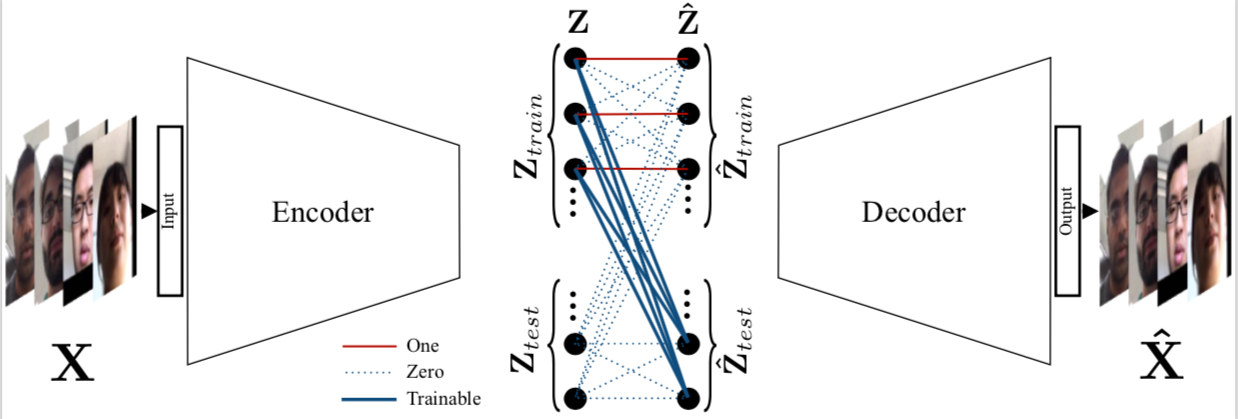
This repository contains the implementation of the paper "Deep sparse representation-based classification" by Mahdi Abavisani and Vishal M. Patel. The paper was published in IEEE Signal Processing Letters.
Deep Sparse Representation-based Classificatio (DSRC) is a transductive classification model based on sparse representations. DSRC is based on convolutional autoencoders. In particular, its network contains an encoder, a sparse coding layer, and a decoder. The encoder receives both the training and test sets as raw data inputs and extracts abstract features from them. The sparse coding layer recovers the test cases by a sparse linear combination of the training samples, and concatenates them along with the training features which are then fed to the decoder. The decoder maps both the training embeddings and the recovered test embeddings back to the original representation of the data. The figure above gives an overview of the proposed deep SRC (DSRC) framework.
Please use the following to refer to this work:
@ARTICLE{dsrc,
author={M. {Abavisani} and V. M. {Patel}},
journal={IEEE Signal Processing Letters},
title={Deep Sparse Representation-Based Classification},
year={2019},
volume={26},
number={6},
pages={948-952},
doi={10.1109/LSP.2019.2913022},
ISSN={1070-9908},
month={June},}
M. Abavisani and V. M. Patel, "Deep Sparse Representation-Based Classification," in IEEE Signal Processing Letters, vol. 26, no. 6, pp. 948-952, June 2019.
Tensorflow, numpy, scipy, random, argparse.
Resize the input images of all the modalities to 32 × 32, and rescale them to have pixel values between 0 and 255. This is for keeping the hyperparameter selections valid.
Save the data in a .mat file that includes verctorized features in a 1024xN matrix with the name features and labels in a vector with the name Label.
A sample preprocessed dataset is available in: data/umd.mat
To keep the regularization parameters valid, please make sure that the preprocessing stage is done correctly. Also, for large datasets since the batch size will be larger, the learning rate (or the maximum number of iterations) may need to be adapted accordingly.
Use the following script to run the included demo for the UMDAA-01 dataset.
python dsrc_main.py --mat umd
Run dsrc_main.py and use
--mat YOUR_DATA to specify your dataset where YOUR_DATA.mat is stored in the "data" folder.
--epoch x to specify the maximum number of iterations.
--pretrain_step x to specify the maximum number of pretraining iterations. (Since the demo uses a larger batch-size than the paper, it is set to have a defult maximum pretraining iteration of 1000 steps.)
--rate x to specify the ratio of number of training samples to total number of samples.
--display_step x to specify the frequency of reports.