A startup called Sparkify wants to analyze the data they've been collecting on songs and user activity on their new music streaming app. The analytics team is particularly interested in understanding what songs users are listening to. Currently, they don't have an easy way to query their data, which resides in a directory of JSON logs on user activity on the app, as well as a directory with JSON metadata on the songs in their app.
They'd like a data engineer to create a Postgres database with tables designed to optimize queries on song play analysis, and bring you on the project. Your role is to create a database schema and ETL pipeline for this analysis. You'll be able to test your database and ETL pipeline by running queries given to you by the analytics team from Sparkify and compare your results with their expected results.
Done for Udacity Data Engineer Nanodegree Project
Star schema optimized for queries on song play analysis. the Schema is populated ETL pipeline using Python
The pipeline and schema allows to obtain insight of songs played by Sparkify users and evaluate their interaction with the music app (app usage, free or paid account, etc.).
Using Pandas library, the data is extracted from JSON files and transoformed into a Pandas DataFrame, then this data gets arranged as required by the design of the schema and loaded into a PosgreSQL database so it can be queried.
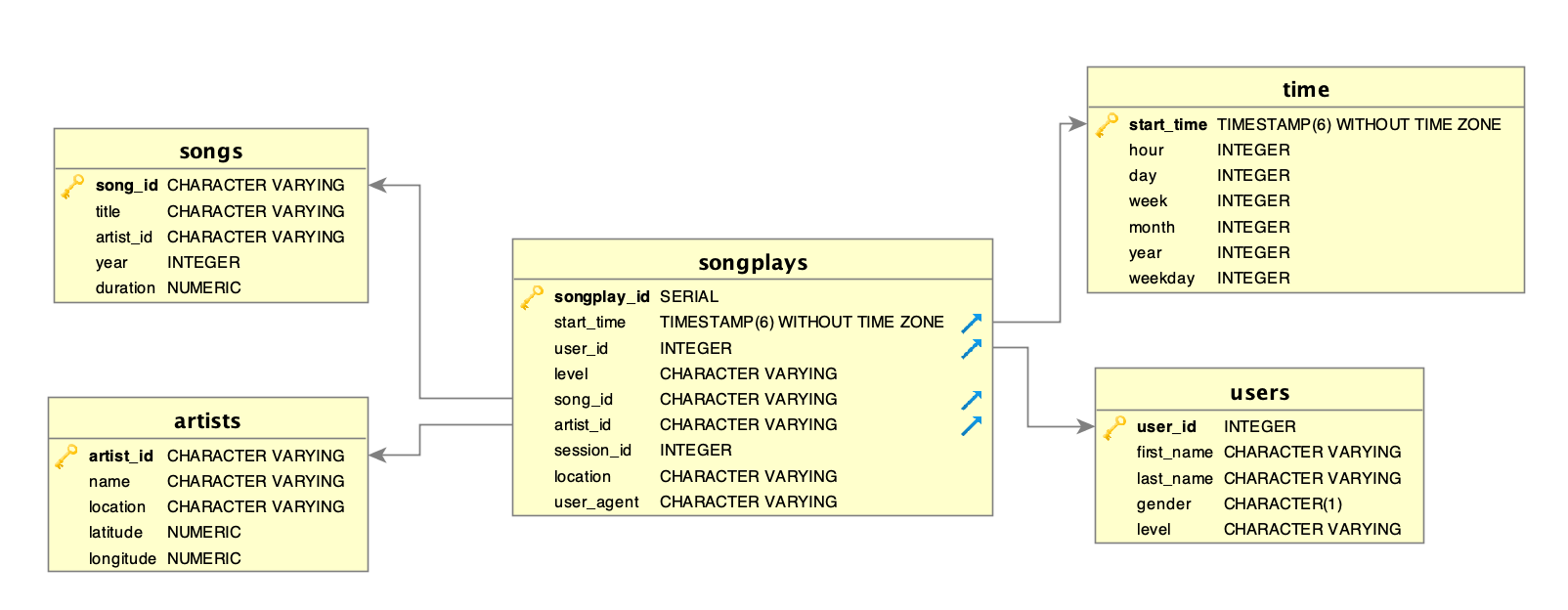
The star schema is the simplest style of data mart schema and is the approach most widely used to develop data warehouses and dimensional data marts. The star schema consists of one or more fact tables referencing any number of dimension tables. The star schema is an important special case of the snowflake schema, and is more effective for handling simpler queries
Source: Wikipedia
- songplays - records in log data associated with song plays i.e. records with page NextSong.
- songplay_id, start_time, user_id, level, song_id, artist_id, session_id, location, user_agent.
- users - users in the app.
- user_id, first_name, last_name, gender, level
- songs - songs in music database.
- song_id, title, artist_id, year, duration
- artists - artists in music database
- artist_id, name, location, latitude, longitude.
- time - timestamps of records in songplays broken down into specific units.
- start_time, hour, day, week, month, year, weekday.
- python3
- psycopg2
- pandas
- postgresql
This application is modularized into multiple python files.
- create_tables.py: Python script that loads SQL queries and creates the Schema and table.
- etl.py: ETL pipeline.
- sql_queries.py: sql queries module.
- data: Folder with Example JSON logfiles.
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install postgresql
By default, the postgres user has no password and can hence only connect if ran by the postgres system user. The following command will assign it:
$ sudo -u postgres psql -c "ALTER USER postgres PASSWORD 'postgres';"
$ sudo -u postgres psql -c "CREATE DATABASE testdb;"
By default Postgres creates a postgres user and is the only user who can connect to the server. We’ll want to create ourselves on the server with superuser capabilities with the same name as our login name:
$ sudo -u postgres createuser --superuser $USER
Enter your desired password when prompted.
Next, we’ll have to create a database with the same name as our login name since this is what Postgres expects by default when connecting to the server with your login name:
$ sudo -u postgres createdb $USER
You can still log in to postgres without creating any users by
$ psql postgres
- Download all files into a directory
- Start a terminal window and make sure all requirements are installed
- Start PosgreSQL server:
$ sudo service postgresql start - execute the following command to create the tables
$ python3 create_tables.py - to extract, load and tranform the data into the database run the following command
$ python3 etl.py - To query the data: run
$ psqland connect to the db with:$ \c <dataBaseName>
- \l - Display database
- \c - Connect to database
- \dn - List schemas
- \dt - List tables inside public schemas
- \dt schema1. - List tables inside particular schemas. For eg: 'schema1'.