A dynamic script engine parsing tool designed by Ali's strong requirements for e-commerce business rules, expressions (Boolean combinations), special mathematical formula calculations (high precision), syntax analysis, and secondary script customization. It has a strong influence in Alibaba Group. At the same time, in order to continuously optimize and carry forward the spirit of open source contribution, it was open sourced in 2012.
The QLExpress script engine is widely used in Ali's e-commerce business scenarios and has the following characteristics:
- Thread safety. Temporary variables generated during engine operation are all threadlocal.
- Efficient execution. The time-consuming script compilation process can be cached on the local machine. The temporary variable creation at runtime uses the technology of buffer pool, which is equivalent to groovy performance.
- Weakly typed scripting language, similar to groovy and javascript, although it is slower than strong typed scripting language, it greatly enhances business flexibility.
- Safety control, you can prevent dead loops and high-risk system api calls by setting relevant operating parameters.
- The code is streamlined and the dependency is minimal. The 250k jar package is suitable for all java operating environments, and it is also widely used in the low-end pos machines of the android system.
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>QLExpress</artifactId>
<version>3.2.0</version>
</dependency>ExpressRunner runner = new ExpressRunner();
DefaultContext<String, Object> context = new DefaultContext<String, Object>();
context.put("a",1);
context.put("b",2);
context.put("c",3);
String express = "a+b*c";
Object r = runner.execute(express, context, null, true, false);
System.out.println(r);//Support +,-,*,/,<,>,<=,>=,==,!=,<>[Equivalent to !=],%,mod[Modulo equal to%],++, --,
//in [similar to sql], like [sql syntax], &&,||,!, and other operators
//Support standard program control logic such as for, break, continue, if then else
n=10;
for(sum=0,i=0;i<n;i++){
sum=sum+i;
}
return sum;
//Logical ternary operation
a=1;
b=2;
maxnum = a>b?a:b;
- Does not support try{}catch{}
- Comments currently only support /** **/, single-line comments are not supported //
- Java8 lambda expressions are not supported
- Does not support for loop collection operation for (GRCRouteLineResultDTO item: list)
- Weakly typed languages, please do not define type declarations, let alone use Templete (Map<String,List> and the like)
- The declaration of array is different
- min, max, round, print, println, like, in are all keywords of the system default functions, please do not use them as variable names
//java syntax: use generics to remind developers to check the type
keys = new ArrayList<String>();
deviceName2Value = new HashMap<String,String>(7);
String[] deviceNames = {"ng","si","umid","ut","mac","imsi","imei"};
int[] mins = {5,30};
//ql writing:
keys = new ArrayList();
deviceName2Value = new HashMap();
deviceNames = ["ng","si","umid","ut","mac","imsi","imei"];
mins = [5,30];
//java syntax: object type declaration
FocFulfillDecisionReqDTO reqDTO = param.getReqDTO();
//ql writing:
reqDTO = param.getReqDTO();
//java syntax: array traversal
for(GRCRouteLineResultDTO item: list) {
}
//ql writing:
for(i=0;i<list.size();i++){
item = list.get(i);
}
//java syntax: map traversal
for(String key: map.keySet()) {
System.out.println(map.get(key));
}
//ql writing:
keySet = map.keySet();
objArr = keySet.toArray();
for (i=0;i<objArr.length;i++) {
key = objArr[i];
System.out.println(map.get(key));
}
import com.ql.util.express.test.OrderQuery;
//The system will automatically import java.lang.*,import java.util.*;
query = new OrderQuery();//Create a class instance, and automatically complete the class path according to the classLoader information
query.setCreateDate(new Date());//Set attributes
query.buyer = "Zhang San";//Call the attribute, it will be converted to setBuyer("Zhang San") by default
result = bizOrderDAO.query(query);//Call the method of the bean object
System.out.println(result.getId());//Static method
function add(int a,int b){
return a+b;
};
function sub(int a,int b){
return a-b;
};
a=10;
return add(a,4) + sub(a,9);
runner.addOperatorWithAlias("if", "if",null);
runner.addOperatorWithAlias("then", "then",null);
runner.addOperatorWithAlias("Otherwise", "else",null);
exp = "If (language+mathematics+English>270) then {return 1;} otherwise {return 0;}";
DefaultContext<String, Object> context = new DefaultContext<String, Object>();
runner.execute(exp,context,null,false,false,null);//Define an operator inherited from com.ql.util.express.Operator
public class JoinOperator extends Operator{
public Object executeInner(Object[] list) throws Exception {
Object opdata1 = list[0];
Object opdata2 = list[1];
if(opdata1 instanceof java.util.List){
((java.util.List)opdata1).add(opdata2);
return opdata1;
}else{
java.util.List result = new java.util.ArrayList();
result.add(opdata1);
result.add(opdata2);
return result;
}
}
}//(1)addOperator
ExpressRunner runner = new ExpressRunner();
DefaultContext<String, Object> context = new DefaultContext<String, Object>();
runner.addOperator("join",new JoinOperator());
Object r = runner.execute("1 join 2 join 3", context, null, false, false);
System.out.println(r);
//Return result [1, 2, 3]
//(2)replaceOperator
ExpressRunner runner = new ExpressRunner();
DefaultContext<String, Object> context = new DefaultContext<String, Object>();
runner.replaceOperator("+",new JoinOperator());
Object r = runner.execute("1 + 2 + 3", context, null, false, false);
System.out.println(r);
//Return result [1, 2, 3]
//(3)addFunction
ExpressRunner runner = new ExpressRunner();
DefaultContext<String, Object> context = new DefaultContext<String, Object>();
runner.addFunction("join",new JoinOperator());
Object r = runner.execute("join(1,2,3)", context, null, false, false);
System.out.println(r);
//Return result [1, 2, 3]
addFunctionOfClassMethod+addFunctionOfServiceMethod
public class BeanExample {
public static String upper(String abc) {
return abc.toUpperCase();
}
public boolean anyContains(String str, String searchStr) {
char[] s = str.toCharArray();
for (char c: s) {
if (searchStr.contains(c+"")) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}
runner.addFunctionOfClassMethod("Take the absolute value", Math.class.getName(), "abs",
new String[] {"double" }, null);
runner.addFunctionOfClassMethod("Convert to uppercase", BeanExample.class.getName(),
"upper", new String[] {"String" }, null);
runner.addFunctionOfServiceMethod("Print", System.out, "println",new String[] {"String" }, null);
runner.addFunctionOfServiceMethod("contains", new BeanExample(), "anyContains",
new Class[] {String.class, String.class }, null);
String exp = "Take the absolute value (-100); convert to uppercase (\"hello world\"); print (\"How are you?\"); contains("helloworld",\"aeiou\")";
runner.execute(exp, context, null, false, false);
runner.addMacro("Calculate average score", "(Chinese+Math+English)/3.0");
runner.addMacro("Is it excellent", "Calculate the average score>90");
IExpressContext<String, Object> context =new DefaultContext<String, Object>();
context.put("语文", 88);
context.put("Mathematics", 99);
context.put("English", 95);
Object result = runner.execute("Is it excellent", context, null, false, false);
System.out.println(r);
//Return the result true
Note the difference between the following script int and no int
String express = "int average score = (language + mathematics + English + comprehensive examination. Subject 2)/4.0; return average score";
ExpressRunner runner = new ExpressRunner(true,true);
String[] names = runner.getOutVarNames(express);
for(String s:names){
System.out.println("var: "+ s);
}
//Output result:
var: mathematics
var: Comprehensive examination
var: English
var: language
@Test
public void testMethodReplace() throws Exception {
ExpressRunner runner = new ExpressRunner();
IExpressContext<String,Object> expressContext = new DefaultContext<String,Object>();
runner.addFunctionOfServiceMethod("getTemplate", this, "getTemplate", new Class[]{Object[].class}, null);
//(1) The default indefinite parameters can be replaced by arrays
Object r = runner.execute("getTemplate([11,'22',33L,true])", expressContext, null,false, false);
System.out.println(r);
//(2) Like java, support function dynamic parameter call, you need to turn on the following global switches, otherwise the following calls will fail
DynamicParamsUtil.supportDynamicParams = true;
r = runner.execute("getTemplate(11,'22',33L,true)", expressContext, null,false, false);
System.out.println(r);
}
//Equivalent to getTemplate(Object[] params)
public Object getTemplate(Object... params) throws Exception{
String result = "";
for(Object obj:params){
result = result+obj+",";
}
return result;
}
@Test
public void testSet() throws Exception {
ExpressRunner runner = new ExpressRunner(false,false);
DefaultContext<String, Object> context = new DefaultContext<String, Object>();
String express = "abc = NewMap(1:1,2:2); return abc.get(1) + abc.get(2);";
Object r = runner.execute(express, context, null, false, false);
System.out.println(r);
express = "abc = NewList(1,2,3); return abc.get(1)+abc.get(2)";
r = runner.execute(express, context, null, false, false);
System.out.println(r);
express = "abc = [1,2,3]; return abc[1]+abc[2];";
r = runner.execute(express, context, null, false, false);
System.out.println(r);
}
In fact, the syntax is similar to java, but ql does not support the syntax of for(obj:list){} and can only be accessed through subscripts.
//Traverse the map
map = new HashMap();
map.put("a", "a_value");
map.put("b", "b_value");
keySet = map.keySet();
objArr = keySet.toArray();
for (i=0;i<objArr.length;i++) {
key = objArr[i];
System.out.println(map.get(key));
}
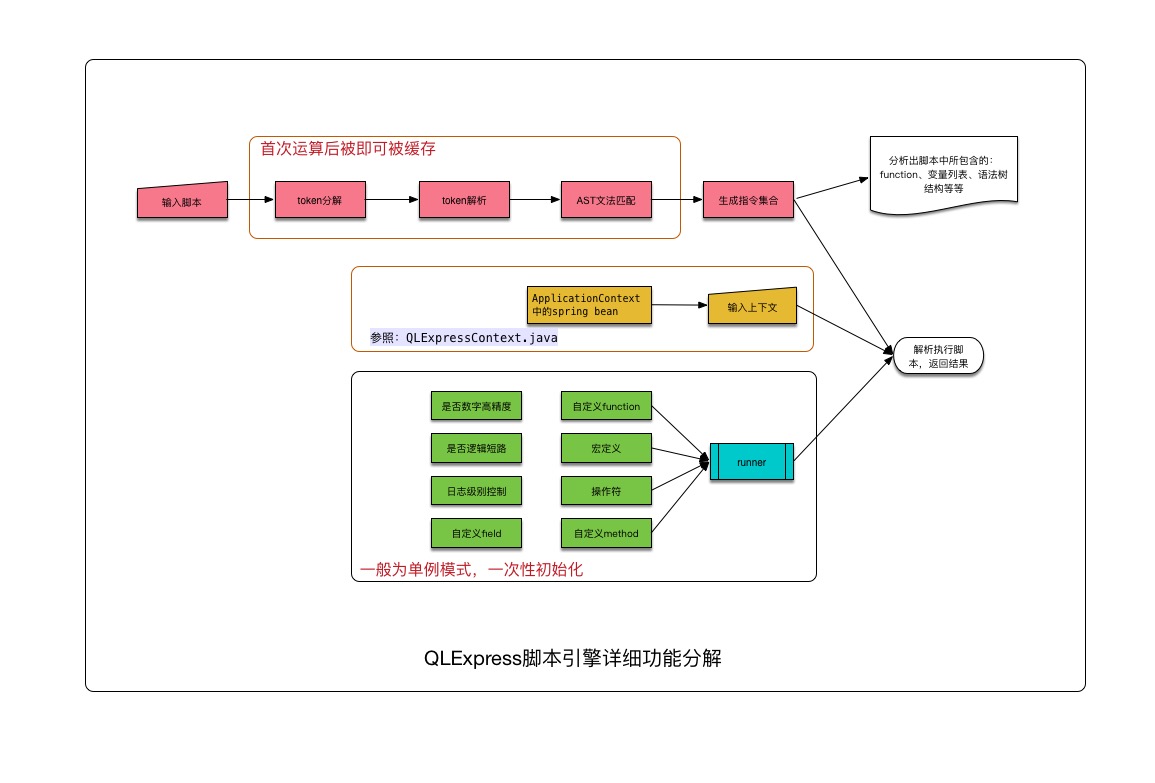
As shown in the figure below, QLExpressRunner provides secondary customized function extensions from three aspects: syntax tree analysis, context, and execution process.
/**
* Whether high precision calculation is required
*/
private boolean isPrecise = false;High-precision calculations are very important in accounting and finance. There are many implicit conversions of float, double, int, and long in java. There are actually a lot of security risks when doing four arithmetic operations and comparisons. So in a system like Huijin, there will be many BigDecimal conversion codes. With QLExpress, you only need to pay attention to the mathematical formula itself _ order total price = unit price * quantity + first weight price + (total weight-first weight) * continued weight unit price_, and then set this attribute, all intermediate calculations will be guaranteed No loss of accuracy.
/**
* Whether to use logic short circuit feature
*/
private boolean isShortCircuit = true;In many business decision-making systems, it is often necessary to analyze and output Boolean conditional expressions. Ordinary Java operations generally reduce performance consumption through logic short-circuits. For example, the rule formula: star>10000 and shoptype in('tmall','juhuasuan') and price between (100,900) Assuming that the first condition star>10000 is not met, stop the operation. However, the business system still hopes to calculate the following logic and output the intermediate process to ensure faster and better decisions.
Refer to unit test: ShortCircuitLogicTest.java
/**
* Whether to output all trace information, and the log level is also required to be DEBUG level
*/
private boolean isTrace = false;This is mainly the process of compiling and analyzing whether to output the script. Generally, the performance of the business system will be improved after it is closed.
/**
* Execute a text
* @param expressString program text
* @param context execution context can be extended to include ApplicationContext
* @param errorList List of error messages output
* @param isCache Whether to use the instruction set in Cache, it is recommended to be true
* @param isTrace Whether to output detailed execution command information, it is recommended to be false
* @param aLog output log
* @return
* @throws Exception
*/
Object execute(String expressString, IExpressContext<String,Object> context,List<String> errorList, boolean isCache, boolean isTrace, Log aLog);QLExpress mainly implements the simplest operator definition through the following methods provided by Operator.java through subclasses, which can then be injected into ExpressRunner through addFunction or addOperator.
public abstract Object executeInner(Object[] list) throws Exception;For example, we can implement a super powerful and very useful join operator with a few lines of code:
list = 1 join 2 join 3; -> [1,2,3] list = join(list,4,5,6); -> [1,2,3,4,5,6]
public class JoinOperator extends Operator{
public Object executeInner(Object[] list) throws Exception {
java.util.List result = new java.util.ArrayList();
Object opdata1 = list[0];
if(opdata1 instanceof java.util.List){
result.addAll((java.util.List)opdata1);
}else{
result.add(opdata1);
}
for(int i=1;i<list.length;i++){
result.add(list[i]);
}
return result;
}
}If you use OperatorBase.java, the base class of Operator, you will get more powerful capabilities and can basically meet all requirements.
//Get the definition of function by name
OperatorBase getFunciton(String name);
//Achieve similar through a custom Operator: fun(a,b,c)
void addFunction(String name, OperatorBase op);
//fun(a,b,c) bind object.function(a,b,c) object method
void addFunctionOfServiceMethod(String name, Object aServiceObject,
String aFunctionName, Class<?>[] aParameterClassTypes,
String errorInfo);
//fun(a,b,c) bind Class.function(a,b,c) class method
void addFunctionOfClassMethod(String name, String aClassName,
String aFunctionName, Class<?>[] aParameterClassTypes,
String errorInfo);
//Add or replace method to Class, and support a.fun(b) and fun(a,b) two method calls
//For example, the isBlank method of extending String.class: "abc".isBlank() and isBlank("abc") can be called
void addFunctionAndClassMethod(String name,Class<?>bindingClass, OperatorBase op);When it comes to the operators of scripting languages, precedence, number of operations, overriding the original operators (+, -, *, / etc.) are all issues that need to be considered. QLExpress will take care of it all for you.
//Add operation symbols, you can set the priority
void addOperator(String name,Operator op);
void addOperator(String name,String aRefOpername,Operator op);
To
//Replacement operator processing
OperatorBase replaceOperator(String name,OperatorBase op);
//Add aliases for operators and keywords, such as if..then..else -> if. . Well. . otherwise. .
void addOperatorWithAlias(String keyWordName, String realKeyWordName,
String errorInfo);The macro definition of QLExpress is relatively simple. It simply replaces a piece of text with a variable, which is different from the traditional function replacement.
//Such as addMacro("Tmall seller","userDO.userTag &1024 ==1024")
void addMacro(String macroName,String express)QLExpress can add or rewrite some methods and fields to java classes, such as chain call: "list.join("1").join("2")", such as Chinese attribute: "list. length".
//Add the attribute field of the class
void addClassField(String field,Class<?>bindingClass,Class<?>returnType,Operator op);
//Method of adding class
void addClassMethod(String name,Class<?>bindingClass,OperatorBase op);Note that the fields and methods of these classes are executed by the executor through parsing syntax, not through bytecode enhancement and other technologies, so they only take effect during the running of the script and will not have any impact on the overall operation of the jvm, so it is absolutely safe.
These interfaces are mainly static analysis of the content of a script, which can be used as a basis for context creation, and can also be used for system business processing. For example: calculate "a+fun1(a)+fun2(a+b)+c.getName()" Variables included: a, b, c Functions included: fun1, fun2
//Get a list of external variable names required by an expression
String[] getOutVarNames(String express);
String[] getOutFunctionNames(String express);Whether the script syntax is correct can be completed through the interface of the ExpressRunner compilation instruction set.
String expressString = "for(i=0;i<10;i++){sum=i+1}return sum;";
InstructionSet instructionSet = expressRunner.parseInstructionSet(expressString);
//If there is no abnormality in the calling process, the instruction set instructionSet can be loaded and run (execute)!Because QLExpress has a local HashMap cache for the text to the instruction set, usually the number of a reasonably designed application script should be limited, the cache is safe and stable, but it also provides some interfaces for management.
//Preferably get the instruction set from the local instruction set cache, if not, generate it and cache it locally
InstructionSet getInstructionSetFromLocalCache(String expressString);
//clear cache
void clearExpressCache(); try {
express = "sum=0;for(i=0;i<1000000000;i++){sum=sum+i;}return sum;";
//The running timeout time of the script can be set through the timeoutMillis parameter: 1000ms
Object r = runner.execute(express, context, null, true, false, 1000);
System.out.println(r);
throw new Exception("The timeout exception was not caught");
} catch (QLTimeOutException e) {
System.out.println(e);
} ExpressRunner runner = new ExpressRunner();
QLExpressRunStrategy.setForbiddenInvokeSecurityRiskMethods(true);
DefaultContext<String, Object> context = new DefaultContext<String, Object>();
try {
express = "System.exit(1);";
Object r = runner.execute(express, context, null, true, false);
System.out.println(r);
throw new Exception("Unsafe method was not caught");
} catch (QLException e) {
System.out.println(e);
}The context parameter IExpressContext context is very useful, it allows to put any variable, and then identify it in the script.
In practice, we very much hope to be able to seamlessly integrate into the spring framework, and we can use a subclass to imitate the following example.
public class QLExpressContext extends HashMap<String, Object> implements
IExpressContext<String, Object> {
private ApplicationContext context;
//Constructor, pass in context and ApplicationContext
public QLExpressContext(Map<String, Object> map,
ApplicationContext aContext) {
super(map);
this.context = aContext;
}
/**
* Abstract method: extract attribute value from attribute list based on name
*/
public Object get(Object name) {
Object result = null;
result = super.get(name);
try {
if (result == null && this.context != null
&& this.context.containsBean((String) name)) {
// If the bean is contained in the Spring container, the String bean is returned
result = this.context.getBean((String) name);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
return result;
}
public Object put(String name, Object object) {
return super.put(name, object);
}
}Complete demo reference SpringDemoTest.java
A custom Operator needs to directly inherit OperatorBase and get the parent. It can be used to directly edit context information when running a set of scripts. It is also very useful in business logic processing.
public class ContextMessagePutTest {
class OperatorContextPut extends OperatorBase {
public OperatorContextPut(String aName) {
this.name = aName;
}
@Override
public OperateData executeInner(InstructionSetContext parent, ArraySwap list) throws Exception {
String key = list.get(0).toString();
Object value = list.get(1);
parent.put(key,value);
return null;
}
}
@Test
public void test() throws Exception{
ExpressRunner runner = new ExpressRunner();
OperatorBase op = new OperatorContextPut("contextPut");
runner.addFunction("contextPut",op);
String exp = "contextPut('success','false');contextPut('error','error information');contextPut('warning','remind information')";
IExpressContext<String, Object> context = new DefaultContext<String, Object>();
context.put("success","true");
Object result = runner.execute(exp,context,null,false,true);
System.out.println(result);
System.out.println(context);
}
}appendix: Version update list