IO - The public services app
The mobile app of the Digital Citizenship project
- FAQ
- Main technologies used
- Architecture
- How to contribute
- Pre-requisites
- Building and launching on the simulator
- Build (release)
- Installation on physical devices (development)
- Development with Backend App and Local Test IDP
- Development with IO dev local server
- Update the app icons
- Internationalization
- Error handling
- Connection monitoring
- Deep linking
- Fonts
- Vector graphics
- Io-Icon-Font (
⚠️ deprecated) - Theming (⚠️ deprecated)
- Custom UI components (
⚠️ deprecated) - End to end test
- Troubleshooting
FAQ
What is the Digital Citizenship project?
Digital Citizenship aims at bringing citizens to the center of the Italian public administrations services.
The project comprises two main components:
- a platform made of elements that enable the development of citizen-centric digital services;
- an interface for citizens to manage their data and their digital citizen profiles.
What is the Digital Citizenship mobile app?
The Digital Citizenship mobile app is a native mobile application for iOS and Android with a dual purpose:
- To be an interface for citizens to manage their data and their digital citizen profile;
- To act as reference implementation of the integrations with the Digital Citizenship platform.
Who develops the app?
The development of the app is carried out by several contributors:
- the Digital Transformation Team
- volunteers who support the project.
Can I use the app?
Sure! However you will need a SPID account or have a CIE to login to the app.
How can I help you?
Reporting bugs, bug fixes, translations and generally any improvement is welcome! Send us a Pull Request!
If you have some time to spare and wish to get involved on a regular basis, contact us.
What permissions are used by the IO app?
Because different platforms have different types of Permissions below we have two sections about permissions requested by the IO app for both environments (iOS and Android). Some permissions may be defined but not used. Their presence is due to dependencies with third-party modules or because they are required by the target store.
android
| Permission (android.permission.*) | Usage / Meaning |
|---|---|
| INTERNET | Allows applications to open network sockets (e.g. simple internet connectivity) |
| ACCESS_NETWORK_STATE | Allows applications to access information about networks (e.g. details about connection quality/state) |
| ACCESS_WIFI_STATE | Allows applications to access information about WIFI state |
| CAMERA | Allows applications to access device camera to scan QR codes |
| FOREGROUND_SERVICE | Allows applications to use foreground service |
| MODIFY_AUDIO_SETTINGS | Allows an application to modify global audio settings. Related to camera usage. |
| NFC | Allows applications to perform I/O operations over NFC |
| RECEIVE_BOOT_COMPLETED | Allows an application to receive the Intent.ACTION_BOOT_COMPLETED that is broadcast after the system finishes booting. Used for push notification. |
| VIBRATE | Allows access to the vibrator. This allow the application to emit vibration |
| WAKE_LOCK | Allows using PowerManager WakeLocks to keep processor from sleeping or screen from dimming. Used for push notification. |
| READ_APP_BADGE | Notification Badges that show on app icons |
| READ_CALENDAR | Allows an application to read the user's calendar data |
| WRITE_CALENDAR | Allows an application to write the user's calendar data. Used to automatically set reminders. |
| READ_EXTERNAL_STORAGE | Allows an application to read from external storage. Used to pick images from gallery with payment QRCode. |
| WRITE_EXTERNAL_STORAGE | Allows an application to write to external storage. Used to store images, e.g.: save bonus information (QRCode for Bonus Vacanze or EuCovid Certificate, etc.) |
| USE_FINGERPRINT | Allows an app to use fingerprint hardware for biometric identification required from API level 23 until API level 28 |
| USE_BIOMETRIC | Allows an app to use device's available biometric identification system (Face unlock, Iris unlock, Fingerprint) required from API Level 28 |
Below there are the permissions required by the main android hardware manufacturers. Mainly used to manage notification badge icons.
| Permission (manufacturer) | Usage / Meaning |
|---|---|
| com.anddoes.launcher.permission.UPDATE_COUNT | used for the notification badge |
| com.google.android.c2dm.permission.RECEIVE | It is used when receiving a broadcast from GCM server that contains a GCM message. Used for push notification. |
| com.google.android.finsky.permission.BIND_GET_INSTALL_REFERRER_SERVICE | It is used by Firebase to recognize where the app was installed from |
| com.htc.launcher.permission.READ_SETTINGS | Used for the notification badge. Specific for HTC vendor. |
| com.htc.launcher.permission.UPDATE_SHORTCUT | used for the notification badge |
| com.huawei.android.launcher.permission.CHANGE_BADGE | Used for the notification badge. Specific for Huawei vendor. |
| com.huawei.android.launcher.permission.READ_SETTINGS | used for the notification badge |
| com.huawei.android.launcher.permission.WRITE_SETTINGS | used for the notification badge |
| com.majeur.launcher.permission.UPDATE_BADGE | used for the notification badge |
| com.oppo.launcher.permission.READ_SETTINGS | used for the notification badge |
| com.oppo.launcher.permission.WRITE_SETTINGS | used for the notification badge |
| com.sec.android.provider.badge.permission.READ | used for the notification badge |
| com.sec.android.provider.badge.permission.WRITE | used for the notification badge |
| com.sonyericsson.home.permission.BROADCAST_BADGE | used for the notification badge |
| com.sonymobile.home.permission.PROVIDER_INSERT_BADGE | used for the notification badge |
| me.everything.badger.permission.BADGE_COUNT_READ | used for the notification badge |
| me.everything.badger.permission.BADGE_COUNT_WRITE | used for the notification badge |
ios (more info about permissions requested by Apple here)
| Permission | Usage / Meaning |
|---|---|
| NSAppleMusicUsageDescription | This key is required if your app uses APIs that access the user’s media library. |
| NSBluetoothAlwaysUsageDescription | This key is required if your app uses the device’s Bluetooth interface. |
| NSBluetoothPeripheralUsageDescription | This key is required if your app uses APIs that access Bluetooth peripherals and has a deployment target earlier than iOS 13. |
| NSContactsUsageDescription | IO needs access to your contacts to let you add them in calendar events. |
| NSLocationAlwaysUsageDescription | This key is required if your iOS app uses APIs that access the user’s location at all times and deploys to targets earlier than iOS 11. |
| NSLocationUsageDescription | This key is required if your app uses APIs that access the user’s location information. |
| NSLocationWhenInUseUsageDescription | This key is required if your iOS app uses APIs that access the user’s location information while the app is in use. |
| NSMicrophoneUsageDescription | IO needs access to the microphone in case you want to leave a voice note. Used in the assistance flow. |
| NSMotionUsageDescription | This key is required if your app uses APIs that access the device’s motion data. |
| NSCalendarsUsageDescription | IO needs access to the calendar to add event reminders. |
| NSCameraUsageDescription | IO needs access to the camera to scan QR codes. |
| NSFaceIDUsageDescription | Enable Face ID for biometric identification. |
| NSPhotoLibraryAddUsageDescription | This key is required if your app uses APIs that have write access to the user’s photo library. |
| NSPhotoLibraryUsageDescription | IO needs access to the Photos to scan QR codes. |
| NSSpeechRecognitionUsageDescription | This key is required if your app uses APIs that send user data to Apple’s speech recognition servers. Used in the assistance flow. |
| Remote Notification | Request permission to receive remote push notification. |
| NFC (Near Field Communication Tag Reading) | Request NFC capability. |
Main technologies used
Architecture
SPID Authentication
The application relies on a backend for the authentication through SPID (the Public System for Digital Identity) and for interacting with the other components and APIs that are part of the digital citizenship project.
The backend implements a SAML2 Service Provider that deals with user authentication with the SPID Identity Providers (IdP).
The authentication between the application and the backend takes place via a session token, generated by the backend at the time of the authentication with the SPID IdP.
Once the backend communicates the session token to the application, it is used for all subsequent calls that the application makes to the API exposed by the backend.
The authentication flow is as follows:
- The user selects the IdP;
- The app opens a webview on the SAML SP authentication endpoint implemented in the backend, which specifies: the entity ID of the IdP selected by the user and, as returns URL, the URL of the endpoint that generates a new session token.
- The SAML SP logic takes over the authentication process by redirecting the user to the chosen IdP.
- After the authentication, a redirect is made from the IdP to the backend endpoint that deals with the generation of a new session token.
- The endpoint that generates a new token receives the SPID attributes via the HTTP header; then, it generates a new random session token and returns to the webview an HTTP redirect to an URL well-known containing the session token.
- The app, which monitors the webview, intercepts this URL before the HTTP request is made, extracts the session token and ends the authentication flow by closing the webview.
- Next, the session token is used by the app to make calls to the backend API.
How to contribute
In the following there are instructions to build the app in your computer for development purposes.
Pre-requisites
You need a recent macOS, Linux or Windows 10 based computer, and a Unix based development environment. On macOS and Linux this environment is available in the base install, while on Windows you need to install WSL, the Windows Subsystem for Linux.
The following instructions have been tested on a macOS running Mojave, on Linux Ubuntu 18.04 and on Windows with Ubuntu 18.04 installed with WSL. The described procedure assume you are using the bash shell; they may work with other shells but you may need to tweak the configuration for your shell. In the following when we will refer to Linux we also mean Windows with WSL.
Install NodeJS and Ruby
To run the project you need to install the correct version of NodeJS and Ruby.
On macOS and Linux we recommend the use of a virtual environment, such as nodenv for NodeJS, rbenv for Ruby or asdf which can manage both of them under its virtual environment.
The node version used in this project is stored in .node-version, while the version of Ruby is stored in .ruby-version.
If you already have nodenv or rbenv installed and configured on your system, the correct version node will be set when you access the app directory.
Please ensure that you are running the correct versions before working on the project.
Install yarn
For the management of javascript dependencies we use Yarn.
You can install it as a global command with:
npm install -g yarn
Remember to set the correct version of Node in advance as suggested above.
Install bundler and cocoapods
Some dependencies are installed via bundler and cocoapods
Note that on Linux you do not need CocoaPods as you can only build for Android.
Bundler is a Ruby application. If you have installed a version of Ruby in your system you can use it to install the required tools with:
sudo gem install bundler:2.0.2
In some version of Linux you may not have Ruby installed. In some versions of macOS, bundler is not able to install the dependencies because the ruby provided by the system is not complete enough.
In those cases, you need to install the bundler using the ruby installed by asdf using the following procedure.
cd <work-dir>/io-app
asdf global ruby 2.7.4
gem install bundler:2.0.2
Verify it was installed correctly with the command which bundle. It should show the installation path of the command.
Only for macOS - install cocoapods
Then install cocoapods, also in this case you can use Ruby to install it:
sudo gem install cocoapods
React Native
Follow the tutorial Setting up the development environment and install React Native CLI for your operating system.
If you have a macOS system, you can follow both the tutorial for iOS and for Android. If you have a Linux or Windows system, you need only to install the development environment for Android.
Building and launching on the simulator
App build configuration
As a first step, if you want to run the app in production mode, set the production configuration.
$ cp .env.production .env
You need to edit it to match your environment. Here is a still NOT complete table of the environment variables you can set (check the comments in the file for more informations)ç
| NAME | DEFAULT | |
|---|---|---|
DEBUG_BIOMETRIC_IDENTIFICATION |
NO | If set to "YES" an Alert is rendered with the exact result code of the biometric identification. |
TOT_MESSAGE_FETCH_WORKERS |
5 | Number of workers to create for message detail fetching. This means that we will have at most a number of concurrent fetches (of the message detail) equal to the number of the workers. |
Note: The sample configuration sets the app to interface with our test environment, on which we work continuously; therefore, it may occur that some features are not always available or are fully working.
Dependencies
Note that IO uses a react native module to allow authentication through CIE (Carta di Identità Elettronica).
You can install the libraries used by the project:
$ bundle install
$ yarn install
$ cd ios # skip on linux
$ pod install # skip on linux
Generating API definitions and translations
Finally, generate the definitions from the OpenAPI specs and from the YAML translations:
$ yarn generate
Installation on the simulator
On Android (the device simulator must be launched manually):
# Perform the port forwarding
$ adb reverse tcp:8081 tcp:8081;adb reverse tcp:3000 tcp:3000;adb reverse tcp:9090 tcp:9090
$ react-native run-android
On iOS (the simulator will be launched automatically):
$ yarn run-ios
Note: the app uses CocoaPods, the project to run is therefore ItaliaApp.xcworkspace instead of ItaliaApp.xcodeproj (run-ios will automatically detect it).
Build (release)
For the release of the app on the stores we use Fastlane.
iOS
The beta distribution is done with TestFlight.
To release a new beta:
$ cd ios
$ bundle exec fastlane testflight_beta
Android
To release a new alpha:
$ bundle exec fastlane alpha
Note: the alpha releases on Android are automatically carried by the alpha-release-android job on circleci on each by merge to the master branch.
Installation on physical devices (development)
iOS
For this step you’ll need to have a proper iOS development certificate on your dev machine that is also installed on your physical device.
To test the io-app on a real iOS device you must:
- Open the project with Xcode and modify the bundle identifier (eg: add ‘.test’ to the existing one)
- Go to the 'Build Settings' tab and in the PROVISIONING_PROFILE section delete the existing ID. Then select 'ios developer' in the debug field of the 'Code Signing Identity'
- In General tab select the 'Automatically Menage Signing' checkbox
- You must have an Apple id developer and select it from the 'Team' drop-down menu
- (Without Xcode) navigate in the io-app project and open the package.json file, in the scripts section add: "build: ios": "react-native bundle --entry-file = 'index.js' - bundle-output = '. / ios / main.jsbundle' --dev = false --platform = 'ios' "
- Open the Terminal and from the root directory project run npm run build: ios
- In Xcode navigate in the project, select 'main.jsbundle' and enable the checkbox on the right labeled 'ItaliaApp'
- Always in Xcode select 'Product' -> 'Clean Build Folder'
- On the real device connected, accept to trust the device
- From Xcode select the device by the drop-down list and run ('Product' -> 'Run') on the iOS device, if the unit tests fail they can be disabled by going to Product -> Scheme -> Edit Scheme -> Build
Development with Backend App and Local Test IDP
To develop the application on your machine using the Backend App and an IDP test, you need to follow some additional steps as described below.
If you prefer a light way to run IO app backend, you should consider using io-dev-api-server. This local server mocks almost totally IO backend behaviours and APIs. Note: about SPID, io-dev-api-server acts a pass throught so you can't test it.
App Backend and test IDP installation
Follow the documentation of the repository italia-backend.
WebView, HTTPS and self-signed certificates
At the moment, react-native does not allow to open WebView on HTTPS url with a self-signed certificate. However, the test IDP uses HTTPS and a self-signed certificate. To avoid this problem, it is possible to locally install a Proxy that acts as a proxy-pass to the Backend App and the IDP.
Installation of mitmproxy
Mitmproxy is a simple proxy to use and is also suitable for our purpose. For installation, follow the documentation page on the official website.
The script scripts/mitmproxy_metro_bundler.py allows the proxy to intercept requests to the Simulator and, only in
case of specific ports, to proxy the localhost. Start the proxy with the following command:
SIMULATOR_HOST_IP=XXXXX mitmweb --listen-port 9060 --web-port 9061 --ssl-insecure -s scripts/mitmproxy_metro_bundler.py
Add in place of XXXXX:
10.0.2.2(Standard Android Emulator)10.0.3.2(Genymotion Android Emulator)
Installing the mitmproxy certificate within the emulator Android
Install certificate mitmproxy within the emulator following the official guide.
Set the proxy for the connection in the Android emulator
In the connection configuration enter:
- Proxy IP:
10.0.2.2(or10.0.3.2if you use Genymotion) - Proxy port:
9060
Development with IO dev local server
It is super easy to setup and run. Here you can find all instructions.
It can be used as it is, or you can run it using the docker image.
.env.local is included in IO app files. It is a pre-filled config file ready to use with the local server.
To use it, just run these commands:
cp .env.local .env && yarn postinstall
Update the app icons
Follow this tutorial.
Internationalization
For multi-language support the application uses:
- react-native-i18n for the integration of translations with user preferences
- YAML files in the directory
locales - A YAML-to-typescript conversion script (
generate:locales).
To add a new language you must:
- Clone the repository
- Create a new directory under locales using the language code as the name (e.g.
esfor Spanish,defor German, etc...). - Copy the content from the base language locales/en(
en). - Proceed with the translation by editing the YAML and Markdown files.
- if is a YAML file (
*.yml) translate only the text following the colon (e.g.today:"today"become in italiantoday:"oggi"). - if is a Mardown file (
*.md) translate the text leaving the formatting as is.
- if is a YAML file (
- Check that the command:
npm run generate:locales(oryarn generate:locales) returns a success message. - Create a PR using as title
Internationalization {New Language}(e.g.Internationalization Italiano)and apply the labelinternationalization.
If you want to see the result in the app you must:
-
Run the command:
npm run generate:locales. -
Edit the file ts/i18n.ts by adding the new language in the variable
I18n.translations.E.g. for German
I18n.translations = { en: locales.localeEN, it: locales.localeIT };become
I18n.translations = { en: locales.localeEN, it: locales.localeIT de: locales.localeDE };
Error handling
The application uses a custom handler to intercept and notify javascript errors caused by unhandled exceptions. The custom handler code is visible in the file ts/utils/configureErrorHandler.ts
Connection monitoring
The application uses the library react-native-offline to monitor the connection status. In case of no connection, a bar is displayed that notifies the user.
The connection status is kept inside the Redux store in the variable state.network.isConnected, you can use this data to disable some functions during the absence of the connection.
Deep linking
The application is able to manage deep links. The URL scheme is: ioit://. The link format is ioit://<route-name>.
Fonts
The application uses the font Titillium Web. Fonts are handled differently than Android and iOS. To use the font, TitilliumWeb-SemiBoldItalic example, you must apply the following properties for Android:
{
fontFamily: 'TitilliumWeb-SemiBoldItalic'
}while in iOS the code to be applied is:
{
fontFamily: 'Titillium Web',
fontWeight: '600',
fontStyle: 'italic'
}To manage fonts and variants more easily, we have created utility functions within the file ts/theme/fonts.ts.
Vector graphics
Most of the images used in the app can be rendered as vector assets using SVG image format. Currently we have these groups:
- Pictograms: assets with an intended size greather than
56px - Icons: assets with an intended size between
16pxand56px - Logos
Once you understand which group you must put the asset in, you must take into consideration the following instructions for the best result in terms of quality and future maintenance:
- In your user interface design app (Figma/Sketch) make the vector path as simple as possible:
- Detach the symbol instance to avoid destructive actions to the original source component. Feel free to use a draft or disposable project document.
- Outline all the present strokes (unless required for dynamic stroke width, but we don't manage this case at the moment)
- Select all the different paths and flatten into one. Now you should have a single vector layer.
- Make sure your vector path is centered (both vertically and horizontally) in a square
- Export your SVG with
1×preset - Delete
widthandheightattributes and leave the originalviewBoxattribute. You could easily process the image using online editors like SVGOmg (enablePrefer viewBox to width/height) - To easily preview the available SVG assets, include the original SVG in the
originalssubfolder with the same filename of your corresponding React component. - If your asset is part of one of the subset, make sure to use the same prefix of the corresponding set. E.g: If you want to add a new pictogram related to a section, you should use the
PictogramSection…prefix. - Copy all the
<path>elements into a new React component and replace the original<path>with the element<Path>(capital P) from thereact-native-svgpackage. Replace all the harcoded fill values with the genericcurrentColorvalue. - Add the dynamic size and colour (if required), replacing the hardcoded values with the corresponding props:
import { Svg, Path } from "react-native-svg";
const IconSpid = ({ size, style }: SVGIconProps) => (
<Svg width={size} height={size} viewBox="0 0 24 24" style={style}>
<Path
d="M13.615 …"
fill="currentColor"
/>
</Svg>
);Note: The icon inherit the color from the parent Svg container
-
Add the key associated to the single pictogram/icon in the corresponding set. If you want to learn more, read the contextual documentation:
-
There's no need to add the new pictogram/icon in the
Design Systemspecific page because it happens automatically.
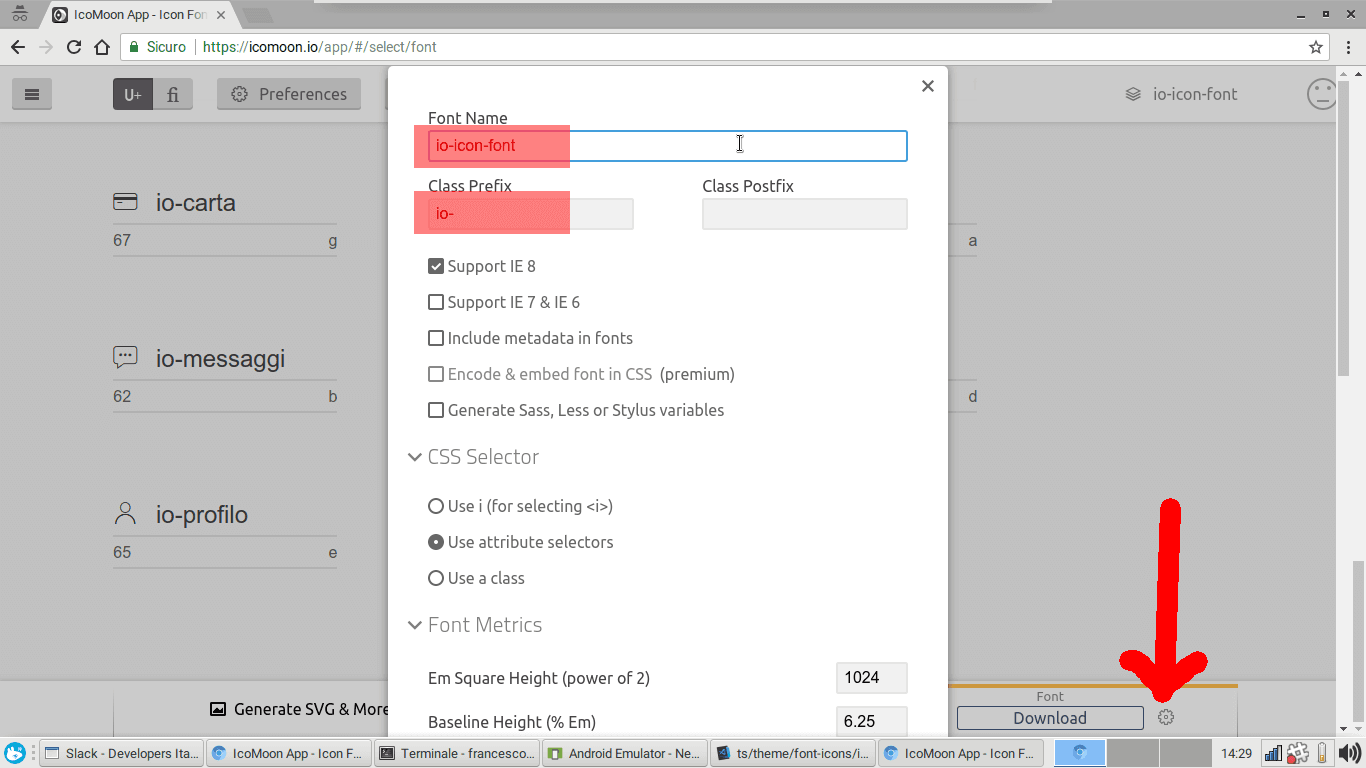
Io-Icon-Font
Note:
The application uses a custom font-icon from the name 'io-icon-font'. Thanks to the library react-native-vector-icons which is included in the project, it is possible to create new IconSets. In particular, among the various methods shown in the appropriate section of the documentation, we decided to use the one that allows to export the font through IcoMoon. When exporting from IcoMoon, you should use the configuration shown in the following picture.
To update the icon-font to a new version, it is necessary to extract and correctly position the following two files from the archive '.zip' generated by IcoMoon:
selection.jsoncontained in the archive root, to be placed in ts/theme/font-icons/io-icon-font/.io-icon-font.ttfcontained in the directory fonts archive, to be placed in assets/fonts/io-icon-font/.
Once the two files have been copied, it is necessary to update the link of the asset by installing globally and running react-native-asset (version 1.1.4):
$ yarn global add react-native-asset@2.0.0
$ react-native-asset
This last command deals in particular with copying the asset within a specific folder of the Android sub-project.
Theming
Note: ⚠️ Deprecated
The application uses native-base and its components for the graphical interface. In particular, we decided to use as a basis the theme material provided by the library. Although native-base allows to customize part of the theme through the use of variables, it was nevertheless necessary to implement ad-hoc functions that allow to go to modify the theme of the individual components.
Extending Native Base default theme
In the ts/theme directory there are some files that allow you to manage the theme in a more flexible way than what native-base permits natively.
Variables
To define new variables to use in the components theme, you need to edit the file ts/theme/variables.ts. This file deals with importing the basic variables defined by the material theme of native-base and allows to overwrite / define the value of new variables.
Components Theme
The native-base library defines the theme of each individual component in a separate .ts file that is named after the specific component. For example, the theme file related to the component Button is named Button.ts. To redefine the theme of the native-base components, it is necessary to create / modify the files in the ts/theme/components directory. Every file in this directory must export an object that defines the components theme. Take the file Content.ts as an example:
import { type Theme } from '../types'
import variables from '../variables'
export default (): Theme => {
const theme = {
padding: variables.contentPadding,
backgroundColor: variables.contentBackground
}
return theme
}In this file, you can see how two attributes are redefined (padding and backgroundColor) using the values in the relative variables. The returned object will be used in the file ts/theme/index.ts to associate it with a specific component type (in this case NativeBase.Component).
A more complex example allows you to use the advanced features of the native-base theming layer.
import { type Theme } from '../types'
import variables from '../variables'
export default (): Theme => {
const theme = {
'.spacer': {
'.large': {
height: variables.spacerLargeHeight
},
height: variables.spacerHeight
},
'.footer': {
paddingTop: variables.footerPaddingTop,
paddingLeft: variables.footerPaddingLeft,
paddingBottom: variables.footerPaddingBottom,
paddingRight: variables.footerPaddingRight,
backgroundColor: variables.footerBackground,
borderTopWidth: variables.footerShadowWidth,
borderColor: variables.footerShadowColor
}
}
return theme
}Within the theme file of a single component, it is possible to define specific attributes that will be used only if this specific component has a specific property. By defining in the theme object something like:
'.footer': {
paddingTop: variables.footerPaddingTop
}If necessary, you can use the component by associating the footer property in the following way <Component footer /> and automatically the theming system will apply to the component the defined attributes (paddingTop: variables.footerPaddingTop).
Another advanced function allows to define the theme of the child components starting from the parent component. Let's take as an example the following code fragment of a generic component:
...
render() {
return(
<Content>
<Button>
<Text>My button</Text>
</Button>
</Content>
)
}
...The native-base library allows you to define the appearance of the child component Text present in the parent Button. For example, to define the size of the text in all the buttons in the application, simply enter the following code in the file ts/theme/components/Button.ts:
import variables from '../variables'
export default (): Theme => {
const theme = {
'NativeBase.Text': {
fontSize: variables.btnTextFontSize
}
}
return theme
}You can go even further and combine the two features seen previously:
import variables from '../variables'
export default (): Theme => {
const theme = {
'.small': {
'NativeBase.Text': {
fontSize: variables.btnTextFontSize
}
}
}
return theme
}In this case, what is defined within the attribute NativeBase.Text will be used only if the button has associated a property with a name small.
Custom UI components
Note:
TextWithIcon
A simple wrapper in which you can insert an icon and a text that will be rendered side by side.
Example of use:
<TextWithIcon danger>
<IconFont name="io-back" />
<Text>{I18n.t('onboarding.pin.confirmInvalid')}</Text>
</TextWithIcon>Troubleshooting
Bundler install error
If you get an error like this Can't find gem bundler (>= 0.a) with executable bundle (Gem::GemNotFoundException) after launching bundle install you can fix it launching this gem install bundler -v "$(grep -A 1 "BUNDLED WITH" Gemfile.lock | tail -n 1)
iOS build warning
If, during the archive process, you see one or more warning like this ...RNTextInputMask.o)) was built for newer iOS version (10.3) than being linked (9.0) you can fix it in this way:
- Open the project io-app/ios with Xcode
- Select the library (es. RNTextInputMask) in 'Libraries'
- Select the name of the library under the label 'PROJECT' and change the iOS Deployment target from 10.3 to 9.0