Phoenix Chat Example


Try it: https://phxchat.herokuapp.com
A step-by-step tutorial for building, testing and deploying a Chat app in Phoenix!
Content
- Why?
- What?
- Who?
- How?
- 0. Pre-requisites (Before you Start)
- 1. Create the App
- 2. Create the (Websocket) "Channel"
- 3. Update the Template File (UI)
- 4. Update the "Client" code in App.js
- 5. Install the Node.js Dependencies
- 6. Create/Configure Database
- 7. Generate Database Schema to Store Chat History
- 8. Run the Ecto Migration (Create the Database Table)
- 9. Insert Messages into Database
- 10. Load Existing Messages (When Someone Joins the Chat)
- 11. Send Existing Messages to the Client when they join
- 12. Checkpoint: Our Chat App Saves Messages!! (Try it!)
- 13. Run the Default/Generated Tests
- 14. Understanding the Channel Tests
- 15. What is Not Tested?
- Continuous Integration
- Deployment!
- Inspiration
- Recommended Reading/Learning
Why?
Chat apps are the "Hello World" of "real time" examples.
Sadly, most example apps show a few basics and then ignore "the rest" ...
So "beginners" are often left "lost" or "confused" as to
what they should do or learn next!
Very few tutorials consider Testing,
Deployment, Documentation or other "Enhancements" which are
all part of the "Real World" of building and running apps;
so those are topics we will cover to "fill in the gaps".
We wrote this tutorial to be easiest way to learn Phoenix, Ecto and "Channels" with a practical example anyone can follow.
What?
A simple step-by-step tutorial showing you how to:
- Create a Phoenix App from scratch
(using the
mix phx.new chat"generator" command) - Add a "Channel" so your app can communicate over "WebSockets".
- Implement a basic "front-end" in "plain" JavaScript (ES5 without any libraries) to interact with Phoenix (send/receive messages via WebSockets)
- Add a simple "Ecto" schema to define the Database Table (to store messages)
- Write the functions ("CRUD") to save message/sender data to a database table.
- Test that everything is working as expected.
- Deploy to Heroku so you can show people your creation!
Initially, we deliberately skip over configuration files and "Phoenix Internals" because you (beginners) don't need to know about them to get started. But don't worry, we will return to them when needed. We favour "just-in-time" (when you need it) learning as it's immediately obvious and practical why we are learning something.
Who?
This example is for complete beginners
as a "My First Phoenix" App.
We try to assume as little as possible,
but if you think we "skipped a step"
or you feel "stuck" for any reason,
or have any questions (related to this example),
please open an issue on GitHub!
Both the @dwyl and Phoenix communities are super beginner-friendly,
so don't be afraid/shy.
Also, by asking questions, you are helping everyone
that is or might be stuck with the same thing!
- Chat App specific questions: https://github.com/dwyl/phoenix-chat-example/issues
- General Learning Phoenix questions: https://github.com/dwyl/learn-phoenix-framework/issues
How?
These instructions show you how to create the Chat app from scratch.
0. Pre-requisites (Before you Start)
- Elixir Installed on your local machine.
see: https://github.com/dwyl/learn-elixir#installation
e.g:
brew install elixir
Note: if you already have
Elixirinstalled on your Mac, and just want to upgrade to the latest version, run:brew upgrade elixir
- Phoenix framework installed.
see: https://hexdocs.pm/phoenix/installation.html
e.g:
mix archive.install hex phx_new 1.4.4
- PostgreSQL (Database Server) installed (to save chat messages)
see: https://github.com/dwyl/learn-postgresql#installation
-
Basic Elixir Syntax knowledge will help,
please see: https://github.com/dwyl/learn-elixir -
Basic JavaScript knowledge is advantageous (but not essential as the "front-end" code is quite basic and well-commented). see: https://github.com/iteles/Javascript-the-Good-Parts-notes
Check You Have Everything Before Starting
Check you have the latest version of Elixir (run the following command in your terminal):
elixir -vYou should see something like:
Erlang/OTP 21 [erts-10.3.4] [source] [64-bit] [smp:8:8] [ds:8:8:10] [async-threads:1] [hipe] [dtrace]
Elixir 1.8.1 (compiled with Erlang/OTP 21)Check you have the latest version of Phoenix:
mix phx.new -vYou should see:
Phoenix v1.4.4Confirm PostgreSQL is running (so the App can store chat messages) run the following command:
lsof -i :5432You should see output similar to the following:
COMMAND PID USER FD TYPE DEVICE SIZE/OFF NODE NAME
postgres 529 Nelson 5u IPv6 0xbc5d729e529f062b 0t0 TCP localhost:postgresql (LISTEN)
postgres 529 Nelson 6u IPv4 0xbc5d729e55a89a13 0t0 TCP localhost:postgresql (LISTEN)This tells us that PostgreSQL is "listening" on TCP Port 5432
(the default port)
With all those "pre-flight checks" performed, let's get going!
1. Create The App
In your terminal program on your localhost, type the following command to create the app:
mix phx.new chatThat will create the directory structure and project files.
When asked to "Fetch and install dependencies? [Yn]",
Type y (the "Y" key) in your terminal,
followed by the [Enter] / [Return] key.
Change directory into the chat directory by running the suggested command:
cd chatNote: at this point there is already an "App" it just does not do anything (yet) ...
you can runmix phx.serverin your terminal - don't worry if you're seeing error
messages, this is because we haven't created our database yet.
We will take care of that in step 6!
For now, open http://localhost:4000 in your browser
and you will see thedefault"Welcome to Phoenix" homepage:
Let's continue to the interesting part!
2. Create the (WebSocket) "Channel"
Generate the (WebSocket) channel to be used in the chat app:
mix phx.gen.channel RoomIf you are prompted to confirm installation, type
yand hit the[Enter]key.
This will create two files:
* creating lib/chat_web/channels/room_channel.ex
* creating test/chat_web/channels/room_channel_test.exsThe room_channel.ex file handles receiving/sending messages
and the room_channel_test.exs tests basic interaction with the channel.
(Don't worry about this yet, we will look at the test file in step 14 below!)
We are informed that we need to update a piece of code into your app:
Add the channel to your `/lib/chat_web/channels/user_socket.ex` handler, for example:
channel "room:lobby", ChatWeb.RoomChannelOpen the file called /lib/chat_web/channels/user_socket.ex
and change the line:
# channel "room:*", ChatWeb.RoomChannelto:
channel "room:lobby", ChatWeb.RoomChannelExample: user_socket.ex#L5
For more detail on Phoenix Channels, (we highly recommend you) read: https://hexdocs.pm/phoenix/channels.html
3. Update the Template File (UI)
Open the the
/lib/chat_web/templates/page/index.html.eex
file
and copy-paste (or type) the following code:
<!-- The list of messages will appear here: -->
<ul id='msg-list' class='row' style='list-style: none; min-height:200px; padding: 10px;'></ul>
<div class="row">
<div class="col-xs-3">
<input type="text" id="name" class="form-control" placeholder="Your Name" autofocus>
</div>
<div class="col-xs-9">
<input type="text" id="msg" class="form-control" placeholder="Your Message">
</div>
</div>This is the basic form we will use to input Chat messages.
The classes e.g: "form-control" and "col-xs-3"
are Bootstrap CSS classes to style the form.
Phoenix includes Bootstrap by default so you can get up-and-running
with your App/Idea/"MVP"!
If you are unfamiliar with Bootstrap UI,
read: https://getbootstrap.com/docs/3.3
and if you specifically want to understand the Bootstrap forms,
see: https://getbootstrap.com/docs/3.3/css/#forms
Your index.html.eex template file should look like this:
/lib/chat_web/templates/page/index.html.eex (snapshot)
4. Update the "Client" code in App.js
Open:
/assets/js/app.js
and uncomment the line:
import socket from "./socket"with the line uncommented our app will import the socket.js file
which will give us WebSocket functionality.
Then add the following JavaScript ("Client") code:
let channel = socket.channel('room:lobby', {}); // connect to chat "room"
channel.on('shout', function (payload) { // listen to the 'shout' event
let li = document.createElement("li"); // create new list item DOM element
let name = payload.name || 'guest'; // get name from payload or set default
li.innerHTML = '<b>' + name + '</b>: ' + payload.message; // set li contents
ul.appendChild(li); // append to list
});
channel.join(); // join the channel.
let ul = document.getElementById('msg-list'); // list of messages.
let name = document.getElementById('name'); // name of message sender
let msg = document.getElementById('msg'); // message input field
// "listen" for the [Enter] keypress event to send a message:
msg.addEventListener('keypress', function (event) {
if (event.keyCode == 13 && msg.value.length > 0) { // don't sent empty msg.
channel.push('shout', { // send the message to the server on "shout" channel
name: name.value, // get value of "name" of person sending the message
message: msg.value // get message text (value) from msg input field.
});
msg.value = ''; // reset the message input field for next message.
}
});Take a moment to read the JavaScript code and confirm your understanding of what it's doing.
Hopefully the in-line comments are self-explanatory, but if anything is unclear, please ask!
At this point your app.js file should look like this:
/assets/js/app.js
4.1 Comment Out Lines in socket.js
By default the phoenix channel (client)
will subscribe to the generic room: "topic:subtopic".
Since we aren't going to be using this,
we can avoid seeing any
"unable to join: unmatched topic" errors in our browser/console
by simply commenting out a few lines in the socket.js file.
Open the file in your editor and locate the following lines:
let channel = socket.channel("topic:subtopic", {})
channel.join()
.receive("ok", resp => { console.log("Joined successfully", resp) })
.receive("error", resp => { console.log("Unable to join", resp) })Comment out the lines so they will not be executed:
// let channel = socket.channel("topic:subtopic", {})
// channel.join()
// .receive("ok", resp => { console.log("Joined successfully", resp) })
// .receive("error", resp => { console.log("Unable to join", resp) })Your socket.js should now look like this:
/assets/js/socket.js
If you later decide to tidy up your chat app, you can
deletethese commented lines from the file.
We are just keeping them for reference of how to join channels and receive messages.
Once that's done, proceed to the next step!
5. Install the Node.js Dependencies
In order to use JS in your Phoenix project, you need to install the node.js dependencies:
cd assets && npm install && cd ..That might take a few seconds (depending on your internet connection speed)
But once it completes you should see:
added 1022 packages from 600 contributors and audited 14893 packages in 32.079s
found 0 vulnerabilitiesStoring Chat Message Data/History
If we didn't want to save the chat history,
we could just deploy this App immediately
and we'd be done!
6. Create/Configure Database
Create the database to store the chat history data:
mix ecto.createYou should see:
The database for Chat.Repo has been created7. Generate Database Schema to Store Chat History
Run the following command in your terminal:
mix phx.gen.schema Message messages name:string message:stringYou should see the following output:
* creating lib/chat/message.ex
* creating priv/repo/migrations/20180107074333_create_messages.exs
Remember to update your repository by running migrations:
$ mix ecto.migrateLet's break down that command for clarity:
mix phx.gen.schema- the mix command to create a new schema (database table)Message- the singular name for record in our messages "collection"messages- the name of the collection (or database table)name:string- the name of the person sending a message, stored as astring.message:string- the message sent by the person, also stored as astring.
The creating lib/chat/message.ex file is the "schema"
for our Message database table.
Additionally a migration file is created, e.g:
creating priv/repo/migrations/20180107074333_create_messages.exs
The "migration" actually creates the database table in our database.
8. Run the Ecto Migration (Create The Database Table)
In your terminal run the following command to create the messages table:
mix ecto.migrateYou should see the following in your terminal:
Compiling 1 file (.ex)
Generated chat app
[info] == Running Chat.Repo.Migrations.CreateMessages.change/0 forward
[info] create table messages
[info] == Migrated in 0.0s8.1 Review the Messages Table Schema
If you open your PostgreSQL GUI (e.g: pgadmin)
you will see that the messages table has been created
in the chat_dev database:
You can view the table schema by "right-clicking" (ctrl + click on Mac)
on the messages table and selecting "properties":
9. Insert Messages into Database
Open the lib/chat_web/channels/room_channel.ex file
and inside the function def handle_in("shout", payload, socket) do
add the following line:
Chat.Message.changeset(%Chat.Message{}, payload) |> Chat.Repo.insert So that your function ends up looking like this:
def handle_in("shout", payload, socket) do
Chat.Message.changeset(%Chat.Message{}, payload) |> Chat.Repo.insert
broadcast socket, "shout", payload
{:noreply, socket}
end10. Load Existing Messages (When Someone Joins the Chat)
Open the lib/chat/message.ex file and add a new function to it:
def get_messages(limit \\ 20) do
Chat.Repo.all(Chat.Message, limit: limit)
endThis function accepts a single parameter limit to only return a fixed/maximum
number of records.
It uses Ecto's all function to fetch all records from the database.
Message is the name of the schema/table we want to get records for,
and limit is the maximum number of records to fetch.
11. Send Existing Messages to the Client when they Join
In the /lib/chat_web/channels/room_channel.ex file create a new function:
def handle_info(:after_join, socket) do
Chat.Message.get_messages()
|> Enum.each(fn msg -> push(socket, "shout", %{
name: msg.name,
message: msg.message,
}) end)
{:noreply, socket} # :noreply
endand at the top of the file update the join function to the following:
def join("room:lobby", payload, socket) do
if authorized?(payload) do
send(self(), :after_join)
{:ok, socket}
else
{:error, %{reason: "unauthorized"}}
end
end12. Checkpoint: Our Chat App Saves Messages!! (Try it!)
Start the Phoenix server (if it is not already running):
mix phx.serverNote: it will take a few seconds to compile but then you should see:
The line:
[info] Running ChatWeb.Endpoint with Cowboy using http://0.0.0.0:4000tells us that our code compiled (as expected) and the Chat App
is running on TCP Port 4000!
Open the Chat web app in
two separate browser windows: http://localhost:4000
(if your machine only has one browser try using one "incognito" tab)
You should be able to send messages between the two browser windows:

Congratulations! You have a working (basic) Chat App written in Phoenix!
The chat (message) history is saved!
This means you can refresh the browser or join in a different browser and you will still see the history!
Testing our App (Automated Testing)
Automated testing is one of the best ways to ensure reliability in your web applications.
Note: If you are completely new to Automated Testing or "Test Driven Development" ("TDD"), we recommend reading/following the "basic" tutorial: github.com/dwyl/learn-tdd
Testing in Phoenix is fast (tests run in parallel!)
and easy to get started!
The ExUnit testing framework is built-in
so there aren't an "decisions/debates"
about which framework or style to use.
If you have never seen or written a test with ExUnit,
don't fear, the syntax should be familiar if you have
written any sort of automated test in the past.
13. Run the Default/Generated Tests
Whenever you create a new Phoenix app or add a new feature (like a channel), Phoenix generates a new test for you.
We run the tests using the mix test command:
In this case one of the tests fails. (7 tests, 1 failure)
The "stacktrace" informs us that location of the failing test is:
test/chat_web/controllers/page_controller_test.exs:4
And that the "assertion" is:
assert html_response(conn, 200) =~ "Welcome to Phoenix!"In English this means we are asserting that the "homepage" returns an "HTML response" which contains the words: "Welcome to Phoenix!"
Since we changed the code in
/lib/chat_web/templates/page/index.html.eex
(in section 3, above),
the page no longer contains the string " Welcome to Phoenix! ".
13.1 Fix The Failing Test
We have two options:
- Add the text "Welcome to Phoenix!" back into
page/index.html.eex - Update the assertion to something that is on the page e.g: "msg-list".
Both are valid approaches, however we prefer the second option because
it "reflects the reality" rather than "altering reality"
to match the exiting assertion.
Let's make the update now. Open the
test/chat_web/controllers/page_controller_test.exs
file and change line 6 to:
assert html_response(conn, 200) =~ "msg-list"We know that "msg-list" is on the page
because that's the id of the <ul>
where our message history is bing displayed.
Your page_controller_test.exs file should now look like this:
/test/chat_web/controllers/page_controller_test.exs#L6
13.2 Re-Run The Test(s)
Now that we have updated the assertion,
we can re-run the tests with the mix test command:
14. Understanding The Channel Tests
It's worth taking a moment (or as long as you need!)
to understand what is going on in the
/room_channel_test.exs
file. Open it if you have not already, read the test descriptions & code.
For a bit of context we recommend reading: https://hexdocs.pm/phoenix/testing_channels.html
14.1 Analyse a Test
Let's take a look at the first test in /test/chat_web/channels/room_channel_test.exs#L14-L17:
test "ping replies with status ok", %{socket: socket} do
ref = push socket, "ping", %{"hello" => "there"}
assert_reply ref, :ok, %{"hello" => "there"}
endThe test get's the socket from the setup function (on line 6 of the file)
and assigns the result of calling the push function to a variable ref
push merely pushes a message (the map %{"hello" => "there"})
on the socket to the "ping" topic.
The handle_in
function clause which handles the "ping" topic:
def handle_in("ping", payload, socket) do
{:reply, {:ok, payload}, socket}
endSimply replies with the payload you send it,
therefore in our test we can use the assert_reply Macro
to assert that the ref is equal to :ok, %{"hello" => "there"}
Note: if you have questions or need any help understanding the other tests, please open an issue on GitHub we are happy to expand this further!
(we are just trying to keep this tutorial reasonably "brief" so beginners are not "overwhelmed" by anything...)
15. What is Not Tested?
Often we can learn a lot about an application (or API) from reading the tests and seeing where the "gaps" in testing are.
Thankfully we can achieve this with only a couple of steps:
15.1 Add excoveralls as a (Development) Dependency to mix.exs
Open your mix.exs file and find the "deps" function:
defp deps do
Add the following line to the end of the List:
{:excoveralls, "~> 0.7.0", only: [:test, :dev]}, # tracking test coverageAdditionally, find the def project do section (towards the top of mix.exs)
and add the following lines to the List:
test_coverage: [tool: ExCoveralls],
preferred_cli_env: ["coveralls": :test, "coveralls.detail": :test,
"coveralls.post": :test, "coveralls.html": :test]Then, install the dependency on excoveralls
we just added to mix.exs:
mix deps.getYou should see:
Resolving Hex dependencies...
Dependency resolution completed:
* Getting excoveralls (Hex package)
... etc.15.2 Create a New File Called coveralls.json
In the "root" (base directory) of the Chat project,
create a new file called coveralls.json and copy-paste the following:
{
"coverage_options": {
"minimum_coverage": 100
},
"skip_files": [
"test/"
]
}This file is quite basic, it instructs the coveralls app
to require a minimum_coverage of 100%
(i.e. everything is tested1)
and to ignore the files in the test/ directory for coverage checking.
1We believe that investing a little time up-front to write tests for all our code is worth it to have fewer bugs later.
Bugs are expensive, tests are cheap and confidence/reliability is priceless.
15.3 Run the Tests with Coverage Checking
To run the tests with coverage, copy-paste the following command into your terminal:
MIX_ENV=test mix do coveralls.json
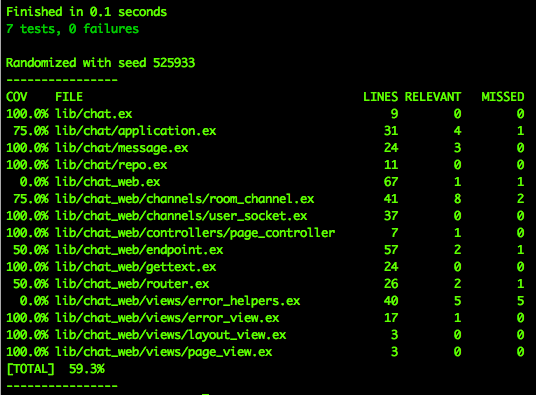
As we can se here, only 59.3% of lines of code in /lib
are being "covered" by the tests we have written.
To view the coverage in a web browser run the following:
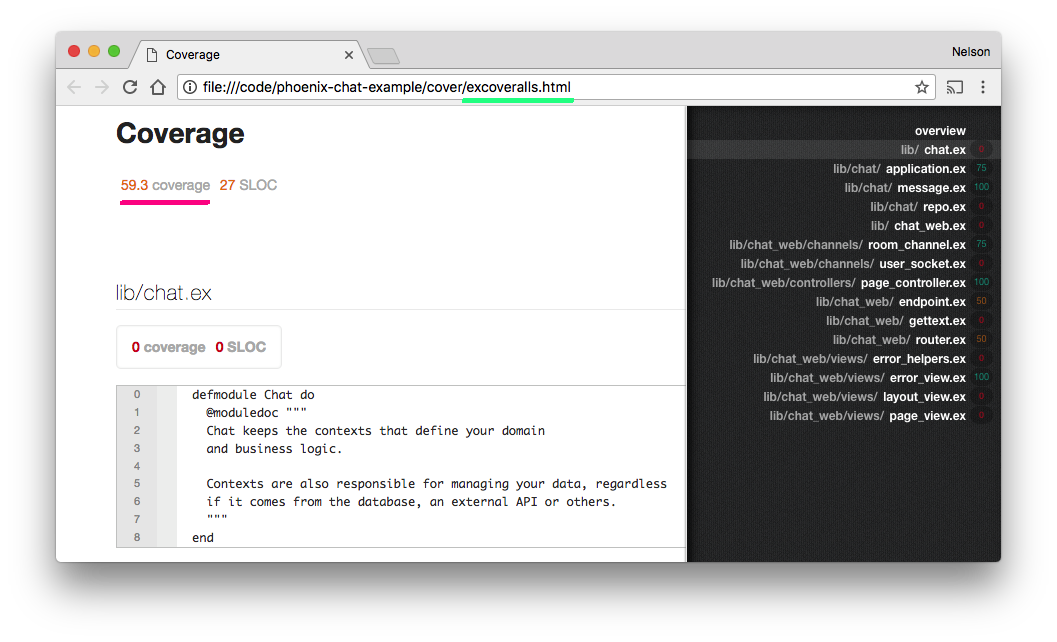
MIX_ENV=test mix coveralls.html && open cover/excoveralls.htmlThis will open the Coverage Report (HTML) in your default Web Browser:
Note: you will need to temporarily lower the coverage threshold in
coveralls.jsonform100to50for this command to work because it's expecting 100% coverage.
Continuous Integration
Continuous integration lets you automate running the tests to check/confirm that your app is working as expected (before deploying). This prevents accidentally "breaking" your app.
Thankfully the steps are quite simple.
If you are
newto Continuous Integration, or need a refresher, we wrote a step-by-step tutorial for it! see: github.com/dwyl/learn-travis
The Elixir-specific section is: https://github.com/dwyl/learn-travis#elixir-lang
We only need to add .travis.yml file to the project
with the following lines:
language: elixir
elixir: # Latest version of Elixir
- 1.6
addons: # ensure that Travis-CI provisions a DB for our test:
postgresql: '9.5'
env:
- MIX_ENV=test
script: # run the tests:
- mix testYou will need to enable your project on Travis-CI
for the build to run.
Please see: https://github.com/dwyl/learn-travis#getting-started
Deployment!
Deployment to Heroku takes a few minutes, but has a few "steps", therefore we have created a separate guide for it: elixir-phoenix-app-deployment.md
Once you have deployed you will will be able to view/use your app in any Web/Mobile Browser.
e.g: https://phxchat.herokuapp.com

What Next?
If you found this example useful, please
If you want to learn more Phoenix and the magic of LiveView,
consider reading our beginner's tutorial:
github.com/dwyl/phoenix-liveview-counter-tutorial
Thank you for learning with us!
Inspiration
This repo is inspired by @chrismccord's Simple Chat Example: https://github.com/chrismccord/phoenix_chat_example
At the time of writing Chris' example is still Phoenix 1.2 see: chrismccord/phoenix_chat_example#40 therefore we decided to write a quick version for Phoenix 1.4 :-)
Recommended Reading / Learning
- ExUnit docs: https://hexdocs.pm/ex_unit/ExUnit.html
- Testing Phoenix Channels: https://quickleft.com/blog/testing-phoenix-websockets
- Phoenix WebSockets Under a Microscope: https://zorbash.com/post/phoenix-websockets-under-a-microscope