Library for manipulating International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA) pronunciations.
Features include:
- Getting the category and details of a phone, e.g. "open front unrounded vowel" for ɶ
- Splitting IPA pronunciations into groups of:
- Phones (
/ˈt͡ʃuːz/toˈt͡ʃ uː z) - Phonemes (
/kˈaʊ/tok ˈaʊfor U.S. English)
- Phones (
- Converting pronunciations between:
Supported Languages:
- U.S. English (
en-us) - U.K. English (
en-gb) - Dutch (
nl) - Czech (
cs-cz) - Italian (
it-it) - German (
de-de) - French (
fr-fr) - Spanish (
es-es) - Russian (
ru-ru)
$ pip install gruut-ipa- Python 3.7 or higher
For command-line usage, you may also want:
Install these with:
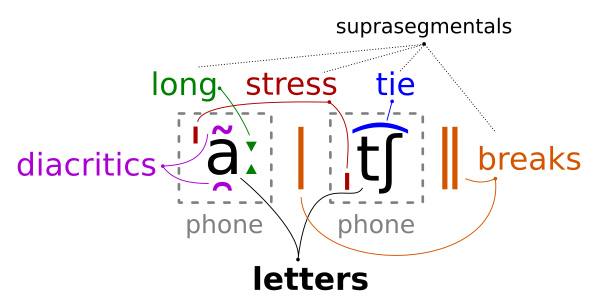
$ sudo apt-get install espeak jqPhones in IPA are composed of different components:
- Letters
- Non-combining Unicode characters that represent a distinct human sound (phone)
- Suprasegmentals
- Non-combining Unicode characters that represent language features above individual vowels or consonants
- Stress (ˈˌ), elongation (ː), linking/ties (t͡s), and short/long breaks (| ‖) are suprasegmentals
- Diacritics
- Combining characters that provide additional information about a phone's pronunciation, such as nasalation
See IPA Chart for more details.
While phones represent individual sounds, phonemes are the phonetic units of a language that meaningfully distinguish words. A phoneme may be realized by many different phones. For example, the /r/ in Standard German can be realized as a uvular fricative (χ/ʁ), a uvular approximant (ɹ), or a uvular tap or trill (ʀ/r).
A phoneme may also be composed of multiple phones, such as the dipthong aʊ in U.S. English (the "ow" in "cow").
Supported languages in gruut-ipa contain a phonemes.txt file in the gruut_ipa/data directory. This file has the following format:
<phoneme> <example> [<replace> ...]
where <phoneme> is a set of IPA letters, like ɶ or aʊ. The <example> is a word whose pronunciation contains the <phoneme>. After that, there are one or more optional <replace> strings that will be replaced with <phoneme>. The German /r/ example from above might be represented as:
r brot χ ʁ ɹ ʀ
Phonemes for a given language come from phonological analyses and from public databases. Ultimately, they are geared towards capturing pronunciations from Wiktionary.
Print JSON information about phones:
$ python3 -m gruut_ipa describe "ˈãː" | jq .
{
"text": "ˈãː",
"letters": "a",
"stress": "primary",
"height": "open",
"placement": "front",
"rounded": false,
"type": "Vowel",
"nasalated": true,
"elongated": true
}Split an IPA pronunciation into phones:
$ python3 -m gruut_ipa phones "ˈjɛs|ˈt͡ʃuːz aɪpiːeɪ‖"
ˈj ɛ s | ˈt͡ʃ uː z a ɪ p iː e ɪ ‖Group phones into phonemes for a specific language:
$ python3 -m gruut_ipa phonemes en-us "/dʒʌst ə kaʊ/"
d͡ʒ ʌ s t ə k aʊConvert between IPA, espeak, and sampa:
$ python3 -m gruut_ipa convert ipa espeak "/mʊmˈbaɪ/"
[[mUm'baI]]
$ python3 -m gruut_ipa convert espeak ipa "[[D,Is Iz sVm f@n'EtIk t'Ekst 'InpUt]]"
ðˌɪs ɪz sʌm fɘnˈɛtɪk tˈɛkst ˈɪnpʊtChain commands together:
$ python3 -m gruut_ipa convert espeak ipa "[[k'aU]]" | \
python3 -m gruut_ipa phonemes en-us --keep-stress
k ˈaʊUse the speak-ipa script to have espeak pronounce IPA. You may need to apt-get install espeak first.
$ echo '/hɛloʊ wɝld/' | bin/speak-ipa en-us -s 60 -w 'hello world.wav'
$ aplay 'hello world.wav'Supported IPA phones can be printed with:
$ python3 -m gruut_ipa print
{"text": "i", "letters": "i", "stress": "none", "height": "close", "placement": "front", "rounded": false, "type": "Vowel", "nasalated": false, "elongated": false, "description": "close front unrounded vowel", "espeak": "i", "sampa": "i"}
{"text": "y", "letters": "y", "stress": "none", "height": "close", "placement": "front", "rounded": true, "type": "Vowel", "nasalated": false, "elongated": false, "description": "close front rounded vowel", "espeak": "y", "sampa": "y"}
...A nice table can be generated with jq:
$ python3 -m gruut_ipa print | \
jq -r '. | "\(.text)\t\(.espeak)\t\(.sampa)\t\(.description)"'Converted to Markdown:
| IPA | eSpeak | Sampa | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| i | i | i | close front unrounded vowel |
| y | y | y | close front rounded vowel |
| ɨ | i" | 1 | close central unrounded vowel |
| ʉ | u" | } | close central rounded vowel |
| ɯ | u- | M | close back unrounded vowel |
| u | u | u | close back rounded vowel |
| ɪ | I | I | near-close near-front unrounded vowel |
| ʏ | I. | Y | near-close near-front rounded vowel |
| ʊ | U | U | near-close near-back rounded vowel |
| e | e | e | close-mid front unrounded vowel |
| ø | Y | 2 | close-mid front rounded vowel |
| ɘ | @ | @\ | close-mid central unrounded vowel |
| ɵ | @. | 8 | close-mid central rounded vowel |
| ɤ | o- | 7 | close-mid back unrounded vowel |
| o | o | o | close-mid back rounded vowel |
| ɛ | E | E | open-mid front unrounded vowel |
| œ | W | 9 | open-mid front rounded vowel |
| ɜ | V" | 3 | open-mid central unrounded vowel |
| ɞ | O" | 3\ | open-mid central rounded vowel |
| ʌ | V | V | open-mid back unrounded vowel |
| ɔ | O | O | open-mid back rounded vowel |
| æ | a | { | near-open front unrounded vowel |
| ɐ | V | 6 | near-open central unrounded vowel |
| a | a | a | open front unrounded vowel |
| ɶ | W | & | open front rounded vowel |
| ɑ | A | A | open back unrounded vowel |
| ɒ | A. | Q | open back rounded vowel |
| m | m | m | voiced bilabial nasal |
| ɱ | M | F | voiced labio-dental nasal |
| n | n | n | voiced alveolar nasal |
| ɳ | n. | n` | voiced retroflex nasal |
| ŋ | N | N | voiced velar nasal |
| ɴ | n" | N\ | voiced uvular nasal |
| p | p | p | voiceless bilabial plosive |
| b | b | b | voiced bilabial plosive |
| t | t | t | voiceless alveolar plosive |
| d | d | d | voiced alveolar plosive |
| ʈ | t. | t` | voiceless retroflex plosive |
| ɖ | d. | d` | voiced retroflex plosive |
| c | c | c | voiceless palatal plosive |
| ɟ | J | J\ | voiced palatal plosive |
| k | k | k | voiceless velar plosive |
| ɡ | g | g | voiced velar plosive |
| g | g | g | voiced velar plosive |
| q | q | q | voiceless uvular plosive |
| ɢ | G | G\ | voiced uvular plosive |
| ʡ | >\ | voiceless pharyngeal plosive | |
| ʔ | ? | ? | voiceless glottal plosive |
| p͡f | pf | pf | voiceless labio-dental affricate |
| b͡v | bv | bv | voiced dental affricate |
| t̪͡s | ts | t_ds | voiceless dental affricate |
| t͡s | ts | ts | voiceless alveolar affricate |
| d͡z | dz | dz | voiced alveolar affricate |
| t͡ʃ | tS | tS | voiceless post-alveolar affricate |
| d͡ʒ | dZ | dZ | voiced post-alveolar affricate |
| ʈ͡ʂ | tS | ts` | voiceless retroflex affricate |
| ɖ͡ʐ | dz | dz` | voiced retroflex affricate |
| t͡ɕ | tS; | ts\ | voiceless palatal affricate |
| d͡ʑ | dZ; | dz\ | voiced palatal affricate |
| k͡x | k | k_x | voiceless velar affricate |
| ɸ | F | p\ | voiceless bilabial fricative |
| β | B | B | voiced bilabial fricative |
| f | f | f | voiceless labio-dental fricative |
| v | v | v | voiced labio-dental fricative |
| θ | T | T | voiceless dental fricative |
| ð | D | D | voiced dental fricative |
| s | s | s | voiceless alveolar fricative |
| z | z | z | voiced alveolar fricative |
| ʃ | S | S | voiceless post-alveolar fricative |
| ʒ | Z | Z | voiced post-alveolar fricative |
| ʂ | s. | s` | voiceless retroflex fricative |
| ʐ | z. | z` | voiced palatal fricative |
| ç | C | C | voiceless palatal fricative |
| x | x | x | voiceless velar fricative |
| ɣ | Q | G | voiced velar fricative |
| χ | X | X | voiceless uvular fricative |
| ʁ | g" | R | voiced uvular fricative |
| ħ | H | X\ | voiceless pharyngeal fricative |
| h | h | h | voiceless glottal fricative |
| ɦ | h<?> | h\ | voiced glottal fricative |
| w | w | w | voiced bilabial approximant |
| ʋ | v# | v\ | voiced labio-dental approximant |
| ɹ | r | r\ | voiced alveolar approximant |
| ɻ | r. | r\` | voiced retroflex approximant |
| j | j | j | voiced palatal approximant |
| ɰ | Q | M\ | voiced velar approximant |
| ⱱ | ⱱ | ⱱ | voiced labio-dental flap |
| ɾ | * | 4 | voiced alveolar flap |
| ɽ | *. | r` | voiced retroflex flap |
| ʙ | b | B\ | voiced bilabial trill |
| r | r | r | voiced alveolar trill |
| ʀ | r" | R\ | voiced uvular trill |
| l | l | l | voiced alveolar lateral-approximant |
| ɫ | l | 5 | voiced alveolar lateral-approximant |
| ɭ | l. | l` | voiced retroflex lateral-approximant |
| ʎ | l^ | L | voiced palatal lateral-approximant |
| ʟ | L | L\ | voiced velar lateral-approximant |
| ə | @ | @ | schwa |
| ɚ | 3 | @` | r-coloured schwa |
| ɝ | 3 | @` | r-coloured schwa |
| ɹ̩ | r- | r\̩ | voiced alveolar approximant |
If you see anything wrong or missing, please let me know.