The purpose of this project is to have a simulation of a bipedal exoskeleton and to train a Reinforcement Learning (RL) algorithm to correctly activate the 3 actuators on each leg in such a way, that the exoskeleton (later with a person inside) would be able to walk.
This is the first stage of the simulation. In the next stage, a 3D model will be developed and the RL algorithm will be improved.
The RL model used is PPO (Proximal Policy Optimization) (John Schulman, Filip Wolski, Prafulla Dhariwal, Alec Radford, Oleg Klimov: Proximal Policy Optimization Algorithms. CoRR abs/1707.06347 (2017)). Using OpenAI's gym library (https://github.com/openai/gym) simplifies the implementation and use of the RL model.
The states are considered as the hip, foot and knee position for each leg. Assuming on the real exoskeleton there will be gyroscope or accelerometer sensors in these positions, they would serve as input data to determine the current system's states.
An action is represented by the power given to each actuator (6 in total - hip, foot, knee on each leg). On the real exoskeleton, these actuators would be placed in the same positions (hip, foot, knee).
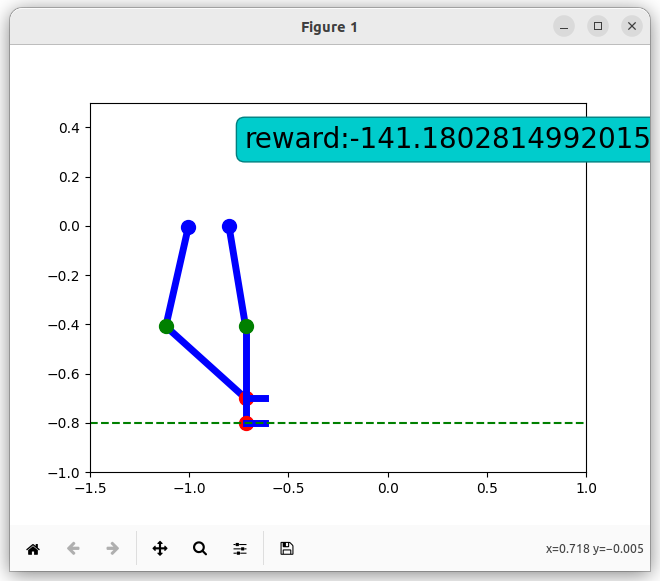
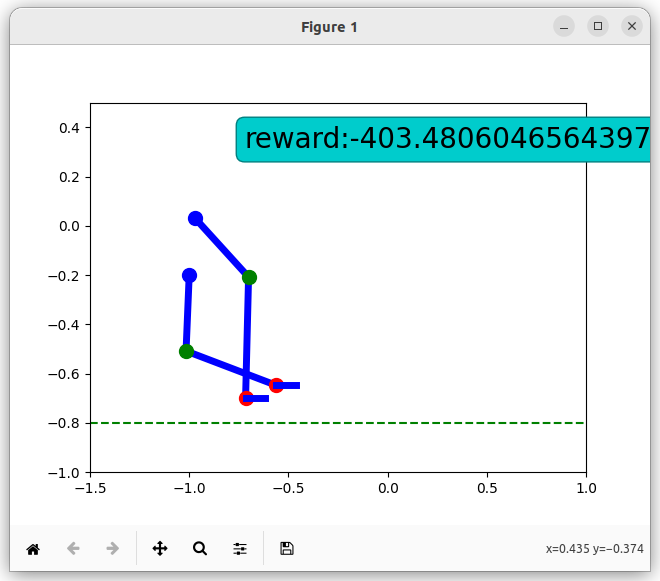
There is a complex reward system defined for the simulation of the exoskeleton. Negative rewards are awarded each time the position of the exoskeleton would cause it to fall. This can happen for a various reasons (e.g hips are not on the same level, the knee/knees are too high above ground etc).
Also, the correct position of the joints should be maintained, therefore a negative reward is given each time a joint is inversed or in a wrong position. At each step, one foot should be on the ground, so this also influences the rewards.
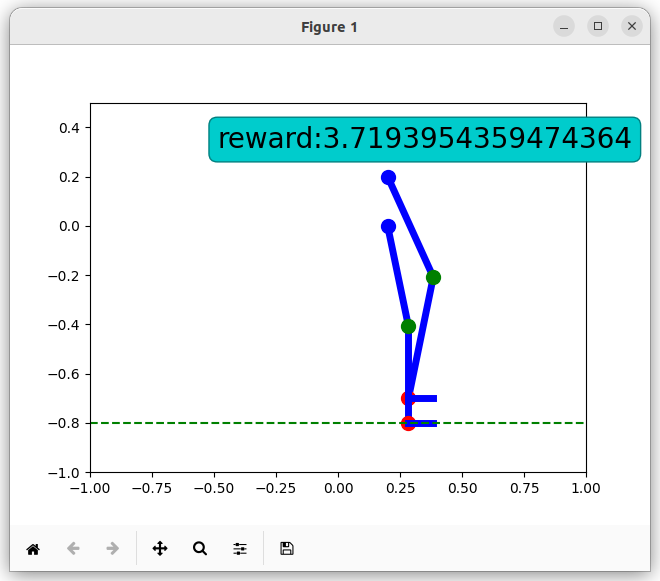
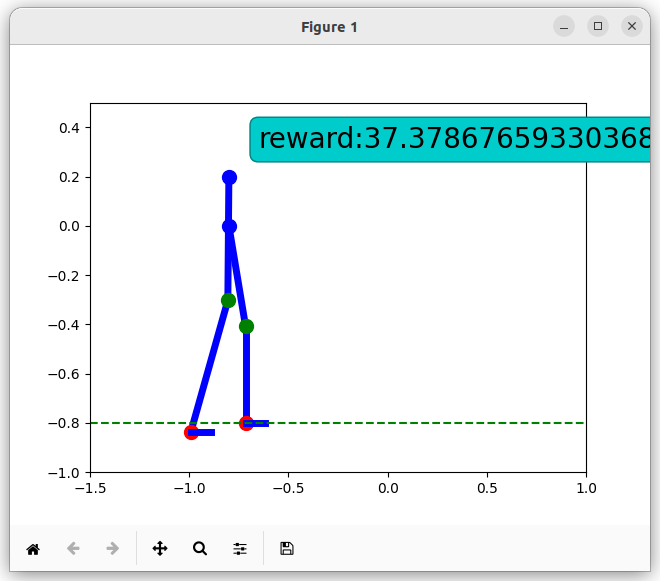
The agent receives positive rewards each time the joints are in the correct position, one foot is on the ground and the exoskeleton is balanced. It also receives additional rewards if it moves forward.
Example of states with positive rewards:
Example of negative rewards: