by slv (Salas leVirve@Github) Update: 2017/06/09
<Intro to crawler>: Crawler / Spider Not complete yet... 😂
Related works of mine:
- dcard-spider: 透過 Dcard API 抓取/下載資料的高效能爬蟲。
- ptt-spider: PTT 高效能爬蟲,使用 lxml 快速解析並利用 asynio/coroutines 提高效率。
- ptt-scrapy: 使用
scrapy穩定爬取 PTT 資料。 - ptt-viewer: 將取得的資訊透過 Web UI 介面視覺化顯示。
在網路上養了一隻蟲,以下就用 PTT 的電影版文章作為我們的爬蟲目標囉!
首先使用 pip 來安裝套件,
-
requests發送接收 HTTP 請求及回應- 官方標語:
HTTP for Humans,這才是真正給人用的介面啊,建議不要直接使用內建的urllib模組!
- 官方標語:
-
beautifulsoup用來分析與抓取 html 中的元素- 簡單好用,沒有嚴格要求解析速度的話是個很好的選擇。
pip install requests pip install beautifulsoup4
-
(選用)
lxml用來解析 html/xml- 簡單好用(?),解析速度快多了!不過想要直接透過 lxml 解需要先熟悉
xpath語法,其實也挺容易學的~ - 可在這邊找到好心人為 Windows 預編譯好的 wheel (Unofficial pre-compiled lxml)
- p.s. 最近作者也提供編譯好的
Windows版本在PyPi上了,各系統應該都能用pip安裝了~
# install through pip pip install lxml # if you have conda, congrats! conda install lxml # if on debain/ubuntu, you may install binary directly... sudo apt-get install python3-lxml # if on windows, you may install from lxml wheel pip install lxml-3.8.0-cp35-cp35m-win_amd64.whl
- 簡單好用(?),解析速度快多了!不過想要直接透過 lxml 解需要先熟悉
What you see is what you retrieve, but all in text!
使用 requests.get() 函式仿造 HTTP GET 方法來「瀏覽」網頁,並取得網址中的內容。
回傳結果是一個 requests.Response 包裝起來的物件,而我們現在的目標是取得頁面原始碼即可;而網頁原始碼就在 response.text 中。
import requests
url = 'https://www.ptt.cc/bbs/movie/index.html'
response = requests.get(url)
print(response.text) # result of setp-1Interpretate the retrieved text like a browser
一般情況下瀏覽器拿到了網頁原始碼之後,會先解析然後把畫面顯示成我們平常看見的樣子;但這邊我們並不做顯示只想分析原始碼內的資訊。所以用 Beautifulsoup 來分析剛剛抓到的文字,在 BeautifulSoup() 的建構式第二個參數放入 'lxml' 讓他使用我們剛剛安裝的 lxml 來解析。
(p.s. 若剛剛未選擇安裝 lxml,則用 Python 內建的 html.parser 解析即可。)
而藉由我們打開瀏覽器查看網頁原始碼 (可用F12 開發者工具) 得知 PTT 網頁版中,每一篇文章的標題訊息皆放在 class="r-ent" 的 div 標籤裡。這裡我們使用到 find_all() 方法來操作 BeautifulSoup 物件並指定尋找目標,找到之後的結果是一串文章列表資訊。
import requests
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
url = 'https://www.ptt.cc/bbs/movie/index.html'
response = requests.get(url)
soup = BeautifulSoup(response.text, 'lxml')
articles = soup.find_all('div', 'r-ent')
print(articles) # result of setp-2Hey, here's some meta data
剛剛說過 find_all() 回傳符合的結果,而這串結果是個 list 型態的東西,所以我們用 for loop 來一個一個印出來看看。
而因為 html 本來就是具有階層式的標記語言,所有的資料都是用 觀察法 判斷到底放在哪個標籤哪一階層裡,以下就不多加贅述!
示範內容抓出:推文數、標題名稱、作者、發文日期和文章網址。
import requests
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
url = 'https://www.ptt.cc/bbs/movie/index.html'
response = requests.get(url)
soup = BeautifulSoup(response.text, 'lxml')
articles = soup.find_all('div', 'r-ent')
for article in articles:
meta = article.find('div', 'title').find('a')
title = meta.getText().strip()
link = meta.get('href')
push = article.find('div', 'nrec').getText()
date = article.find('div', 'date').getText()
author = article.find('div', 'author').getText()
print(push, title, date, author) # result of setp-3特殊處理: 沒事多寫點程式碼啊!把天賦通通點在美化上吧~ (字元寬度處理參考自 urwid)
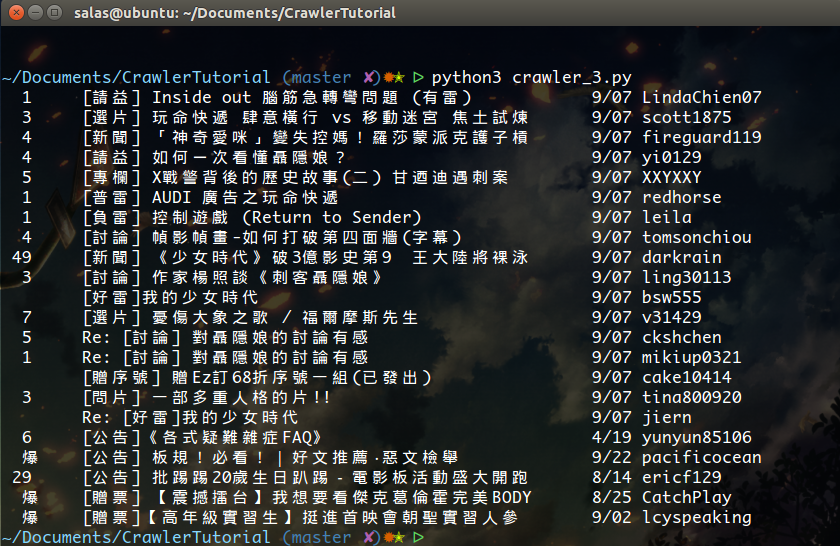
把這段程式碼貼到剛剛的 crawler_3.py 裡,並把 print 換成 pretty_print。漂亮的輸出就出現囉!
widths = [
(126, 1), (159, 0), (687, 1), (710, 0), (711, 1),
(727, 0), (733, 1), (879, 0), (1154, 1), (1161, 0),
(4347, 1), (4447, 2), (7467, 1), (7521, 0), (8369, 1),
(8426, 0), (9000, 1), (9002, 2), (11021, 1), (12350, 2),
(12351, 1), (12438, 2), (12442, 0), (19893, 2), (19967, 1),
(55203, 2), (63743, 1), (64106, 2), (65039, 1), (65059, 0),
(65131, 2), (65279, 1), (65376, 2), (65500, 1), (65510, 2),
(120831, 1), (262141, 2), (1114109, 1),
]
def calc_len(string):
def chr_width(o):
global widths
if o == 0xe or o == 0xf:
return 0
for num, wid in widths:
if o <= num:
return wid
return 1
return sum(chr_width(ord(c)) for c in string)
def pretty_print(push, title, date, author):
pattern = '%3s\t%s%s%s\t%s'
padding = ' ' * (50 - calc_len(title))
print(pattern % (push, title, padding, date, author))Give me data!
好,那就再用 觀察法 模式,去找找上一頁的連結在哪裡?
找到了嗎?不是問你頁面上的按鈕在哪裡喔!是看原始碼啊,同學!
相信都有發現了,關於頁面跳轉的超連結就放在 <div class='btn-group-paging'> 的 <a class='btn'> 裡,所以我們可以像這樣抓到他們:
# 控制頁面選項: 最舊/上頁/下頁/最新
controls = soup.find('div', 'btn-group-paging').find_all('a', 'btn')而我們需要的是上一頁的功能,為什麼呢?因為 PTT 是最新的文章顯示在前面啊~所以要挖資料必須往前翻。
那怎麼使用呢?先去抓出 control 中第二個(index: [1])的 href,然後他可能長這樣 /bbs/movie/index3237.html;而完整的網址(URL)必須要有 https://www.ptt.cc/ 開頭,所以用 urljoin() 把 Movie 首頁連結和新的 link 比對合併成完整的 URL!
link = controls[1].get('href')
page_url = urllib.parse.urljoin(INDEX, link)另外,或許會發現怎麼前面的程式有時候會出錯啊?!看看網頁版發現原來當該頁面中有文章被刪除時,網頁上的 <本文已被刪除> 這個元素的原始碼 結構 和原本不一樣哇!所以我們用 BeautifulSoup 生一個 <a> 元素來替代,方便後面存取時使用 (避免 title 和 link 的地方對 None 存取,產生上述提到的錯誤)。
NOT_EXIST = BeautifulSoup('<a>本文已被刪除</a>', 'lxml').a
...
# meta = A or B,當前面 A 的 .find() 抓到的是空的,則讓 meta 等於 B
meta = article.find('div', 'title').find('a') or NOT_EXIST現在我們將函式重新定義,讓:
get_posts_on_page(url): 抓取一頁中所有的文章的 metadata (很潮的後設資料),並回傳一串key-value類型的資料,以及前一頁的 link。get_pages(num): 抓取最新的 N 個頁面,並指派get_posts_on_page去抓每頁面中的資料,把每一串資料合併成一大串後回傳。
# 每筆資料長這樣子,dict() 類型資料:key-value pairs data
{
'title': meta.getText().strip(),
'link': meta.get('href'),
'push': article.find('div', 'nrec').getText(),
'date': article.find('div', 'date').getText(),
'author': article.find('div', 'author').getText(),
}而 get_posts_on_page(url) 和 get_pages(num) 回傳的就是這樣的一串資料:
[
{'push': '4', 'link': '/bbs/movie/M.1441633354.A.961.html', 'title': '[新聞] 侯孝賢:「一個導演,沒有自覺,就不用玩', 'date': ' 9/07', 'author': 'soulx'},
{'push': '', 'link': '/bbs/movie/M.1441636396.A.D64.html', 'title': '[請益] 倖存者(The Remaining)的結局', 'date': ' 9/07', 'author': 'Takuri'},
{'push': '', 'link': None, 'title': '本文已被刪除', 'date': ' 9/07', 'author': '-'},
{'push': '1', 'link': '/bbs/movie/M.1441637098.A.854.html', 'title': '[好雷] Hero電影版', 'date': ' 9/07', 'author': 'peichuan'},
{'push': '', 'link': '/bbs/movie/M.1441637150.A.DA1.html', 'title': '[新聞] 「夢想海洋」主題曲 魏德聖王大陸力挺', 'date': ' 9/07', 'author': 'fireguard119'},
{'push': '', 'link': '/bbs/movie/M.1441637513.A.14E.html', 'title': '[贈票] 未知之境 餘鬼狂歡~2015女性影展特映會', 'date': ' 9/07', 'author': 'epmt'},
{'push': '', 'link': '/bbs/movie/M.1441637531.A.E5A.html', 'title': '[問片] 問幾部港片/國片', 'date': ' 9/07', 'author': 'ogcxd'},
...
]附上crawler_4.py 完整程式碼
另外要說明的是 from utils import pretty_print,把剛剛 crawler_3.py 那個漂亮的輸出功能數十行的程式碼放到同目錄底下的新檔案 utils.py 中(檔案名字你喜歡就好,只要記得 from xxx import pretty_print 要記得一起改),然後在這邊 import(相當於 C語言中的 include )就能繼續沿用功能!
import requests
import urllib.parse
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
from utils import pretty_print
INDEX = 'https://www.ptt.cc/bbs/movie/index.html'
NOT_EXIST = BeautifulSoup('<a>本文已被刪除</a>', 'lxml').a
def get_posts_on_page(url):
response = requests.get(url)
soup = BeautifulSoup(response.text, 'lxml')
posts = list()
for article in soup.find_all('div', 'r-ent'):
meta = article.find('div', 'title').find('a') or NOT_EXIST
posts.append({
'title': meta.getText().strip(),
'link': meta.get('href'),
'push': article.find('div', 'nrec').getText(),
'date': article.find('div', 'date').getText(),
'author': article.find('div', 'author').getText(),
})
next_link = soup.find('div', 'btn-group-paging').find_all('a', 'btn')[1].get('href')
return posts, next_link
def get_pages(num):
page_url = INDEX
all_posts = list()
for i in range(num):
posts, link = get_posts_on_page(page_url)
all_posts += posts
page_url = urllib.parse.urljoin(INDEX, link)
return all_posts
if __name__ == '__main__':
pages = 5
for post in get_pages(pages):
pretty_print(post['push'], post['title'], post['date'], post['author'])Come on! Run! Run faster!
取得文章列表資訊(meta list)後,重要的是接下來取得文章內容(post content)
在 metadata 中的 link 就是每篇文章的連結,所以用 urllib.parse.urljoin 串接出完整網址之後發出 request 取得該頁面的內容。但在這裡並沒有做進一步的文章內容解析(parse),並沒有解析文章標題、作者、內容、推文等等,請大家自行練習分析頁面取得資訊。
def fetch_article_content(link):
url = urllib.parse.urljoin(INDEX, link)
response = requests.get(url)
return response.text這一步使用 Python 的內建 library multiprocessing 來加速爬蟲的效率!
使用 Python 內建寫好的 ProcessPool 來做 high-level 的 multiprocessing programming~
from multiprocessing import Pool然後在使用時使用 with statement 語法讓使用完之後將 process 資源自動釋放,with Pool(processes=8) as pool,而中間的 processes=8 則代表要開多少的 processes 來完成任務。而 ProcessPool 的用法也很簡單,pool.map(function, items),有點像 functional programming 的概念,將 function 套用在每一個 item 上,最後得出跟 items 一樣數量的結果清單(list)。
使用在前面介紹的抓取文章內容的任務上:
def get_articles(metadata):
post_links = [meta['link'] for meta in metadata]
with Pool(processes=8) as pool:
contents = pool.map(fetch_article_content, post_links)
return contents取得的 contents 會是 list type 的內容,所以最後可以疊袋拿出其中的資訊,以下附上完整的範例程式碼以及操作 contents 的方法。
import time
import urllib.parse
from multiprocessing import Pool
import requests
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
INDEX = 'https://www.ptt.cc/bbs/movie/index.html'
NOT_EXIST = BeautifulSoup('<a>本文已被刪除</a>', 'lxml').a
def get_posts_list(url):
response = requests.get(url)
soup = BeautifulSoup(response.text, 'lxml')
articles = soup.find_all('div', 'r-ent')
posts = list()
for article in articles:
meta = article.find('div', 'title').find('a') or NOT_EXIST
posts.append({
'title': meta.getText().strip(),
'link': meta.get('href'),
'push': article.find('div', 'nrec').getText(),
'date': article.find('div', 'date').getText(),
'author': article.find('div', 'author').getText(),
})
next_link = soup.find('div', 'btn-group-paging').find_all('a', 'btn')[1].get('href')
return posts, next_link
def get_paged_meta(page):
page_url = INDEX
all_posts = list()
for i in range(page):
posts, link = get_posts_list(page_url)
all_posts += posts
page_url = urllib.parse.urljoin(INDEX, link)
return all_posts
def get_articles(metadata):
post_links = [meta['link'] for meta in metadata]
with Pool(processes=8) as pool:
contents = pool.map(fetch_article_content, post_links)
return contents
def fetch_article_content(link):
url = urllib.parse.urljoin(INDEX, link)
response = requests.get(url)
return response.text
if __name__ == '__main__':
pages = 5
start = time.time()
metadata = get_paged_meta(pages)
articles = get_articles(metadata)
print('花費: %f 秒' % (time.time() - start))
print('共%d項結果:' % len(articles))
for post, content in zip(metadata, articles):
print('{0} {1: <15} {2}, 網頁內容共 {3} 字'.format(
post['date'], post['author'], post['title'], len(content)))這份程式 crawler_multiprocess.py 中用到 time.time() 計時,可以試看看用多少 process 和不用 multiprocessing 的時間差距~
上面的程式碼都在 src/ 中可以找到!