async-ui
A prototype demonstrating JavaFX or Swing GUI programming with clojure.core.async.
Here's a working example.
What it shows
- A UI form with all its state represented by pure data.
- Specification of UI forms and event processing is free of access to JavaFX APIs, and can therefore be tested without any GUI test robots.
- Event processing and communication among UI forms is free of callbacks or direct thread-handling, and uses core.async channels instead.
Overview
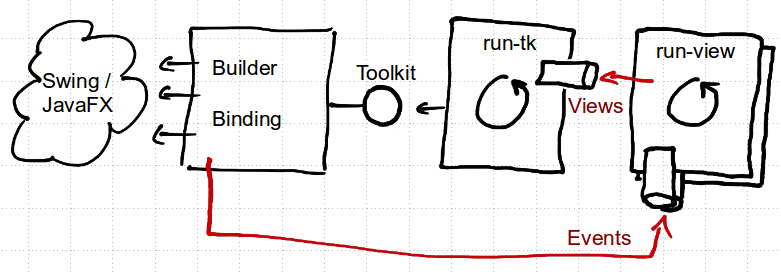
A View is a map that contains a specification of the visual
component tree, the domain data, a mapping between both, validation
rules and validation results (for more details see the Concepts
section). This data represents the state of a UI form. Each view has
it's own events channel. For each view, one process is started using
the run-view function, which processes events for that view. "Event
processing" means that the data contained in the event is merged into
the view state, validation is applied, an individual handler is
invoked and the resulting view is passed via a central channel to
another process that is responsible for synchronization with the UI
Toolkit.
As mentioned in the previous paragraph there is a single toolkit
oriented process, started via run-tk, which processes views it
receives via a central channel. "Processing a view" means initially to
actually create the visual component tree using the UI
Toolkit. Further updates of the view are processed by writing the data
from the view into the property values of the visual components.
The concrete UI toolkit like JavaFX or Swing is hidden behind the Toolkit protocol. It is mainly implemented by a builder and a binding. The builder takes views specification of a form and produces a visual component tree. The binding registers listeners that put an event onto the views own events channel and creates setters that update the visual components properties with the data contained in the view.
Concepts
A Spec is a map representing a UI form. A spec can be created with expressions like this:
(window "Item Editor"
:content
(panel "Content" :lygeneral "wrap 2, fill" :lycolumns "[|100,grow]"
:components
[(label "Text") (textfield "text" :lyhint "growx")
(panel "Actions" :lygeneral "ins 0" :lyhint "span, right"
:components
[(button "OK") (button "Cancel")])]))A Component Path is a vector of visual component names.
A Property Path is a component path conj'ed with a keyword representing a property within a visual component.
A Mapping is a vector of maps. Each of these maps contains
- :data-path -- A vector or single keyword pointing to a piece of data in a map
- :property-path -- A vector consisting of a Component Path conj'ed with a keyword denoting the property in the visual component.
- :formatter -- A function converting from a value to a human readable text
- :parser -- A function converting a human readable text to a value
A View is a map containing all data necessary for a UI form and the visual component tree.
- :id -- A string uniquely identifing this view
- :spec -- A model of the form (see forml namespace for the metamodel)
- :vc -- The tree of visual components
- :data -- A map with all domain and view-state data of the form
- :mapping -- A vector of mappings between visual component properties and data in the :data map
- :events -- The channel for receiving events
- :setter-fns -- A map of data-path to 1-arg functions used to update visual component properties values
- :validation-rule-set -- A vector of validation rules (see examine library)
- :validation-results -- Current validation results (see examine library)
A view is created like so:
(defn item-editor-view
[data]
(-> (v/make-view "item-editor"
(window "Item Editor"
:content
(panel "Content" :lygeneral "wrap 2, fill" :lycolumns "[|100,grow]"
:components
[(label "Text") (textfield "text" :lyhint "growx")
(panel "Actions" :lygeneral "ins 0" :lyhint "span, right"
:components
[(button "OK") (button "Cancel")])])))
(assoc :mapping (v/make-mapping :text ["text" :text])
:validation-rule-set (e/rule-set :text (c/min-length 1))
:data data)))An Event is a map with keys
- :source -- Points to a visual components property or other source
- :type -- A keyword denoting the type of event. Common event types are :update or :action.
- :payload -- Arbitrary data
An Event Handler is a function that is invoked by the view process to process an event and possibly create a new version of the view.
Here's an example of a simple event handler:
(defn item-editor-handler
[view event]
(go (case ((juxt :source :type) event)
["OK" :action]
(assoc view :terminated true)
["Cancel" :action]
(assoc view
:terminated true
:cancelled true)
view)))A Component Map contains all visual components indexed by their corresponding component paths.
A Toolkit provides uniform access to functionalities of Swing or JavaFX.
(defprotocol Toolkit
(run-now [tk f]
"Executes function f in toolkits event processing thread.")
(show-view! [tk view]
"Makes the root of the visual component tree visible.")
(hide-view! [tk view]
"Makes the root of the visual component tree invisible.")
(build-vc-tree [tk view]
"Creates a visual component tree from the data in the :spec slot of the view.
Returns the view with an updated :vc slot.")
(bind-vc-tree! [tk view]
"Attaches listeners to visual components that put events to the :events channel of the view.
Returns the view with :setter-fns slot updated.")
(vc-name [tk vc]
"Returns the name of the visual component.")
(vc-children [tk vc]
"Returns a seq with the children of the visual component or [] if it doesn't have any.")
(set-vc-error! [tk vc msgs]
"Updates the error state of a visual component according to the messages seq msgs.
Empty msgs remove the error state."))Adding visual component types
This prototype supports only a small number of component types. To add support for a type of visual component one has to add at least one datatype in src/async_ui/forml.clj with corresponding defaults.
To support a type of visual component within a specific toolkit there are three methods to add:
buildin builder.clj that produces a component instance from the spec.bind!in binding.clj that registers event listeners that put events to the views:eventschannel.setter-fnsin binding.clj that returns a map of component specific functions that update a property of component from a value.
Usage
Make sure you're on JDK 1.8.0_25. Clone this project.
REPL
- Open the file
src/async_ui/ex_master_detail.cljand compile it. (do (ns async-ui.ex-master-detail) (start!))
Standalone
- You can run the application using
lein run. - Alternatively you can create an all-in-one Jar using
lein uberjarand execute the resulting Jar (java -jar ...).
NOTE: For some weird technical reasons JavaFX needs to have its
Application Thread started for some of the classes to be loaded
properly. In other words, the compilation process starts a JavaFX
thread, which blocks JVM termination after compilation finished. As a
remedy, an environment var in the uberjar profile is used to detect
compilation and a Platform/exit is issued after some seconds, but
termination still takes about 1 minute. Be patient.
NOTE: If you start the Jar from the project directory with
java -jar target/async-ui-0.1.0-SNAPSHOT-standalone.jar make sure
you delete .lein-env beforehand.
Currently there is no proper application exit. Ctrl-C helps.
License
Copyright 2014 F.Riemenschneider
Distributed under the Eclipse Public License, the same as Clojure.