The von Mises-Fisher (vMF) is a well-known density model for directional random variables. The recent surge of the deep embedding methodologies for high-dimensional structured data such as images or texts, aimed at extracting salient directional information, can make the vMF model even more popular. In this article, we will review the vMF model and its mixture, provide detailed recipes of how to train the models, focusing on the maximum likelihood estimators, in Python/PyTorch. In particular, implementation of vMF typically suffers from the notorious numerical issue of the Bessel function evaluation in the density normalizer, especially when the dimensionality is high, and we address the issue using the MPMath library that supports arbitrary precision. For the mixture learning, we provide both minibatch-based large-scale SGD learning, as well as the EM algorithm which is a full batch estimator. For each estimator/methodology, we test our implementation on some synthetic data, while we also demonstrate the use case in a more realistic scenario of image clustering. The technical report for the details can be found in http://arxiv.org/abs/2102.05340.
- vMF density estimation via near-closed-form Maximum Likelihood Estimator (MLE) or Stochastic Gradient Descent (SGD)
- Estimation of mixture of vMFs via Expectation-Maximization (EM) or SGD
- Numerically stable estimation of the vMF normalizer through mpmath's Bessel function estimation
- Examples of image clustering application
- Python 3.7
- PyTorch >= 1.4.0
- NumPy >= 1.18.1
- mpmath >= 1.1.0
- scikit-learn >= 0.23.2 (Required for metric computation in image clustering)
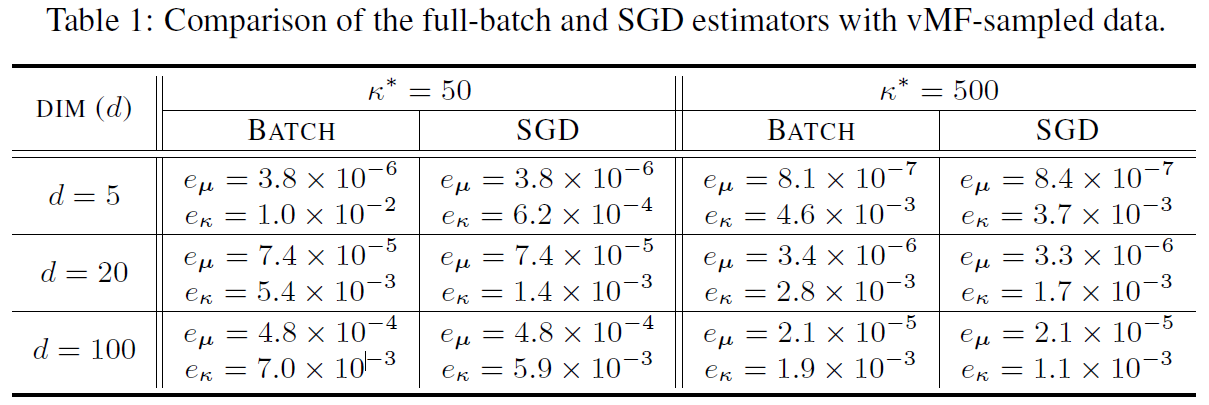
We generate samples from a true vMF model, and aim to estimate the true model parameters by either the near-closed-form full-batch MLE or the SGD estimator. See the demo code in mle_for_vmf.py for the details. The results are briefly summarized in the following Table 1. As shown, both estimators are equally accurate.
We also generate samples from a true mixture of three vMFs, and aim to estimate the true mixture parameters by either the EM or the SGD estimator. See the demo code in mle_for_mix_vmf.py for the details. The results are briefly summarized in the following Figure 2. As shown, both estimators are equally accurate.
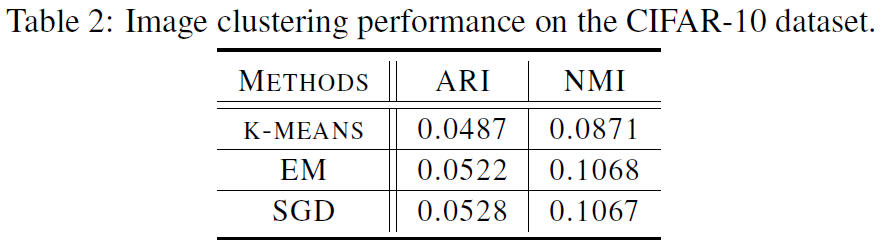
We aim to cluster the images in the CIFAR-10 dataset. Our pipeline approach consists of estimating first the unit-hyperspherical latent space by minimizing the reconstruction error in the auto-encoding process, then learning a vMF mixture model in the latent space. See the demo code in image_clustering_cifar10.py for the details. The results are briefly summarized in the following Table 2. The results indicate that the vMF mixture learning approaches (EM and SGD) significantly outperform the famous k-means algorithm in terms of the two clustering performance metrics, Adjusted Rand Index (ARI) and Normalized Mutual Information (NMI). And both the EM and SGD estimators perform equally well.
If you found this library useful in your research, please cite:
@inproceedings{mkim2021vmf,
title = {On PyTorch Implementation of Density Estimators for von Mises-Fisher and Its Mixture},
author = {Kim, Minyoung},
year = {2021},
URL = {http://arxiv.org/abs/2102.05340},
booktitle = {arXiv preprint}
}