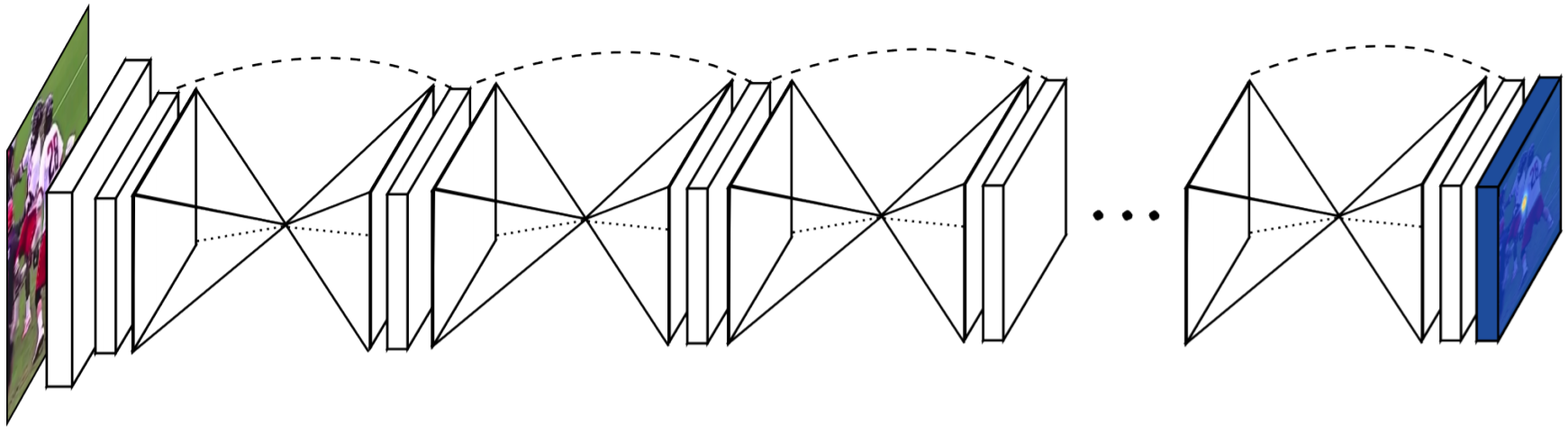
The repository implements the Stacked Hourglass Networks for Human Pose Estimation paper and provides an easy-to-follow mechanism for performing network pruning.
The code is tested on Ubuntu 18.04 LTS powered machine having a single Quadro RTX 6000 GPU with Python 3.8.8, PyTorch 1.8.1 and Torchvision 0.9.1. The code has not been tested on CPU.
Follow the following steps to prepare the environment for training and evaluation.
- Clone the repository
git clone https://github.com/mmaaz60/pytorch-stacked-hourglass. - Download the dataset from the link and extract the images in a directory (let's say "./data/images").
- Conda environment is recommended. Please follow the following steps to create environment and install the dependencies.
- Create new conda environment
conda create --name=hg python=3.8. - Activate newly created environment
conda activate hg. - Install dependencies
pip install -r requirements.txt.
- Create new conda environment
The repository contains scripts train_mpii.py and evaluate_mpii.py for training and evaluate hourglass network
on MPII dataset.
The below table lists the command line parameters available for train_mpii.py and evaluate_mpii.py scripts.
| Parameter | Description | Possible Values |
|---|---|---|
| --image-path | Path to directory containing training images. | string: path to dataset |
| --arch | Model architecture, specifically the number of stacked hourglasses. | string: hg1, hg2, hg3, hg4, hg5, hg6, hg7, hg8 |
| --input_shape | Input shape of the model. Given as: (H, W). | tuple: (256, 256), etc. |
| --workers | Number of dataloader workers. | int: any integer value, e.g. 4, 16, etc. |
| --epochs | Number of training epochs. | int: any integer value, e.g. 20, 50, etc. |
| --resume | Path to the latest checkpoints to resume training. | string: path to checkpoints |
| --start-epoch | Start epoch number when resuming the training. | int: any integer value, e.g. 17, 47, etc. |
| --train-batch | Training batch size. | int: any integer value, e.g. 16, 24, etc. |
| --test-batch | Testing/Validation batch size. | int: any integer value, e.g. 1, 2, etc. |
| --lr | Learning rate for training. | float: any float value, e.g. 0.001, 0.00025, etc. |
| --momentum' | Momentum parameter for the optimizer. | float: any float value, e.g. 0.0, 0.9, etc. |
| --weight-decay | Weight decay parameter for the optimizer. | float: any float value, e.g. 0.001, 0.0001, etc. |
| --schedule | List of epochs where to decrease the learning rate. | List of integers: [20, 35, 45], [100, 150], etc. |
| --gamma | Learning rate is multiplied by gamma on schedule epochs. | float: any float value, e.g. 0.1, 0.02, etc. |
| --checkpoint | Directory path to save the checkpoints. | string: path to checkpoints |
| --snapshot | Save models for every #snapshot epochs. | int: any integer value, e.g. 0, 1, etc. |
| --N | No. of channels in earlier layers of Residual Block. | int: any integer value, e.g. 64, 128, etc. |
| --M | No. of channels in the final layer of Residual Block. | int: any integer value, e.g. 128, 256, etc. |
| Parameter | Description | Possible Values |
|---|---|---|
| --image-path | Path to directory containing training images. | string: path to dataset |
| --arch | Model architecture, specifically the number of stacked hourglasses. | string: hg1, hg2, hg3, hg4, hg5, hg6, hg7, hg8 |
| --model-file | Path to the saved model checkpoints. | string: path to saved weights |
| --workers | Number of dataloader workers. | int: any integer value, e.g. 4, 16, etc. |
| --batch-size | Testing/Validation batch size. | int: any integer value, e.g. 1, 2, etc. |
| --visualize | Either to save the qualitative results or not. | bool: True, False |
| --visualization_path | Directory path to save the visualizations. | string: path to save visualizations. |
| --N | No. of channels in earlier layers of Residual Block. | int: any integer value, e.g. 64, 128, etc. |
| --M | No. of channels in the final layer of Residual Block. | int: any integer value, e.g. 128, 256, etc. |
The script train_mpii.py is used for training. A sample training command to run training for hg7 is given below.
Adjust the number of workers as per the number of available CPU cores.
$ python train_mpii.py \
--arch=hg7 \
--image-path=./data/images \
--checkpoint=./checkpoints/hg7 \
--epochs=50 \
--train-batch=24 \
--test-batch=24 \
--lr=1e-3 \
--schedule 20 35 45 \
--workers=16 \
--N=128 \
--M=256The script evaluate_mpii.py is used for evaluation on validation dataset. A sample command to evaluate trained hg7 mdoel is given below.
Adjust the number of workers as per the number of available CPU cores.
$ python evaluate_mpii.py \
--arch=hg7 \
--image-path=./data/images \
--model-file=./checkpoints/hg7/model_best.pth.tar \
--batch-size=1 \
--workers=16 \
--visualize True \
--visualization_path=./hg7_qualitative_results \
--N=128 \
--M=256Our pretrained models and compiled results can be found here. The technical report on the analysis of the results will be updated soon on the same link.
The figure below shows some qualitative results of our pruned hg7 model.
The repository has been forked from anibali/pytorch-stacked-hourglass and modified to perform Network Pruning.