Version 0.1
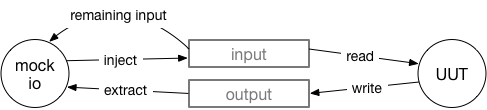
A simple mock of the Erlang I/O protocol, to allow unit testing code that performs I/O operations (io:fwrite, io:fread, file:read, file:write, ...).
By default, it mocks the standard_io device by manipulating the group leader, but you can mock any device/file.
Focuses on simplicity and allowing painless mocking of I/O, not on performance.
Usable, but still beta code. Missing functionalities and API might change without attempting to maintain backward compatibility as long as the version is 0.x.
Please, before proposing a PR, open a ticket to discuss the use case. Once agreed upon, please focus on simplicity and provide full test coverage.
UUT:
-module(uut).
write_to_stdout() ->
io:fwrite("~p ~p ~s~n", [1, a, "ciao"]).EUnit test:
capture_stdout_test() ->
{IO, GL} = mock_io:setup(),
uut:write_to_stdout(),
?assertEqual(<<"1 a ciao\n">>, mock_io:extract(IO)),
mock_io:teardown({IO, GL}).UUT:
-module(uut).
read_from_stdin() ->
io:get_line("prompt").EUnit test:
inject_to_stdin_test() ->
{IO, GL} = mock_io:setup(),
mock_io:inject(IO, <<"pizza pazza puzza\n">>),
?assertEqual("pizza pazza puzza\n", uut:read_from_stdin()),
?assertEqual(<<>>, mock_io:remaining_input(IO)),
mock_io:teardown({IO, GL}).See also the first tests in mock_io_test.erl that show how to use mock_io from the point of view of a client.
Q: Why the examples perform the setup/teardown themselves instead of using a EUnit fixture?
A: Because EUnit performs tricks on the group leader to be able to capture the output of the UUT, and this somehow breaks mock_io if we put setup/teardown in a fixture :-( Solving this will probably require to change EUnit code, patches are more than welcome!
- I would love to see
mock_iobeing part of EUnit, and also be usable transparently from Common Test.
Uses semantic versioning.
-spec extract(IO :: pid()) -> Bin :: binary().Extract everything that has been written by the UUT to the output channel
captured by the mock IO and return it as Bin.
-spec inject(IO :: pid(), Bin :: binary()) -> ok.Inject Bin into the input channel that is mocked for UUT by mock IO.
-spec remaining_input(IO :: pid()) -> binary().Return a copy of what is still available in the input channel of mock IO.
-spec start_link() -> IO :: pid().Start-link a new mock_io and return its pid IO. If used as-is (as
opposed to call setup/1), you must pass IO to the UUT (dependency
injection). Often this is not the right function to use; use setup/0
instead.
-spec stop(IO :: pid()) -> ok.Stop synchronously mock_io IO. Use this function only if you called
start_link/0 directly.
-spec setup() -> {IO :: pid(), GL :: pid()}.Start-link a new mock_io and replace the current group leader. This allows
to intercept all I/O done by the UUT either implicitly (e.g.
io:fwrite(Fmt, Args)) or by using the default IO server standard_io
(e.g. io:fwrite(standard_io, Fmt, Args)).
Return tuple {IO, GL} containing the mock_io IO and the old group leader
GL. Normally you can treat GL as opaque. When done with the test, you
have to call teardown/2.
-spec teardown({IO :: pid(), GL :: pid()}) -> ok.Stop synchronously mock_io IO and reset the current group leader to GL,
the one we found when starting the test.