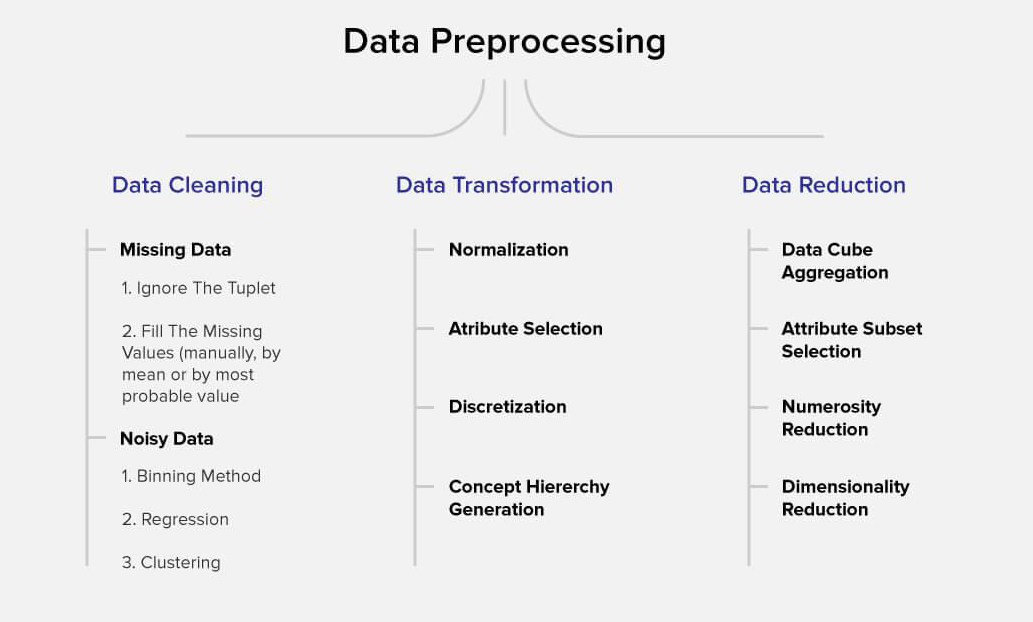
Welcome to the Preprocessing Library for Machine Learning, where we will be using the Scikit-learn preprocessing API to streamline our data preprocessing tasks. This repository provides utilities for handling missing data, scaling features, encoding categorical variables, and more.
Data preprocessing is the process of preparing data for machine learning algorithms. The goal of data preprocessing is to transform raw data into a format that can be used by machine learning algorithms. Data preprocessing involves a range of tasks such as handling missing data, scaling data, encoding categorical variables, and performing other functions.
| Preprocessing Technique | Description |
|---|---|
Standardization or mean removal and variance scaling |
Scaling the data to have a zero mean and unit variance. Useful when features have different scales. |
Non-linear transformation |
Applying a non-linear function to the data to make it more amenable to analysis. |
Normalization |
Scaling the data so that it falls within a certain range. Useful when the distribution of the data is skewed. |
Encoding categorical features |
Converting categorical data to numerical data using techniques like one-hot encoding and label encoding. |
Discretization |
Transforming continuous variables into discrete variables by creating bins or categories. |
Imputation of missing values |
Handling missing data by filling in reasonable estimates for missing values. |
Generating polynomial features |
Creating new features by taking combinations of existing features. |
Custom transformers |
Developing custom transformers to transform data into a format suitable for analysis by machine learning algorithms. |
Outlier removal |
Removing extreme values that are significantly different from other values in the dataset. |
Feature selection |
Identifying and selecting the most relevant features for the model, and discarding less relevant or redundant features. |
Dimensionality reduction |
Reducing the number of features in the dataset by projecting them onto a lower-dimensional space, while preserving most of the important information. Techniques like Principal Component Analysis (PCA) and t-SNE are used for this. |
Feature scaling |
Scaling the features so that they have similar ranges or magnitudes, to prevent certain features from dominating the others. |
Feature engineering |
Creating new features by combining or transforming existing features. This is often done to capture domain-specific knowledge and improve the performance of the model. |
Text preprocessing |
Converting raw text data into a format suitable for machine learning algorithms, by performing tasks like tokenization, stemming, lemmatization, stopword removal, and vectorization. |
Image preprocessing |
Preparing images for analysis by converting them into a common format, resizing or cropping them, and normalizing their pixel values. |
Time series preprocessing |
Handling time-dependent data by smoothing, differencing, or detrending the time series, or by aggregating the data into different time intervals. |
Data augmentation |
Creating new samples by applying random transformations to existing samples. This is often used in computer vision and natural language processing to increase the size of the dataset and improve the generalization of the model. |
The Scikit-learn preprocessing API provides a range of tools for data preprocessing. The preprocessing API includes tools for handling missing data, scaling data, encoding categorical variables, and performing other functions. The Scikit-learn preprocessing API is used by many machine learning algorithms in the Scikit-learn library.
| API | Description |
|---|---|
Binarizer |
Binarizes continuous data by setting feature values above a threshold to 1 and those below it to 0. This is useful when you want to convert continuous data into a binary format for use in some algorithms. |
FunctionTransformer |
Constructs a transformer from an arbitrary callable. This allows you to apply any custom function to your data as a part of a scikit-learn pipeline. |
KBinsDiscretizer |
Bins continuous data into intervals using equal width or equal frequency. This transformer can be useful when you want to discretize a continuous variable into a categorical variable, e.g. to prepare it for use in a decision tree model. |
KernelCenterer |
Centers an arbitrary kernel matrix by subtracting the row and column means from each element. This is useful when you want to center a kernel matrix that has been constructed using some kernel function, e.g. in a support vector machine. |
LabelBinarizer |
Binarizes labels in a one-vs-all fashion, where each class is treated as a binary classification problem. This transformer is useful when you have a multi-class classification problem and want to convert your labels into a binary format. |
LabelEncoder |
Encodes target labels with a value between 0 and n_classes-1. This transformer is useful when you have a multi-class classification problem and want to convert your labels into a numerical format. |
MultiLabelBinarizer |
Transforms between an iterable of iterables and a multilabel format. This transformer is useful when you have a multi-label classification problem and want to convert your labels into a binary format. |
MaxAbsScaler |
Scales each feature by its maximum absolute value. This transformer is useful when you want to scale your features to a range between -1 and 1, but want to preserve the sparsity of sparse matrices. |
MinMaxScaler |
Scales each feature to a given range, typically [0, 1] or [-1, 1]. This transformer is useful when you want to scale your features to a specific range for use in some algorithms. |
Normalizer |
Normalizes samples individually to unit norm. This transformer is useful when you want to scale your samples to have a unit norm, which can be useful in some distance-based algorithms. |
OneHotEncoder |
Encodes categorical features as a one-hot numeric array. This transformer is useful when you have categorical features that need to be converted into a numerical format. |
OrdinalEncoder |
Encodes categorical features as an integer array. This transformer is useful when you have categorical features that need to be converted into a numerical format, but the order of the categories is important. |
PolynomialFeatures |
Generates polynomial and interaction features up to a specified degree. This transformer is useful when you want to add polynomial or interaction features to your data, e.g. to capture non-linear relationships. |
PowerTransformer |
Applies a power transform featurewise to make data more Gaussian-like. This transformer is useful when you have data that is not normally distributed and want to make it more amenable to certain statistical models. |
QuantileTransformer |
Transforms features using quantiles information. This transformer is useful when you want to transform your features to have a specified distribution, e.g. to make them more Gaussian-like or uniform. |
RobustScaler |
Scales features using statistics that are robust to outliers. This transformer is useful when you have data with outliers and want to scale your features |
SplineTransformer |
Generate univariate B-spline bases for features. |
StandardScaler |
Standardize features by removing the mean and scaling to unit variance. |
add_dummy_feature |
Augment dataset with an additional dummy feature. |
binarize |
Boolean thresholding of array-like or scipy.sparse matrix. |
label_binarize |
Binarize labels in a one-vs-all fashion. |
maxabs_scale |
Scale each feature to the [-1, 1] range without breaking the sparsity. |
minmax_scale |
Transform features by scaling each feature to a given range. |
normalize |
Scale input vectors individually to unit norm (vector length). |
quantile_transform |
Transform features using quantiles information. |
robust_scale |
Standardize a dataset along any axis. |
scale |
Standardize a dataset along any axis. |
power_transform |
Parametric, monotonic transformation to make data more Gaussian-like. |
The repository is organized into modules that correspond to different preprocessing tasks, making it easy to find and use the tools you need.
├── imputation
│ ├── simple_imputer.ipynb
├── encoding
│ ├── label_encoder.ipynb
│ ├── onehot_encoder.ipynb
├── scaling
│ ├── standard_scaler.ipynb
│ ├── normalizer.ipynb
├── binning
│ ├── binarizer.ipynb
│ ├── kbins_discretizer.ipynb
├── feature_expansion
│ ├── polynomial_features.ipynb
├── feature_selection
│ ├── select_k_best.ipynb
│ ├── select_from_model.ipynb
└── README.mdTo use this library, clone the repository and install the required dependencies:
git clone <https://github.com/mohd-faizy/Preprocess_ML.git>
cd Preprocess_ML
pip install -r requirements.txtHere's an example of how to use the preprocessing tools in this library:
from sklearn.datasets import load_iris
from preprocessing.scaling import StandardScaler
from preprocessing.encoding import LabelEncoder
# Load dataset
data = load_iris()
X = data.data
y = data.target
# Standardize features
scaler = StandardScaler()
X_scaled = scaler.fit_transform(X)
# Encode labels
encoder = LabelEncoder()
y_encoded = encoder.fit_transform(y)
print("Scaled Features:", X_scaled)
print("Encoded Labels:", y_encoded)This project is licensed under the MIT License. See LICENSE for details.
If you find this repository helpful, show your support by starring it! For questions or feedback, reach out on Twitter(X).
🔃 ➤ If you have questions or feedback, feel free to reach out!!!