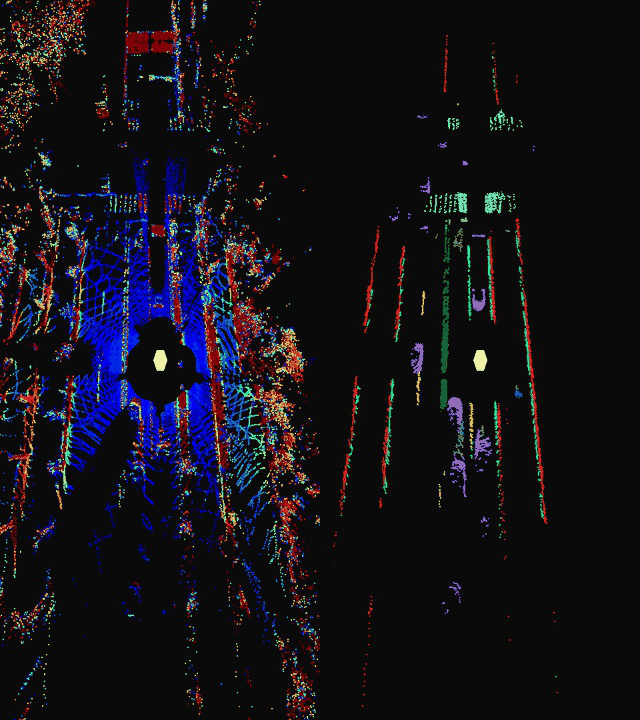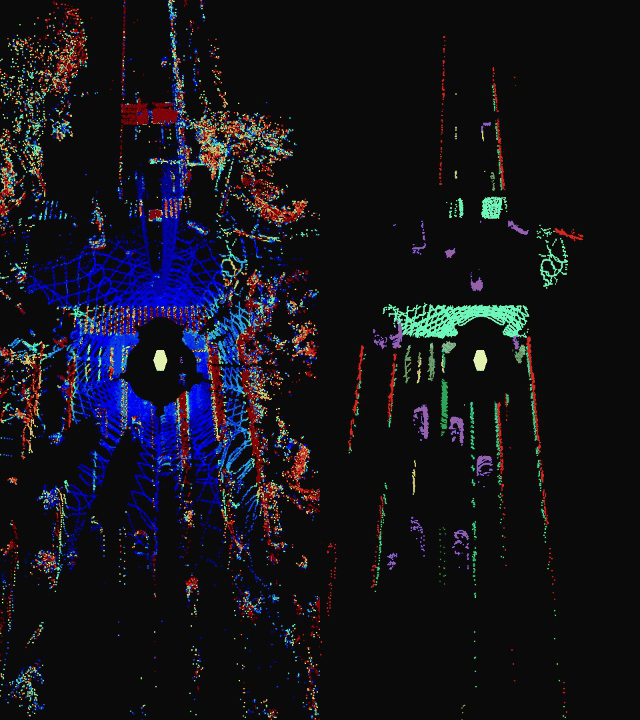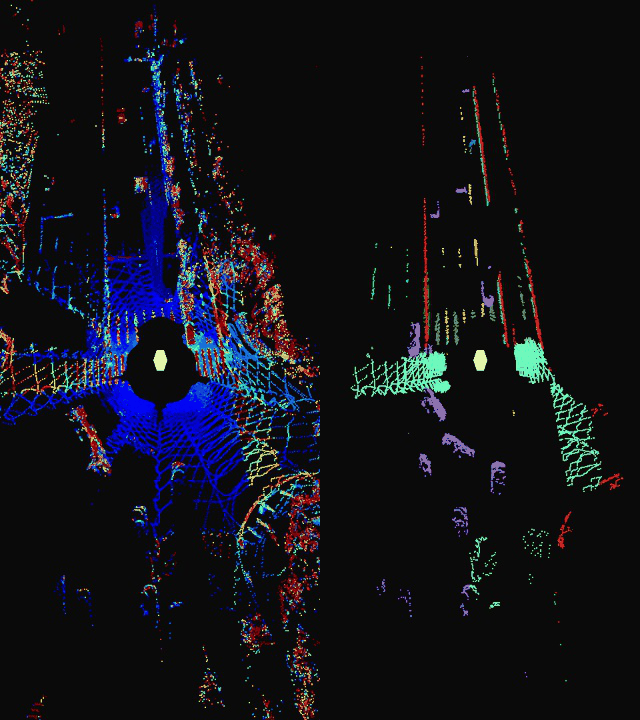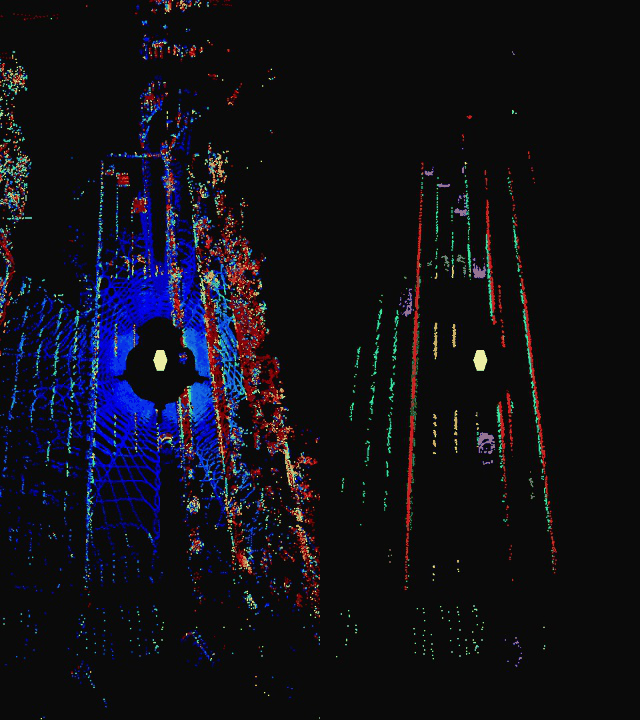This repository serves as a inference suite for Livox point cloud lane detection. It supports semantic segmentation of general lane line types and objects near the road.
Python3.6+Pytorch1.0+(tested on 1.4.0)OpenCV PythonNumpy
If you find this repository useful, please consider citing it using a link to the repo :)
- test_lane_detection.py: Testing lane detection
- visualize_points_with_class.py: Visualizing the points with semantic specific colors.
- config.py: Parameter configurations used in this repository.
- data_process: Folder containing data processing scripts for point cloud.
- model: Folder containing model files.
- network: Folder containing network architecure implementations.
We use the data format as in Livox Dataset V1.0. There's an example in test_data folder. To test, run directly:
$ python test_lane_detection.pyThe lane detection results are saved in result/points_with_class.
You can visualize the results by:
$ python visualize_points_with_class.pyThe visualized results are saved in result/points_vis.
The configuration parameters used in this repository are listed in config.py. The parameter details are as follows:
LIDAR_IDs # Selected lidar ids
BV_COMMON_SETTINGS = { # Bird view map setttings
"train_height_shift", # Height shift to make the z-axis value of ground be 0
"shifted_min_height", # Minimum z-axis value of the interval to select points near the ground
"shifted_max_height", # Maximum z-axis value of the interval to select points near the ground
"distance_resolution_train", # 1 meter in x-axis corresponds to "distance_resolution_train" pixels on the bird view map
"width_resolution_train", # 1 meter in y-axis corresponds to "width_resolution_train" pixels on the bird view map
"point_radius_train", # point radius on the bird view
"truncation_max_intensiy", # If intensity value of one point is bigger than "truncation_max_intensiy", the intensity will be set to this value
"train_background_intensity_shift",# Intensity shift to make the area with points (intensity may be 0) different with that without points
}
BV_RANGE_SETTINGS = {
"max_distance", # Farthest detection distnace in front of the car
"min_distance", # Farthest detection distnace behind the car
"left_distance", # Farthest detection distance to the left of the car
"right_distance" # Farthest detection distance to the right of the car
}
MODEL_NAME # Model name
GPU_IDs # GPU
TEST_DATA_FOLDER # Path to input data
POINTS_WITH_CLASS_FOLDER # Path to lane detection results
VIS_FOLDER # Path to visulization results
Download the Livox Dataset V1.0. Unzip it to some folder. Then specify the "TEST_DATA_FOLDER" in config.py to that folder. You can also specify the "POINTS_WITH_CLASS_FOLDER" and "VIS_FOLDER" for your convenience.
The Livox Dataset V1.0 perceive the environment using 6 lidars. The default setting is to use all of them for lane detection. If you want to do lane detection using a few of the lidars, you can change the "LIDAR_IDs" in config.py for your need.
For example, if you want to detect the lane in front of the car, you can configure as:
LIDAR_IDs = ["1", "6"]livox网络输入:torch.Size([1,2,84,1200])
def ProduceBVData(points, bv_common_settings, bv_range_settings, if_square_dilate = True):
bv_im_width = int((right_distance + left_distance)*width_resolution)
bv_im_height = int((max_distance - min_distance) * distance_resolution)
im_intensity = np.zeros((bv_im_height, bv_im_width, 1)).astype(np.float32)
height_map = np.zeros((bv_im_height, bv_im_width, 1)).astype(np.float32)
#这里先设置bv长宽
point_num = points.shape[0]
for i in range(point_num):
x = points[i, 0]*distance_resolution
y = points[i, 1]*width_resolution
start_x = max(0, np.ceil(im_x - vis_point_radius))
end_x = min(bv_im_width -1, np.ceil(im_x + vis_point_radius) - 1) + 1
start_y = max(0, np.ceil(im_y - vis_point_radius))
end_y = min(bv_im_height -1, np.ceil(im_y + vis_point_radius) - 1) + 1
im_intensity[start_y:end_y, start_x:end_x, 0] = np.maximum(points[i, 3], im_intensity[start_y:end_y, start_x:end_x, 0])
height_map[start_y:end_y, start_x:end_x, 0] = np.maximum(points[i, 2], height_map[start_y:end_y, start_x:end_x, 0])
concat_data = np.concatenate((im_intensity, height_map), axis=2)
return concat_data
送入网络后:
输出为torch.Size([1,33,84,1200]) 33为设定的参数num_class 随后进行argmax操作得到 label_map(84,1200)
if im_x >= 0 and im_x < bv_im_width and im_y >= 0 and im_y < bv_im_height:
point_classes[i] = bv_label_map[im_y, im_x]
随后将label_map值放入point_class 最后可视化点云为图片:
def VisualizePointsClass(points_input):
output_img_h = 1080
output_img_w = 1920
output_img_w1 = int(output_img_w / 2)
K, P, P_world = GetMatrices([output_img_h, output_img_w1])
intensity_show = GetProjectImage(points_input,
points_input[:, 3]*255,
[output_img_h, output_img_w1],
K, P, P_world, color_table)
class_show = GetProjectImage(points_input,
points_input[:, 4],
[output_img_h, output_img_w1],
K, P, P_world, color_table_for_class)
vis_img = np.concatenate([intensity_show, class_show], axis = 1)
return vis_img
intensity图和class图