This repository provides the PyTorch implementation of the following paper:
MultiPathGAN: Structure Preserving Stain Normalization using Unsupervised Multi-domain Adversarial Network with Perception Loss
Haseeb Nazki1, Ognjen Arandjelović1, InHwa Um1, David Harrison1
1University of St-Andrews.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2204.09782Abstract: Histopathology relies on the analysis of microscopic tissue images to diagnose disease. A crucial part of tissue preparation is staining whereby a dye is used to make the salient tissue components more distinguishable. However, differences in laboratory protocols and scanning devices result in significant confounding appearance variation in the corresponding images. This variation increases both human error and the inter-rater variability, as well as hinders the performance of automatic or semi-automatic methods. In the present paper we introduce an unsupervised adversarial network to translate (and hence normalize) whole slide images across multiple data acquisition domains. Our key contributions are: (i) an adversarial architecture which learns across multiple domains with a single generator-discriminator network using an information flow branch which optimizes for perceptual loss, and (ii) the inclusion of an additional feature extraction network during training which guides the transformation network to keep all the structural features in the tissue image intact. We: (i) demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method firstly on H&E slides of 120 cases of kidney cancer, as well as (ii) show the benefits of the approach on more general problems, such as flexible illumination based natural image enhancement and light source adaptation.
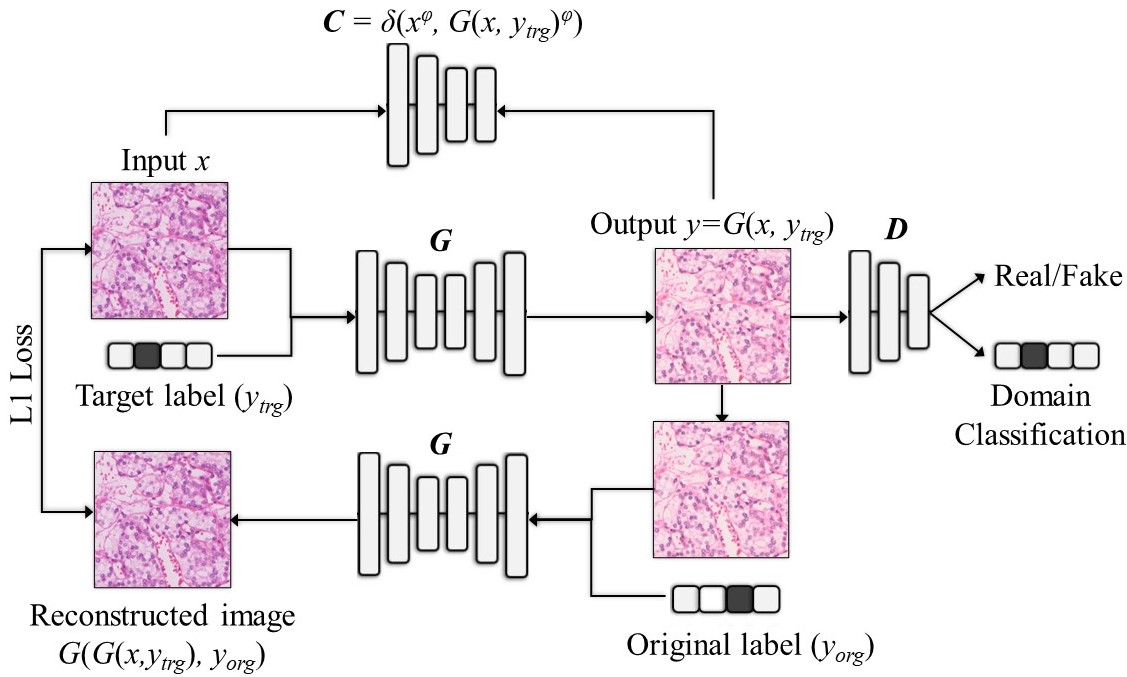
Figure 1. Model Architecture
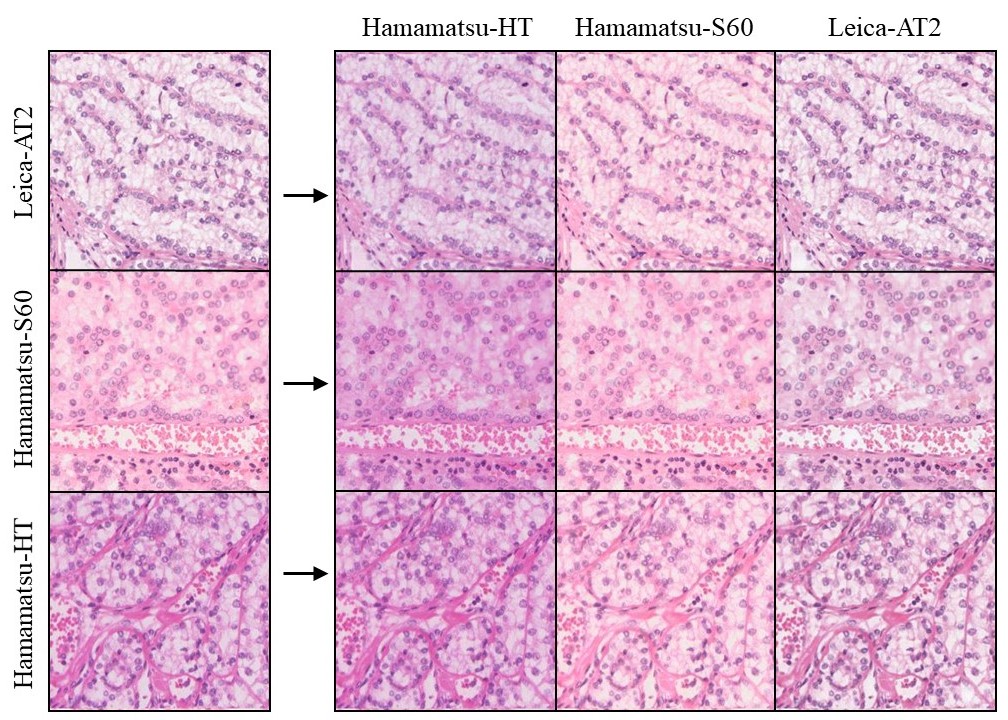
Figure 2. Translation results between WSI patches from three different scanning devices
Figure 3. Translating input to 5 color temperatures (MultiPathGAN trained on VIDIT)
- Python 3.5+
- PyTorch 0.4.0+
- TensorFlow 1.14+ (optionally to use tensorboard)
data
└── WSI
├── train
| ├── Domain 1
| | ├── a.jpg (name doesn't matter)
| | ├── b.jpg
| | └── ...
| ├── Domain 2
| | ├── c.jpg
| | ├── d.jpg
| | └── ...
| ...
|
└── test
| ├── Domain 1
| | ├── e.jpg
| | ├── f.jpg
| | └── ...
| ├── Domain 2
| | ├── g.jpg
| | ├── h.jpg
| | └── ...
| ...
|
└── input_sample_dir
└── Input_Domain
├── e.jpg
├── f.jpg
└── ...
To train on your own dataset, run the script provided below.
# Train MultiPathGAN
python main.pyTo resume training from a particular checkpoint.
# Train MultiPathGAN
python main.py --resume_training CP#where "CP#" is the checkpoint number from /multipathgan/models directory.
To test your trained network, run the script provided below.
# Test MultiPathGAN
python main.py --mode test To sample (translate images in input_sample_directory) into any particular target domain, run the script provided below.
# Sample MultiPathGAN
python main.py --mode sample --which_domain 0 --batch_size 1where "--which_domain" determines the target domain. Additionally, we can change necessary arguments provided here-main.py.
If you find this work useful for your research, please cite our paper. For more information on the dataset, available pretrained weights for MultiPathGAN trained on our WSI dataset and VIDIT sub-dataset Contact Us.
[1] StarGAN_Implementation and paper. Yunjey Choi, Minje Choi, Munyoung Kim, Jung-Woo Ha, Sunghun Kim, and Jaegul Choo. 2018. Stargan: Unified generative adversarial networks for multi-domain image-to-image translation. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. 8789–8797.
[2] AR-GAN_Implementation and paper. Haseeb Nazki, Sook Yoon, Alvaro Fuentes, and Dong Sun Park. 2020. Unsupervised image translation using adversarial networks for improved plant disease recognition. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture 168 (2020), 105117.