MATE: Multi-Attribute Table Extraction
Here you can find the code and datasets for the MATE: Multi-Attribute Table Extraction paper, which is published at VLDB 2022.
Abstract
A core operation in data discovery is to find joinable tables for a given table. Real-world tables include both unary and n-ary join keys. However, existing table discovery systems are optimized for unary joins and are ineffective and slow in the existence of n-ary keys. In this paper, we introduce Mate, a table discovery system that leverages a novel hash-based index that enables n-ary join discovery through a space-efficient super key. We design a filtering layer that uses a novel hash, Xash. This hash function encodes the syntactic features of all column values and aggregates them into a super key, which allows the system to efficiently prune tables with non-joinable rows. Our join discovery system is able to prune up to 1000𝑥 more false positives and leads to over 60𝑥 faster table discovery in comparison to state-of-the-art.
Running example
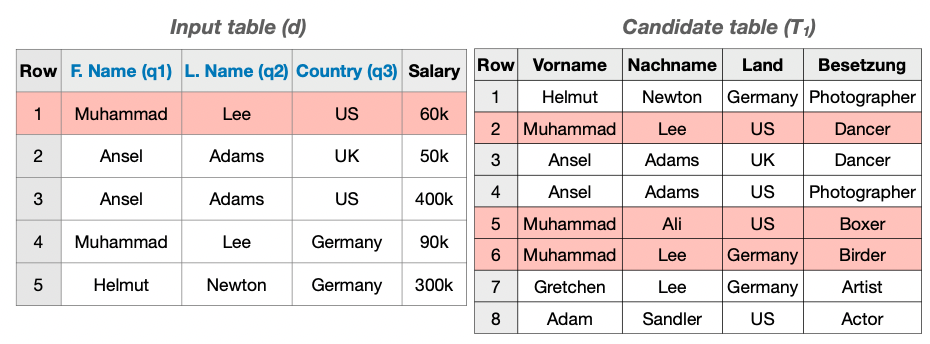
In this example, we consider two tables: An input table d and a candidate table T1.
The user selects F.Name, L.Name and Country as query columns. We use MATE to find the three columns with highest joinablility score J from T1. To do so, we have to find the mapping from query to target columns that allows as many joins as possible. In this case, we map F.Name to Vorname, L.Name to Nachname, and Country to Land and obtain J = 5.
Datasets
Three categories of datasets are used in our paper either as query dataset or corpus of tables from which we extract the candidate joinable tables. These categories are: 1- Webtables, 2- German Open data, 3- Kaggle datasets, and 4- School datasets.
For webtables, we used Dresden WebTable Corpus. To download the whole corpus, one could use the following command:
for i in $(seq -w 0 500); do wget http://wwwdb.inf.tu-dresden.de/misc/dwtc/data_feb15/dwtc-$i.json.gz; doneAfter downloading all the tables, we store them in a Vertica database as an inverted index.
German opendata is also used in the experiment in the paper. We extracted all the CSV data from the website and store them in a Vertica database as an inverted index.
We used Kaggle datasets only as input queries. These datasets can be access HERE along with other input datasets used in the paper.
School corpus is used both as data lake and input query.
XASH Index Generation
Having the traditional inverted index defined in the DataXFormer paper, in a Vertica database, the user should generate our novel index (XASH) using the following function:
def generate_index(main_table: str = 'main_tokenized',
super_key_column: str = 'super_key',
hash_size: int = 128
) -> None:in index_generation.py. Depending on your system architecture this might take a few hours or even days.
Usage
After creating the index you can use MATE to find the top-k joinable tables for your dataset using the following class
MATETableExtractionin MATE.py.
In our example, we would like to run MATE on the movie dataset in movie.csv
in order to find tables which can be joined with both director_name and movie_title columns.
First we create a MATETableExtraction instance as follows:
top_k = 10
one_bits = 5
bits = 128
mate = MATETableExtraction('movie', 'datasets/movie.csv', ['director_name', 'movie_title'], top_k, 'main_tokenized',
one_bits, f'MATE_datasets_k_bits_ones_{top_k}_{bits}_{one_bits}')Then we can run MATE on our dataset, which will give us the top-10 joinable tables:
mate.MATE(bits)Experiments
Figure 4: Runtime comparison between Mate and SCI.
top_k = 10
one_bits = 6
bits = 128
for file_path in glob.glob('datasets/webtable/10/sampled_file/*.csv'):
file_name = file_path.split('/')[-1].split('.')[0]
tbl = df.read_csv(file_path, index_col=False)
mate_table_extraction(file_name, file_path, tbl.columns.values, top_k, 'main_tokenized', one_bits, 'MATE_WT10').MATE(bits, True)
mate_table_extraction(file_name, file_path, tbl.columns.values, top_k, 'main_tokenized', 0, 'SCR_WT10').SCR(bits, True)
mate_table_extraction(file_name, file_path, tbl.columns.values, top_k, 'main_tokenized', 0, 'MCR_WT10').MCR(bits, True)
for file_path in glob.glob('datasets/webtable/100/sampled_file/*.csv'):
file_name = file_path.split('/')[-1].split('.')[0]
tbl = df.read_csv(file_path, index_col=False)
mate_table_extraction(file_name, file_path, tbl.columns.values, top_k, 'main_tokenized', one_bits, 'MATE_WT100').MATE(bits, True)
mate_table_extraction(file_name, file_path, tbl.columns.values, top_k, 'main_tokenized', 0, 'SCR_WT100').SCR(bits, True)
mate_table_extraction(file_name, file_path, tbl.columns.values, top_k, 'main_tokenized', 0, 'MCR_WT100').MCR(bits, True)
for file_path in glob.glob('datasets/webtable/1000/sampled_file/*.csv'):
file_name = file_path.split('/')[-1].split('.')[0]
tbl = df.read_csv(file_path, index_col=False)
mate_table_extraction(file_name, file_path, tbl.columns.values, top_k, 'main_tokenized', one_bits, 'MATE_WT1000').MATE(bits, True)
mate_table_extraction(file_name, file_path, tbl.columns.values, top_k, 'main_tokenized', 0, 'SCR_WT1000').SCR(bits, True)
mate_table_extraction(file_name, file_path, tbl.columns.values, top_k, 'main_tokenized', 0, 'MCR_WT1000').MCR(bits, True)
for file_path in glob.glob('datasets/opendata/100/sampled_file/*.csv'):
file_name = file_path.split('/')[-1].split('.')[0]
tbl = df.read_csv(file_path, index_col=False)
mate_table_extraction(file_name, file_path, tbl.columns.values, top_k, 'main_tokenized', one_bits, 'MATE_OD100').MATE(bits, True)
mate_table_extraction(file_name, file_path, tbl.columns.values, top_k, 'main_tokenized', 0, 'SCR_OD100').SCR(bits, True)
mate_table_extraction(file_name, file_path, tbl.columns.values, top_k, 'main_tokenized', 0, 'MCR_OD100').MCR(bits, True)
for file_path in glob.glob('datasets/opendata/1000/sampled_file/*.csv'):
file_name = file_path.split('/')[-1].split('.')[0]
tbl = df.read_csv(file_path, index_col=False)
mate_table_extraction(file_name, file_path, tbl.columns.values, top_k, 'main_tokenized', one_bits, 'MATE_OD1000').MATE(bits, True)
mate_table_extraction(file_name, file_path, tbl.columns.values, top_k, 'main_tokenized', 0, 'SCR_OD1000').SCR(bits, True)
mate_table_extraction(file_name, file_path, tbl.columns.values, top_k, 'main_tokenized', 0, 'MCR_OD1000').MCR(bits, True)
for file_path in glob.glob('datasets/opendata/10000/sampled_file/*.csv'):
file_name = file_path.split('/')[-1].split('.')[0]
tbl = df.read_csv(file_path, index_col=False)
mate_table_extraction(file_name, file_path, tbl.columns.values, top_k, 'main_tokenized', one_bits, 'MATE_OD10000').MATE(bits, True)
mate_table_extraction(file_name, file_path, tbl.columns.values, top_k, 'main_tokenized', 0, 'SCR_OD10000').SCR(bits, True)
mate_table_extraction(file_name, file_path, tbl.columns.values, top_k, 'main_tokenized', 0, 'MCR_OD10000').MCR(bits, True)Table 2: Runtime experiment (seconds) and Table 3: Precision experiment. To obtain the results of these tables, one should run the following python codes:
top_k = 10
one_bits = 6
bits = 128
corpus = 'webtable' # or opendata
corpus_query_size = '100' # [10, 100, 1000, 10000]
for file_path in glob.glob('datasets/{}/{}/sampled_file/*.csv'.format(corpus, corpus_query_size)):
file_name = file_path.split('/')[-1].split('.')[0]
tbl = df.read_csv(file_path, index_col=False)
mate_table_extraction(file_name, file_path, tbl.columns.values, top_k, 'main_tokenized', one_bits, 'MATE').MATE(bits, True)
mate_table_extraction(file_name, file_path, tbl.columns.values, top_k, 'main_tokenized', 18, 'BF').BF(bits, True)
mate_table_extraction(file_name, file_path, tbl.columns.values, top_k, 'main_tokenized', 1, 'HT').BF(bits, True)
mate_table_extraction(file_name, file_path, tbl.columns.values, top_k, 'main_tokenized', 0, 'SCR').SCR()
mate_table_extraction(file_name, file_path, tbl.columns.values, top_k, 'main_tokenized', 0, 'Simhash').SIMHASH(bits, True)
mate_table_extraction(file_name, file_path, tbl.columns.values, top_k, 'main_tokenized', 0, 'Cityhash').CITYHASH(bits, True)
mate_table_extraction(file_name, file_path, tbl.columns.values, top_k, 'main_tokenized', 0, 'Murmurhash').MURMURHASH(bits, True)
mate_table_extraction(file_name, file_path, tbl.columns.values, top_k, 'main_tokenized', 0, 'Md5').MD5(bits, True)
mate_table_extraction(file_name, file_path, tbl.columns.values, top_k, 'main_tokenized', 2, 'LHBF').BF_Less_Hash(bits, True)mate_table_extraction('movie', 'datasets/movie.csv', ['director_name', 'movie_title'], top_k, 'main_tokenized', one_bits, 'Joinability_kaggle'.format(bits)).MATE(bits, True)
mate_table_extraction('city', 'datasets/worldcitiespop_country_city_pop_non_zero.csv', ['Country', 'City'], top_k, 'main_tokenized', one_bits, 'Joinability_kaggle'.format(bits)).MATE(bits, True)
mate_table_extraction('universities', 'datasets/national_universities_rankings.csv', ['Name', 'Location'], top_k, 'main_tokenized', one_bits, 'Joinability_kaggle'.format(bits)).MATE(bits, True)
mate_table_extraction('pageview', 'datasets/pageviews_final_11000_multi_attr.csv', ['name', 'country'], top_k, 'main_tokenized', one_bits, 'Joinability_kaggle'.format(bits)).MATE(bits, True)
mate_table_extraction('presidential', 'datasets/presidential_final_multi_attr_all.csv', ['State', 'County'], top_k, 'main_tokenized', one_bits, 'Joinability_kaggle'.format(bits)).MATE(bits, True)
mate_table_extraction('airbnb', 'datasets/AB_NYC_2019.csv', ['neighbourhood_group', 'neighbourhood'], top_k, 'main_tokenized', one_bits, 'Joinability_kaggle'.format(bits)).MATE(bits, True)
mate_table_extraction('beer', 'datasets/datasets_673_1282_beers.csv', ['name', 'style'], top_k, 'main_tokenized', one_bits, 'Joinability_kaggle'.format(bits)).MATE(bits, True)
mate_table_extraction('airline', 'datasets/datasets_2253_3806_airlines.csv', ['Name', 'Country'], top_k, 'main_tokenized', one_bits, 'Joinability_kaggle'.format(bits)).MATE(bits, True)
mate_table_extraction('food', 'datasets/kaggle_food.csv', ['product_name', 'brands'], top_k, 'main_tokenized', one_bits, 'Joinability_kaggle'.format(bits)).MATE(bits, True)
mate_table_extraction('hfi_two_queries', 'datasets/kaggle_hfi.csv', ['countries', 'region'], top_k, 'main_tokenized', one_bits, 'Joinability_kaggle'.format(bits)).MATE(bits, True)
mate_table_extraction('wine', 'datasets/kaggle_wine.csv', ['country', 'province'], top_k, 'main_tokenized', one_bits, 'Joinability_kaggle'.format(bits)).MATE(bits, True)
mate_table_extraction('vgsales_two_queries1', 'datasets/vgsales.csv', ['Name', 'Platform'], top_k, 'main_tokenized', one_bits, 'Joinability_kaggle'.format(bits)).MATE(bits, True)
mate_table_extraction('pollution1', 'datasets/pollution_us_2000_2016.csv', ['State', 'City'], top_k, 'main_tokenized', one_bits, 'Joinability_kaggle'.format(bits)).MATE(bits, True)
mate_table_extraction('park', 'datasets/datasets_15295_20358_SF_Park_Scores.csv', ['Park', 'State'], top_k, 'main_tokenized', one_bits, 'Joinability_kaggle'.format(bits)).MATE(bits, True)for file_path in glob.glob('datasets/school/query/*.csv'):
file_name = file_path.split('/')[-1].split('.')[-1]
tbl = df.read_csv(file_path, index_col=False)
mate_table_extraction(file_name, file_path, ['Program Type', 'School Name'], top_k, 'school', one_bits, 'Joinability_school').MATE(bits, True)For the Kaggle and School experiments, replace the function MATE() with any of the other hash functions.
Figure 5: The influence of Xash components on Precision. To run this experiment, one should tun the following python code:
top_k = 10
bits = 128
one_bits = 6
for file_path in glob.glob('datasets/webtable/100/sampled_file/*.csv'):
file_name = file_path.split('/')[-1].split('.')[0]
if file_name not in valid_files:
continue
tbl = pd.read_csv(file_path, index_col=False)
mate_table_extraction(file_name, file_path, tbl.columns.values, top_k, 'main_tokenized', one_bits, 'SCR').SCR()
mate_table_extraction(file_name, file_path, tbl.columns.values, top_k, 'main_tokenized', one_bits, 'MATE_only_length').MATE_only_length(bits, True)
mate_table_extraction(file_name, file_path, tbl.columns.values, top_k, 'main_tokenized', one_bits, 'MATE_only_chars').MATE_only_chars(bits, True)
mate_table_extraction(file_name, file_path, tbl.columns.values, top_k, 'main_tokenized', one_bits, 'MATE_only_chars_and_loc').MATE_only_chars_and_loc(bits, True)
mate_table_extraction(file_name, file_path, tbl.columns.values, top_k, 'main_tokenized', one_bits, 'MATE_only_chars_and_loc_and_length').MATE_only_chars_and_loc_and_length(bits, True)
mate_table_extraction(file_name, file_path, tbl.columns.values, top_k, 'main_tokenized', one_bits, 'MATE_128').MATE(bits, True)
mate_table_extraction(file_name, file_path, tbl.columns.values, top_k, 'main_tokenized', one_bits, 'MATE_512').MATE(512, True)Figure 6: Key size experiment.
for k in ['1290']:
for i in np.arange(2, 11, 1):
tbl = pd.read_csv("datasets/benchmark/{}.csv".format(k))
mate_table_extraction(k, "datasets/benchmark/{}.csv".format(k),
list(tbl.columns.values)[:i], top_k, 'open_data_main_tokenized', 6,
'key_size_exp_MATE_{}'.format(k)).MATE(128, True)
mate_table_extraction(k, "datasets/benchmark/{}.csv".format(k),
list(tbl.columns.values)[:i], top_k, 'open_data_main_tokenized', 3,
'key_size_exp_BF_{}'.format(k)).BF(128, True)
mate_table_extraction(k, "datasets/benchmark/{}.csv".format(k),
list(tbl.columns.values)[:i], top_k, 'open_data_main_tokenized', 1,
'key_size_exp_HT_{}'.format(k)).BF(128, True)
mate_table_extraction(k, "datasets/benchmark/{}.csv".format(k),
list(tbl.columns.values)[:i], top_k, 'open_data_main_tokenized', 0,
'key_size_exp_SCR_{}'.format(k)).SCR()