when we have to do a work again and again then we can think about loop.loop is the most important thing for every programming language.
- for Loop
- while Loop
- do while Loop
- structure of for loop
for (data_type variable_name = index_number; condition; increase or decrease){
}
- structure of while loop
data_type variable_name = index_number
while(condition){
/*code*/
increase or decrease
}
- structure of do while loop
do{
/*code*/
}while(condition)
Basically the array is one kind of data structure. there are three type of array.
- One dimensional array
- Two dimensional array
- Multi dimensional array
1. one dimensional array.
A simple array is called one-dimensional array.
- structure of one dimensional array
data_type array_name[size] = {35,45,10} etc;
memory allocation means how much space an array taking.
-
array_name[0] = 35;
-
array_name[1] = 45;
-
array_name[2] = 10;
basically array start from 0
2. two dimensional array.
The two dimensional array can be defined as an array of arrays. Two-dimensional array as like a matrix. It has some collection of rows and columns.
- structure of two dimensional array
data_type array_name[row][column] ={{1,2,3,4,5,6},
{1,2,3,4,5,6}
}
array_name[0][0] = 1;
array_name[0][1] = 2;
array_name[0][2] = 3;
array_name[0][3] = 4;
array_name[0][4] = 5;
array_name[0][5] = 6;
array_name[1][0] = 1;
array_name[1][1] = 2;
array_name[1][2] = 3;
array_name[1][3] = 4;
array_name[1][4] = 5;
array_name[1][5] = 6;
we can Traverse the array using nested for loop..
For example : our main for loop using for rows second for loop using for columns.
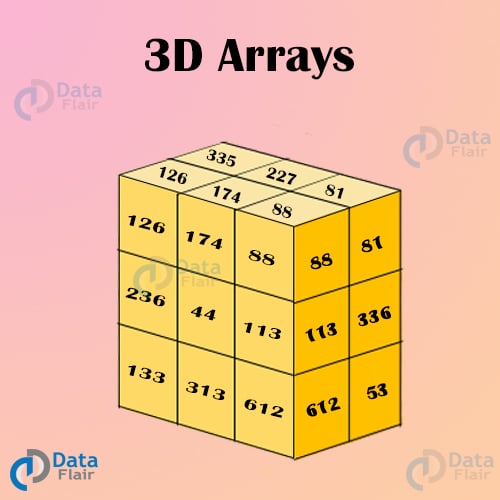
Multi Dimensional Array
A multidimensional array is called an array of arrays.
- structure of multi dimensional array.
data_type array_name[2][2][4]..........[n] = {}
data_type array_name[row][column][4] = {
}
int array[2][2][4] = {
{{1,2,3,4},{1,2,3,4}},
{{1,2,3,4},{1,2,3,4}}
}
array[0][0][0] = 1
array[0][0][1] = 2
array[0][0][2] = 3
array[0][0][3] = 4
array[0][1][0] = 1
array[0][1][1] = 2
array[0][1][2] = 3
array[0][1][3] = 4
array[1][0][0] = 1
array[1][0][1] = 2
array[1][0][2] = 3
array[1][0][3] = 4
array[1][1][0] = 1
array[1][1][1] = 2
array[1][1][2] = 3
array[1][1][3] = 4
we can initialize a three-dimensional array in a similar way like a two-dimensional array. Here's an example:
data_type array_name[2][2][4] = {
{{1,2,3,4},{1,2,3,4}},
{{1,2,3,4},{1,2,3,4}}
}
This is anohter example suppose we have a 3d array, the name of this array is arr . we've to traverse this array. Obviously we've to use for loop.
we're defining integer type data.
int arr[2][2][4] = { {{1,2,3,4},{1,2,3,4}}, {{1,2,3,4},{1,2,3,4}} }
first of all we have to remember that how much rows, columns and value have in a 3d array. This array shows us 2 rows, 2 columns, and every column has 4 value.
we have to traverse this array using for loop.. therefore this array has 2 rows 2 columns and inside the column has 4 values.
Rows could be one for loop and columns could be nested for loop and finally the exact value could be another nested for loop.
for example:
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int i,j,k; /_initializer_/
int arr[2][2][4];
printf("enter 16 value: ");
for(i = 0; i < 2; i++){
for(j = 0; j < 2; j++){
for(k = 0; k < 4; k++){
scanf("%d",&arr[i][j][k]);
}
}
}
for(i = 0; i< 2; i++){
for(j = 0; j<2; j++){
for(k = 0; k < 4; k++){
printf("arr[%d][%d][%d] = %d \n",i,j,k,arr[i][j][k]);
}
}
}
return 0;
}
enter 16 value
11
22
33
44
55
66
77
88
99
11
22
33
44
55
66
77
arr[0][0][0] = 11
arr[0][0][1] = 22
arr[0][0][2] = 33
arr[0][0][3] = 44
arr[0][1][0] = 55
arr[0][1][1] = 66
arr[0][1][2] = 77
arr[0][1][3] = 88
arr[1][0][0] = 99
arr[1][0][1] = 11
arr[1][0][2] = 22
arr[1][0][3] = 33
arr[1][1][0] = 44
arr[1][1][1] = 55
arr[1][1][2] = 66
arr[1][1][3] = 77
for loop
- Width Height
#include <stdio.h>
int main(){
int i, j,width = 5,height = 5;
for(i = 0; i < height; i++ ){
for(j = 0; j<width; j++){
printf("* ");
}
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}
* * * * *
* * * * *
* * * * *
* * * * *
* * * * *
- Right-angled triangle
#include <stdio.h>
int main(){
int i, j,rows = 5;
for(i = 0; i <= rows; i++ ){
for(j = 0; j<i; j++){
printf("* ");
}
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}
*
* *
* * *
* * * *
* * * * *
- Pyramid
#include <stdio.h>
int main(){
int i, j,rows = 5, spaces = 5;
for(i = 0; i < rows; i++ ){
for(j = 0; j< spaces; j ++){
printf(" ");
}
for(j = 0; j<(2 * i) - 1; j++){
printf("*");
}
spaces--;
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}
*
***
*****
*******
- Reverse diamond
int i, j, stars = 5, rows = 5, spaces = 1;
for (i = 0; i < rows * 2; i++)
{
for (j = 1; j < spaces; j++)
{
printf(" ");
}
for (j = 0; j < 2 * stars + 1; j++)
{
printf("*");
}
printf("\n");
if (i < rows)
{
spaces++;
stars--;
}
else
{
spaces--;
stars++;
}
}
return 0;
}
output
*********
*******
*****
***
*
***
*****
*******
*********
2. Array
- One dimensional array
#include <stdio.h>
#define NUMBERS 10
int main()
{
int i;
float numbers[NUMBERS], total = 0.0, value;
printf("Enter ten numbers : ");
for (i = 0; i < NUMBERS; i++)
{
scanf("%f", &value);
numbers[i] = value;
total += numbers[i] * numbers[i];
}
for (i = 0; i < NUMBERS; i++)
{
printf("numbers[%d] = %.2f\n", i + 1, numbers[i]);
}
printf("total = %.2f", total);
return 0;
}
output
Enter ten numbers:12.3 6.3 5.6 8.3 1.2 14.3 5.5 1.0 1.33 2.2
number[1] = 12.30
number[2] = 6.3
number[3] = 5.6
number[4] = 8.3
number[5] = 1.2
number[6] = 14.3
number[7] = 5.5
number[8] = 1.0
number[9] = 1.33
number[10] = 2.2
total = 535.01
- Bouble sort (using nested for loop)
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int i, j, arr[10], temp;
printf("Enter 10 values: ");
for (i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
scanf("%d", &arr[i]);
}
for (i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j < 10; j++)
{
if (arr[j] > arr[j + 1])
{
temp = arr[j];
arr[j] = arr[j + 1];
arr[j + 1] = temp;
}
}
}
for (i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
printf("%d\n", arr[i]);
}
return 0;
}
output
Enter 10 values: 3 2 1 4 5 6 9 8 7 11
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
11
- Two dimensional array
#include <stdio.h>
#define ROW 4
#define COLUMN 3
int main()
{
int array[4][3] = {
{1, 4, 7},
{7, 8, 9},
{1, 2, 3},
{4, 5, 6}},
array2[4][3] = {{1, 4, 7}, {7, 8, 9}, {1, 2, 3}, {4, 5, 6}};
for (int i = 0; i < ROW; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < COLUMN; j++)
{
printf("%d\t", array[i][j] + array2[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}
output
2 8 14
14 16 18
2 4 3
8 10 6
- Popularity Table (city wise car)
#include <stdio.h>
#define GETINPUT 50
#define ROWS 5
#define COLUMNS 5
int main()
{
int i, j, car_code, frequency[ROWS][COLUMNS] = {
{0}, {0},{0},{0},{0}
};
char city;
printf("for each person, enter the city code\nfollowed by the car code\nenter the letter x to indicate end.\n");
for (i = 0; i < GETINPUT; i++)
{
scanf("%c", &city);
if (city == 'x')
{
break;
}
scanf("%d", &car_code);
if (city == 'b')
{
frequency[1][car_code]++;
}
else if (city == 'c')
{
frequency[2][car_code]++;
}
else if (city == 'd')
{
frequency[3][car_code]++;
}
else if (city == 'm')
{
frequency[4][car_code]++;
}
}
printf("popularity table\n");
printf("_______________________________\n");
printf("city ambassdor fiat dolphin maruti\n");
printf("_______________________________\n");
for (i = 1; i <= 4; i++)
{
if (i == 1)
{
printf("bombay ");
}
else if (i == 2)
{
printf("calcutta");
}
else if (i == 3)
{
printf("delhi ");
}
else if (i == 4)
{
printf("madras ");
}
for (j = 1; j <= 4; j++)
{
printf("%7d", frequency[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}
output
for each person, enter the city code
followed by the car code
enter the letter x to indicate end.
m 1 c 2
x
popularity table
_______________________________
city ambassdor fiat dolphin maruti
_______________________________
bombay 0 0 0 0
calcutta 0 1 0 0
delhi 0 0 0 0
madras 1 0 0 0
- multi table using nested for loop and two dimensional array
output
1 2 3 4 5
---------------------
1 | 1 2 3 4 5
2 | 2 4 6 8 10
3 | 3 6 9 12 15
4 | 4 8 12 16 20
5 | 5 10 15 20 25