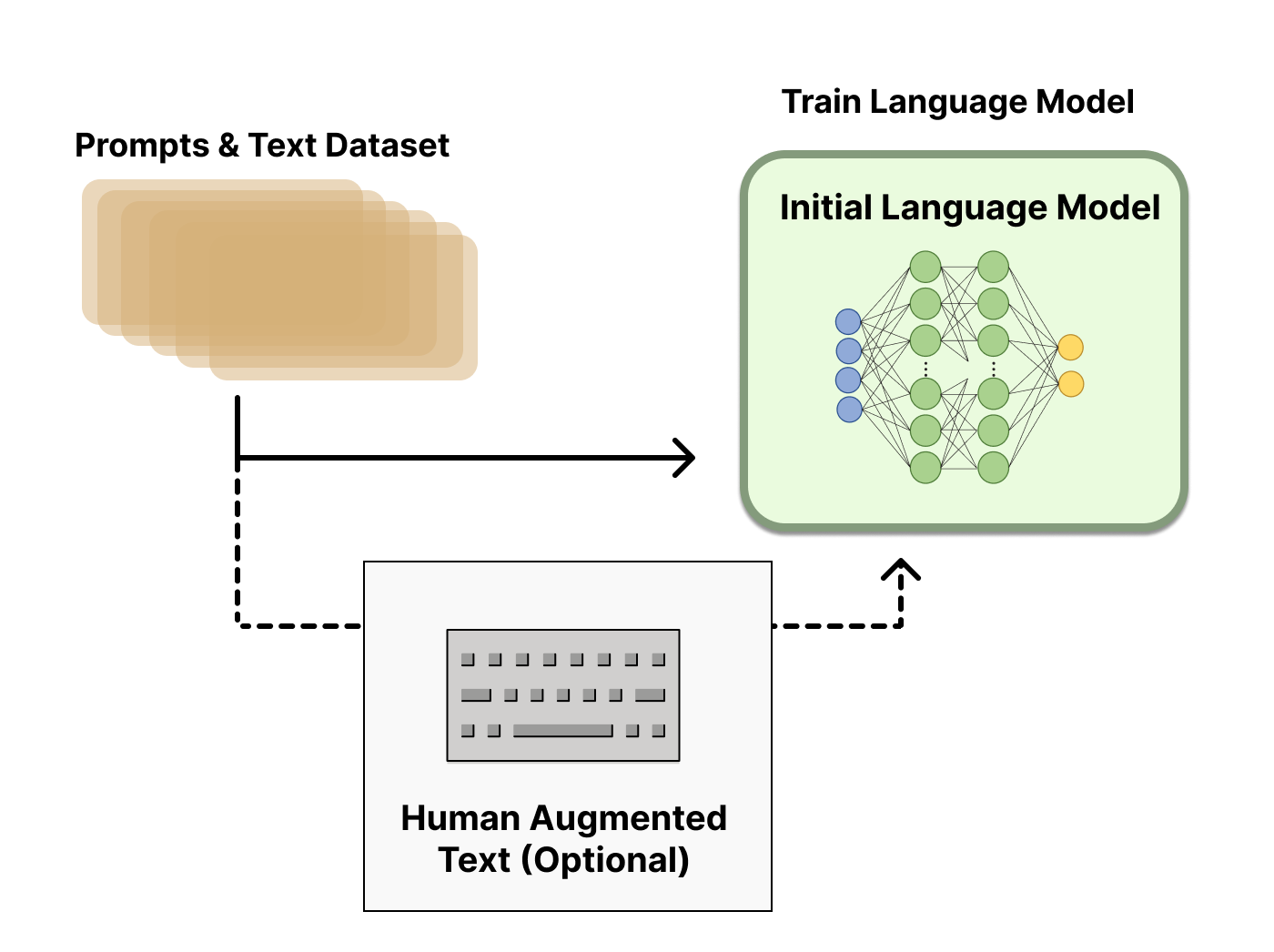
GPT 3.5 itself has difficulty in understanding the different intentions implied in various types of human instructions, and it is also difficult to judge whether the generated content is of high quality. To make GPT 3.5 initially understand the intent of instructions, high-quality answers are given by human annotators for randomly selected questions in the dataset, and the GPT-3.5 model is fine-tuned with these manually labeled data to obtain the SFT model (Supervised Fine-Tuning).
The SFT model at this point is already better than GPT-3 in following instructions/dialogues, but may not necessarily align with human preferences.
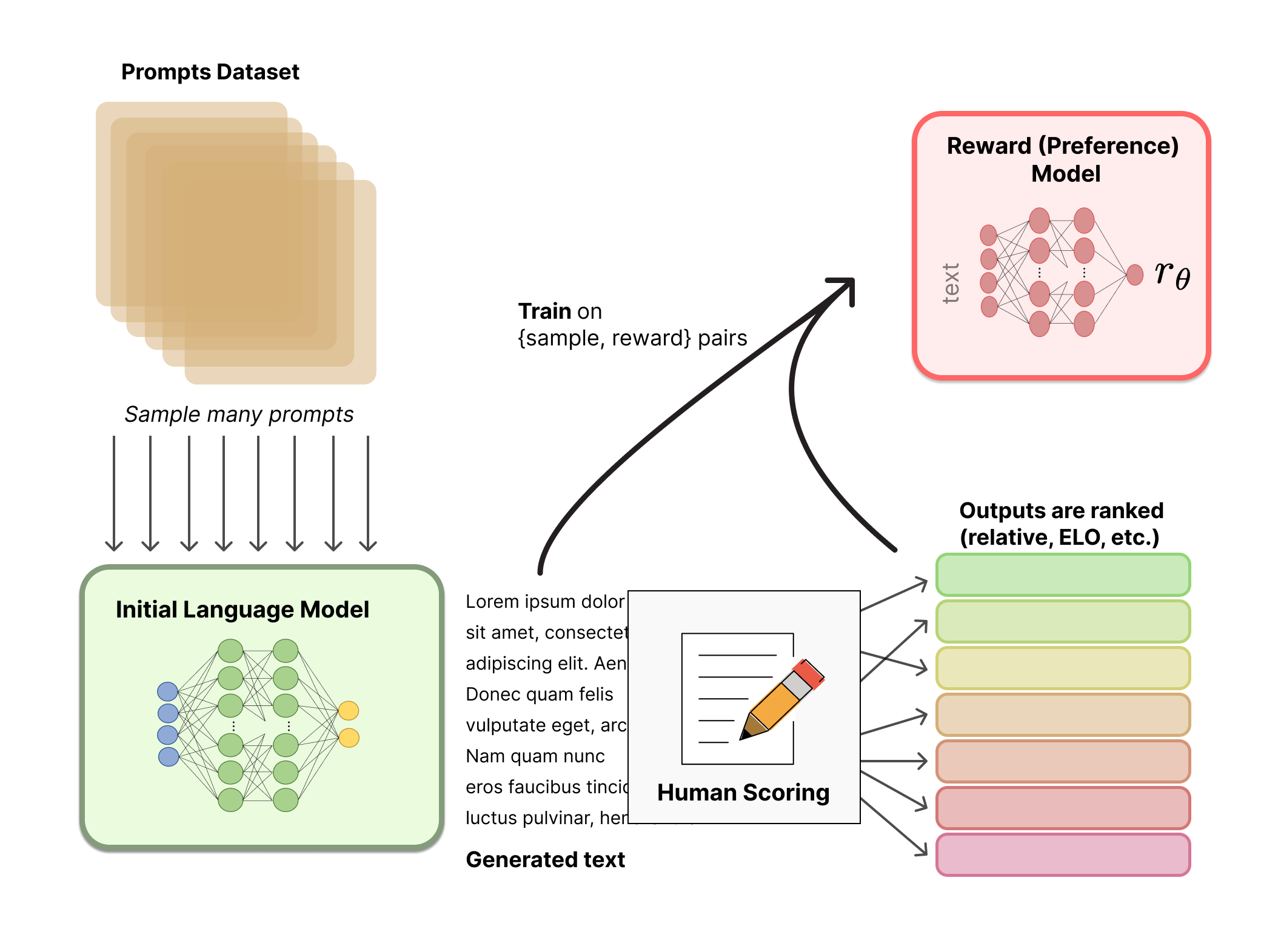
The main objective of this stage is to train a reward model by manually labeled training data (about 33K data). Questions are randomly selected from the dataset, and multiple different answers are generated for each question using the model generated in the first stage. Human annotators consider these results comprehensively and provide a ranking order. This process is similar to a coach or teacher's guidance.
Next, use this ranking result data to train the reward model. For multiple ranking results, pairwise combinations form multiple training data pairs. The RM model accepts an input and provides a score that evaluates the quality of the answer. Thus, for a pair of training data, the parameters are adjusted so that the score for a high-quality answer is higher than that for a low-quality answer.
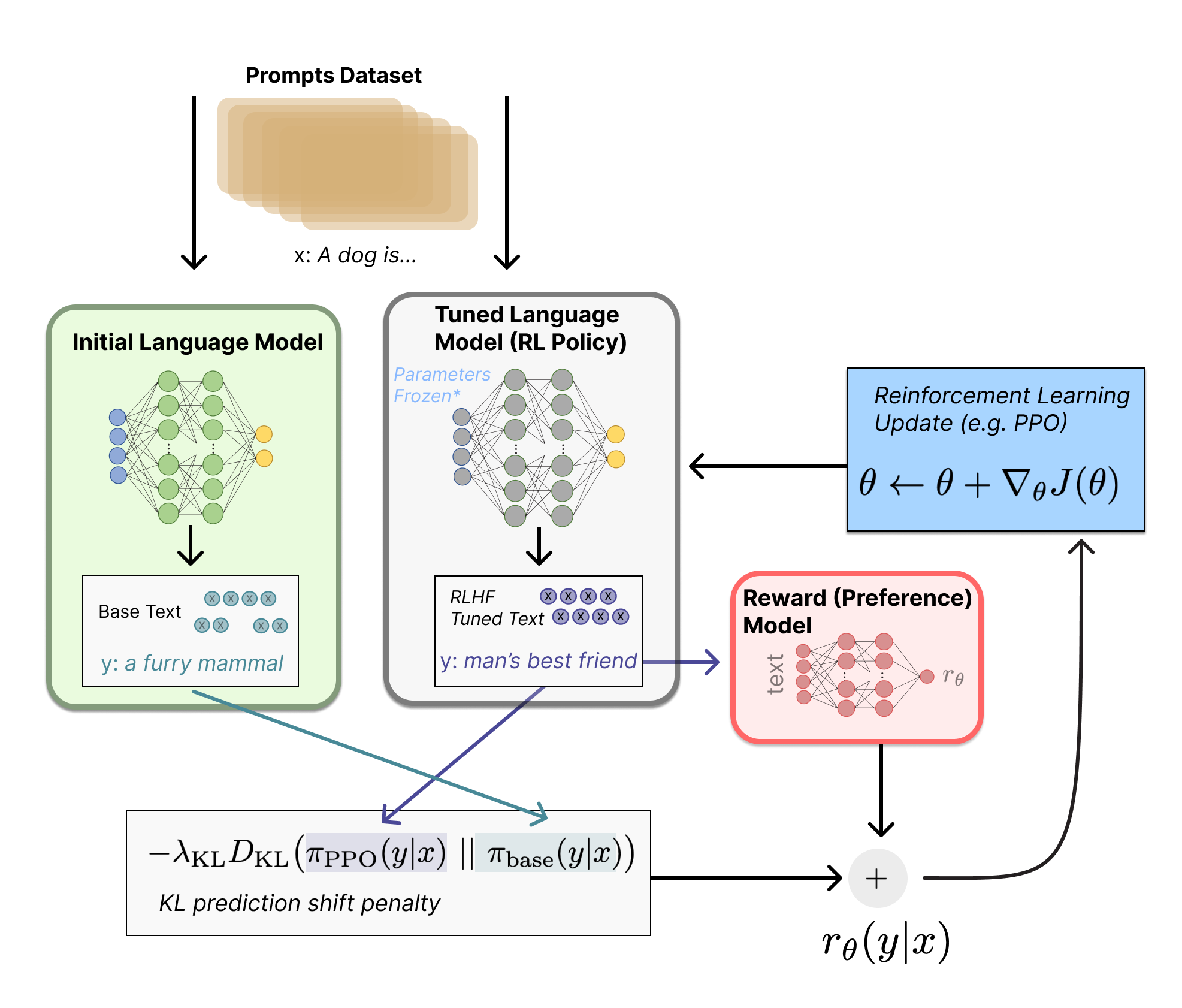
Finally, once we have the trained SFT model and reward model (RM), we can use reinforcement learning (RL) to fine-tune the SFT model based on feedback using RM. This step keeps our SFT model aligned with human preferences.
This stage uses the reward model trained in the second stage and updates the pre-trained model parameters based on the reward score. Questions are randomly selected from the dataset, and the PPO model is used to generate answers, and the RM model trained in the previous stage is used to provide quality scores. The reward scores are passed in sequence, resulting in a policy gradient, and the PPO model parameters are updated through reinforcement learning.
If you want to learn more details about RLHF technology, I strongly recommend reading Huggingface's blog Illustrating Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF) and the 中文翻译版.
To successfully train a ChatGPT-like assistant, you need 3 different datasets: actor_training_data, rlhf_training_data and reward_training_data.
Alternatively, training can be bootstrapped using a pre-existing dataset available on HuggingFace. High quality candidates are namely the Anthropic HH RLHF and the Stanford Human Preference datasets, Reddit TL;DR dataset and Comparisons datasets.
| Dataset | Description | |
|---|---|---|
| Anthropic HH RLHF | This dataset consists of structured question/response pairs with a LLM chatbot that include chosen and rejected responses. | |
| Stanford Human Preferences Dataset (SHP) | This dataset is curated from selected "ask" subreddits and contains questions spanning a wide array of question/answer pairs based on the most upvoted responses. | |
| Reddit TL;DR dataset | The TL;DR Summary Dataset is a collection of carefully selected Reddit posts that contain both the main content and a summary created by a human. | |
| Comparisons dataset | It includes Reddit posts and two summaries for each post, as well as a selection value indicating which of the two summaries the human annotator preferred. |
To find more datasets, please check out the following links: jianzhnie/awesome-prompt-datasets: A collection of open-source dataset to train instruction-following LLMs (ChatGPT,LLaMA,Alpaca)
git clone https://github.com/jianzhnie/open-chatgpt.git
pip install -r requirements.txtFirstly, we will fine-tune the transformer model for text summarization on the TL;DR dataset.
This is relatively straightforward. Load the dataset, tokenize it, and then train the model. The entire pipeline is built using HuggingFace.
- Training with huggingface transformers trainer api.
First, modify the training_args in train_fintune_summarize.py file with your own param.
cd scripts/
python train_reward_model.py- Speedup training with deepspeed
First, add the deepspeed param in train_fintune_summarize.py file.
# Prepare the trainer and start training
training_args = TrainingArguments(
output_dir=output_dir,
num_train_epochs=5,
gradient_accumulation_steps=4,
per_device_train_batch_size=16,
per_device_eval_batch_size=16,
eval_steps=500,
save_steps=1000,
warmup_steps=100,
learning_rate=1e-5,
weight_decay=0.001,
half_precision_backend=True,
fp16=True,
adam_beta1=0.9,
adam_beta2=0.95,
fp16_opt_level='02', # mixed precision mode
do_train=True, # Perform training
do_eval=True, # Perform evaluation
save_strategy='steps',
save_total_limit=5,
evaluation_strategy='steps',
eval_accumulation_steps=1,
load_best_model_at_end=True,
gradient_checkpointing=True,
logging_steps=50,
logging_dir='./logs',
deepspeed='./ds_config_opt.json',
)Then, run the following command to start training.
deepseed train_fintune_summarize.pyThe model is evaluated using the ROUGE score. The best model is selected based on the average ROUGE score on the validation set. This model will be used to initialize the reward model, which will be further fine-tuned using PPO.
Our reward model is trained on a collected human quality judgement dataset Comparisons dataset, You can download the dataset from huggingface automatically.
We will initialize the reward model from the SFT model and attach a randomly initialized linear head to output a scalar value on top.
Next, we will delve into how the data is input to the model, the loss function, and other issues with the reward model.
Use these code to train your reward model.
cd scripts/
python train_reward_model.pyWe use awesome-chatgpt-prompts as example dataset. It is a small dataset with hundreds of prompts.
python train_ppo_rlhf.pypython gpt2-sentiment.pyLLM
We support models that can be run efficiently with a limited amount of compute. These are the models with less than 20B parameters currently supported :
- GPTJ: 6B
- GPTNeoX: 1.3B, 20B
- OPT: 125M, 359M, 1.3B, 2.7B, 6.7B, 13B
- BLOOM: 560M, 1.1B, 1.7B, 3B, 7.1B
- BLOOMZ: 560M, 1.1B, 1.7B, 3B, 7.1B
Our purpose is to make this repo even better. If you are interested in contributing, please refer to HERE for instructions in contribution.
Openn-ChatGPT is released under the Apache 2.0 license.