This project is the practical implementation of the Bachelor's Thesis's topic: Benchmarking Post-Training Quantization for Optimizing Machine Learning Inference on compute-limited edge devices.
The task of the topic is using TensorFlow Lite to optimize two machine learning models focused on image classification and semantic segmentation, respectively using the post-training quantization technique provided by TensorFlow Lite. After the model was quantized/optimized, inference was ran using the unoptimized and optimized models on a laptop (Intel-processor based) and on a Raspberry Pi 4 (ARM-processor based). Inference results were compared after running inference with both models in their quantized/unquantized formats.
The image classification model was trained on the MNIST dataset and the semantic segmentation model was trained on the Cityscapes dataset.
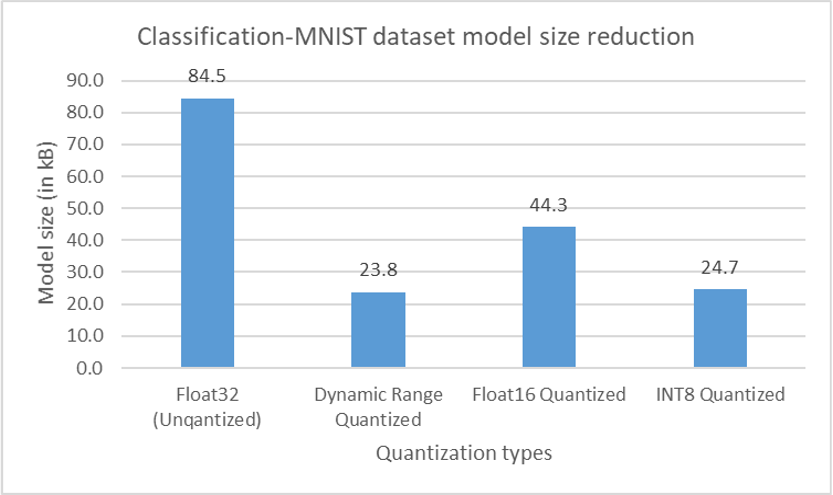
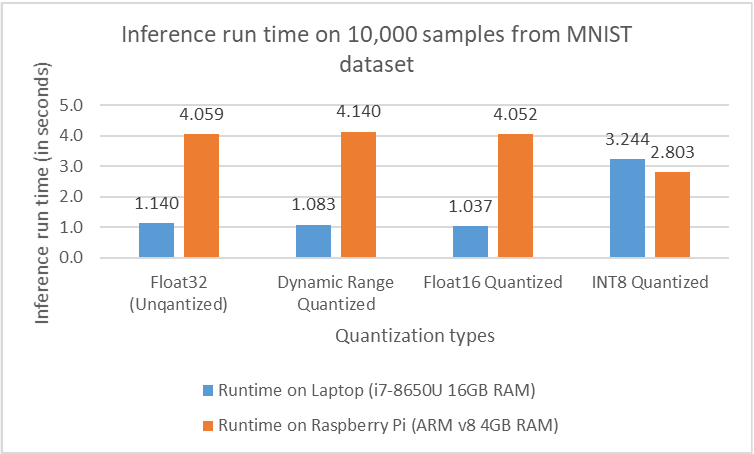
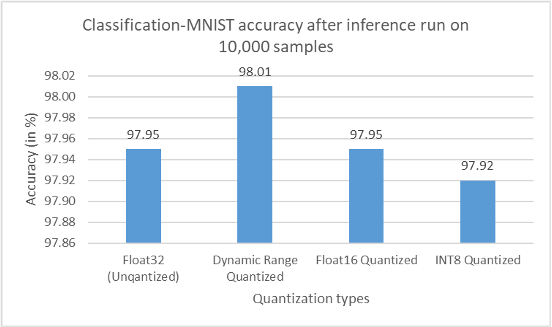
The evaluation metrics for the MNIST-classification model are inference time, model size reduction after quantization and accuracy. While for the semantic segmentation task, the evaluation metrics are inference time, number of frames processed per second, model size reduction after quantization, pixel accuracy and Mean Intersection over Union (mIoU).
In the docker_config directory, there are two directories that contain the Docker Configuration to create Docker image for each of the models to be deployed and ran on Raspberry Pi.
The models directory contains two directories:
- image_classification_mnist, which contains the following directories:
srcdirectory which contains the python code for:- Training the MNIST-classification model and saving the model as
model.h5. This is done using the train_mnist_and_save_into_disk.py python script. - Converting the original MNIST-classification TensorFlow model into TensorFlow Lite models (Float32 unquantized model, Float16 quantized model, dynamic range quantized model and INT8 quantized model). This is done using the convert_mnist_model_to_tflite.py python script.
- Running inference using the all types of quantization on the 10,000 photos from the MNIST test dataset and evaluating the accuracy and inference run time. This is done using the run_inference_tflite.py python script.
- Training the MNIST-classification model and saving the model as
modelsdirectory which contains the original TensorFlow model inh5format and the all other formats to be used for inference.outputcontains the results of running inference, it contains information about the size reduction, accuracy and inference run time.
- semantic_segmentation_cityscapes, which contains the following directories:
input_model/cityscapes/directory which contains the following directories:evaluation_output_single_imagecontains the results after running inference with all types of models on a single image.evaluation_output_videocontains the results after running inference with all types of models on a defined number of frames of the video in the video directory.frozen_graphcontains the frozen_graph of the semantic segmentation model, which was downloaded from available deeplab models.imgcontains theground_truth,input_imageand the output images (segmentation map and segmentation overlay) for the single image and video evaluation.quantized_modelscontains the models used for inference run.videocontains the video, from which the frames are being taken to run inference on.
convert_to_tflitedirectory contains a shell file and a python script to convert the frozen graph to quantized and unquantized models.run_inferencedirectory contains a shell file and python script to define which type to run inference with and saves results on the disk.
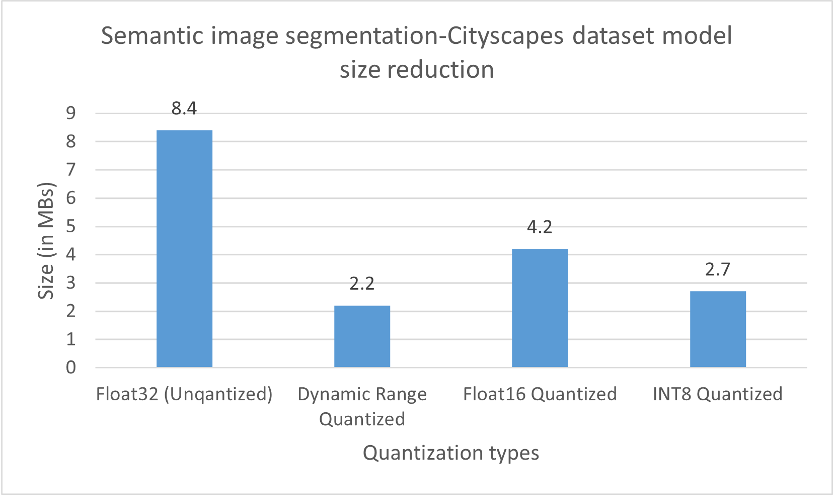
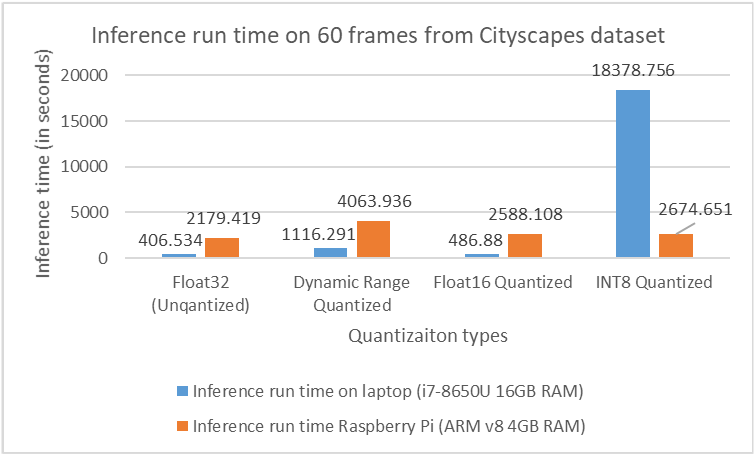
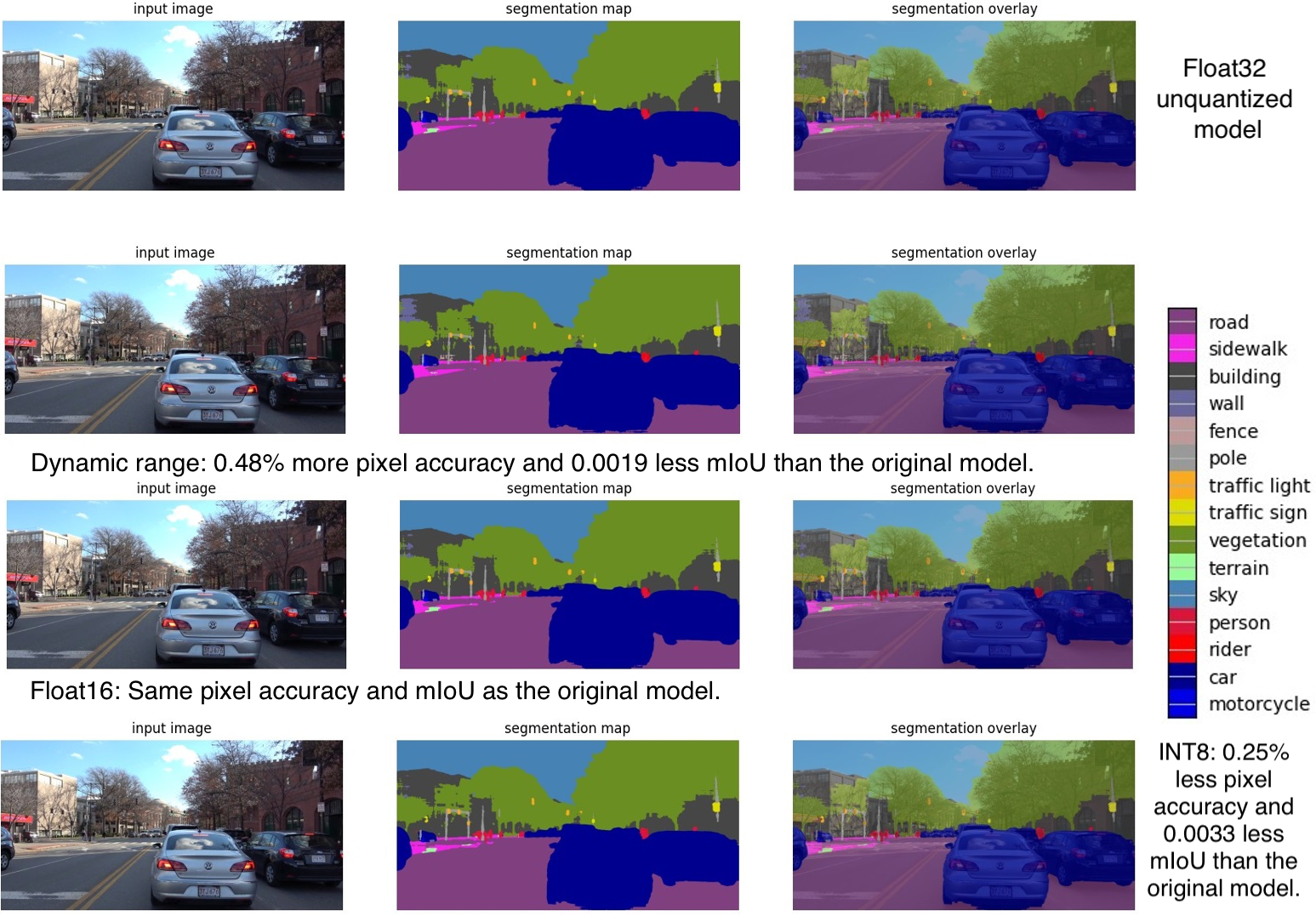
For both image classification and semantic segmentation models, results showed an expected reduction in model size when different quantization techniques were applied. Accuracy and mIOU, in both the cases didn’t change by a huge margin from that obtained on the original model. In fact, in some cases, applying quantization actually led to an improvement in accuracy. The inference speed regarding the image classification model has improved adequately. On the other hand, no improvement was obtained on inference speed concerning the semantic segmentation model. In fact, in some cases, latency on Raspberry Pi increasedby a factor of 10.