dblab 


Interactive client for PostgreSQL, MySQL and SQLite3.
Overview
dblab is a fast and lightweight interactive terminal based UI application for PostgreSQL, MySQL and SQLite3, written in Go and works on OSX, Linux and Windows machines. Main idea behind using Go for backend development is to utilize ability of the compiler to produce zero-dependency binaries for multiple platforms. dblab was created as an attempt to build very simple and portable application to work with local or remote PostgreSQL/MySQL/SQLite3 databases.
Features
- Cross-platform support OSX/Linux/Windows 32/64-bit
- Simple installation (distributed as a single binary)
- Zero dependencies
Installation
Homebrew
It works with Linux, too.
$ brew install danvergara/tools/dblab
Or
$ brew tap danvergara/tools
$ brew install dblab
Binary Release (Linux/OSX/Windows)
You can manually download a binary release from the release page.
Automated install/update, don't forget to always verify what you're piping into bash:
curl https://raw.githubusercontent.com/danvergara/dblab/master/scripts/install_update_linux.sh | bashThe script installs downloaded binary to /usr/local/bin directory by default, but it can be changed by setting DIR environment variable.
Help
dblab is a terminal UI based interactive database client for Postgres, MySQL and SQLite3.
Usage:
dblab [flags]
dblab [command]
Available Commands:
help Help about any command
version The version of the project
Flags:
--config get the connection data from a config file (default is $HOME/.dblab.yaml or the current directory)
--db string Database name
--driver string Database driver
-h, --help help for dblab
--host string Server host name or IP
--limit int Size of the result set from the table content query (default 100)
--pass string Password for user
--port string Server port
--ssl string SSL mode
-u, --url string Database connection string
--user string Database user
Use "dblab [command] --help" for more information about a command.
Usage
You can start the app passing no flags or parameters, you'll be asked for connection data instead.
$ dblab --host localhost --user myuser --db users --pass password --ssl disable --port 5432 --driver postgres --limit 50
$ dblab --db path/to/file.sqlite3 --driver sqlite3Connection URL scheme is also supported:
$ dblab --url postgres://user:password@host:port/database?sslmode=[mode]
$ dblab --url mysql://user:password@tcp(host:port)/db
$ dblab --url file:test.db?cache=shared&mode=memoryNow, you can use a configuration file to make a connection to the database.
$ dbladb --configdblab is going to look for a file called .dblab.yaml. For now, the only two places where you can drop a config file are $HOME ($HOME/.dblab.yaml) and the current directory where you run the command line tool.
.dblab.yaml example:
database:
host: "localhost"
port: 5432
db: "users"
password: "password"
user: "postgres"
driver: "postgres"
limit: 50Or for sqlite3:
database:
db: "path/to/file.sqlite3"
driver: "sqlite3"Only the host and ssl fields are optionals. 127.0.0.1 and disable, respectively.
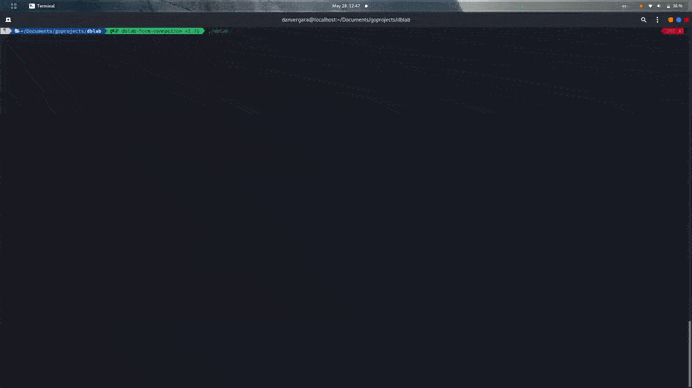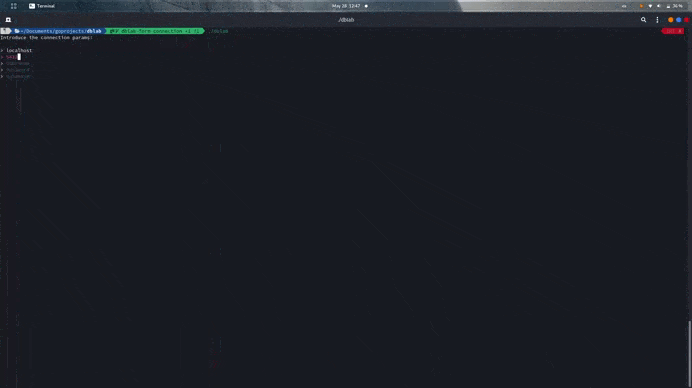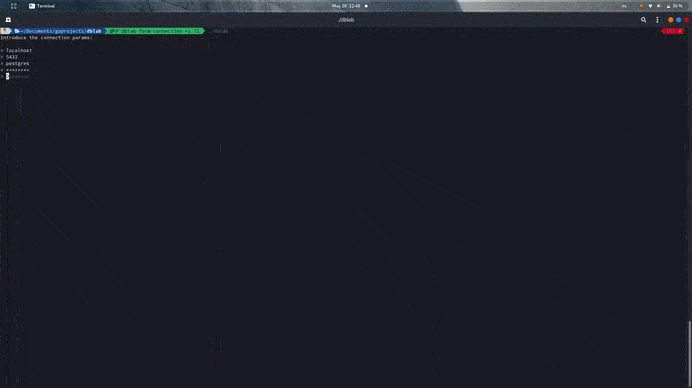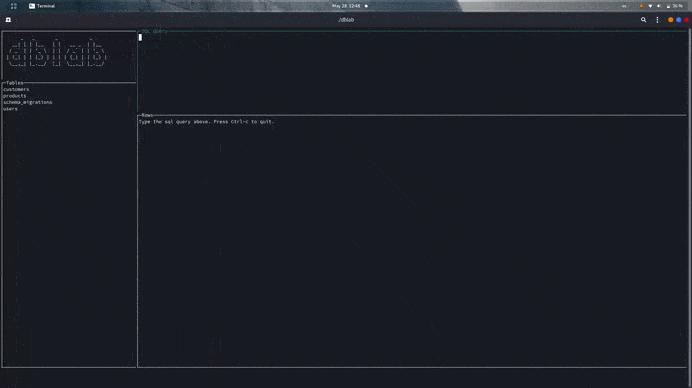
If the query panel is active, type the desired query and press Ctrl+Space to see the results on the rows panel below.
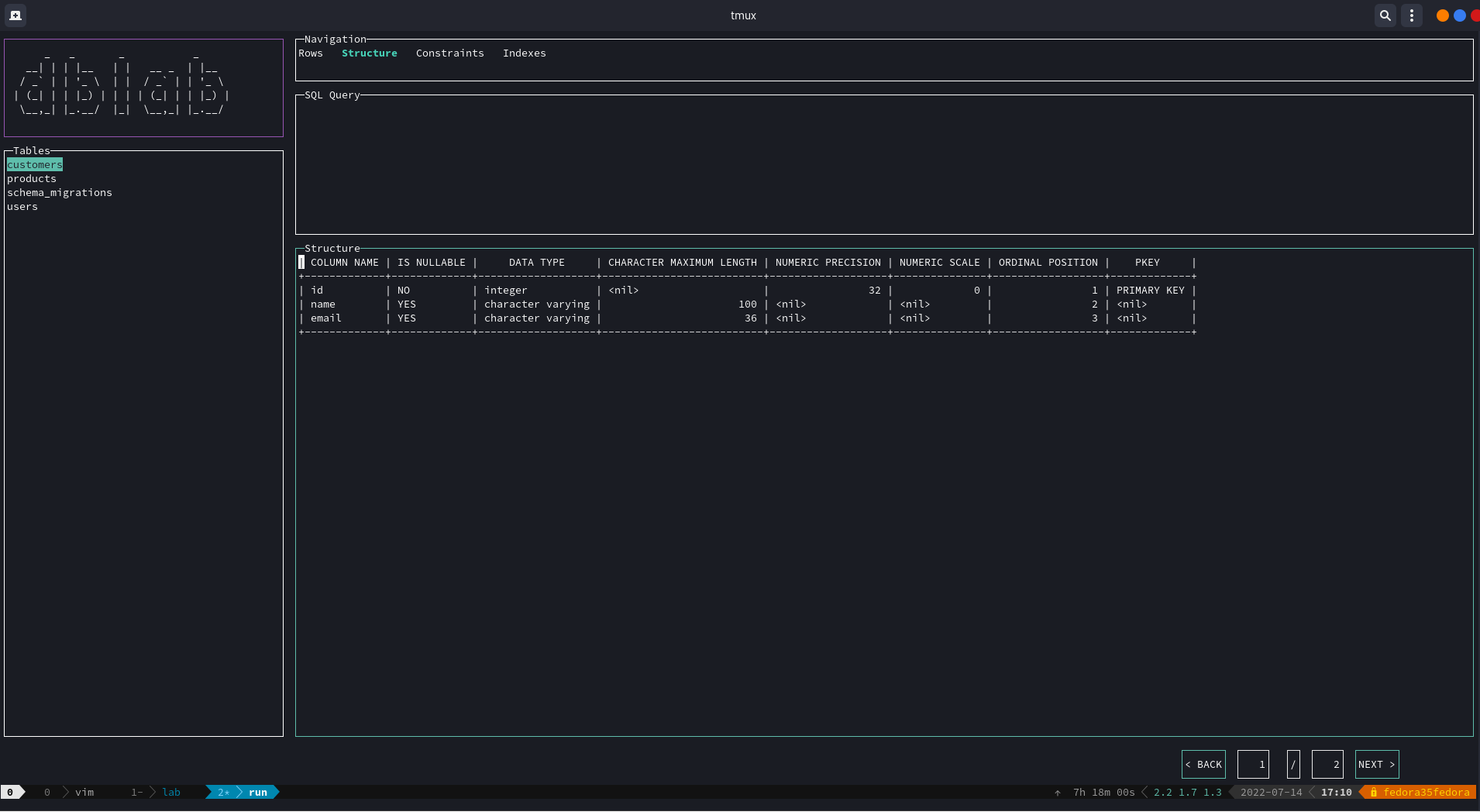
Otherwise, you might me located at the tables panel, then you can navigate by using the arrows Up and Down (or the keys k and j respectively). If you want to see the rows of a table, press Enter. To see the the schema of a table, locate yourself on the rows panel and press Ctrl+S to switch to the structure panel, then switch Ctrl+S to switch back.
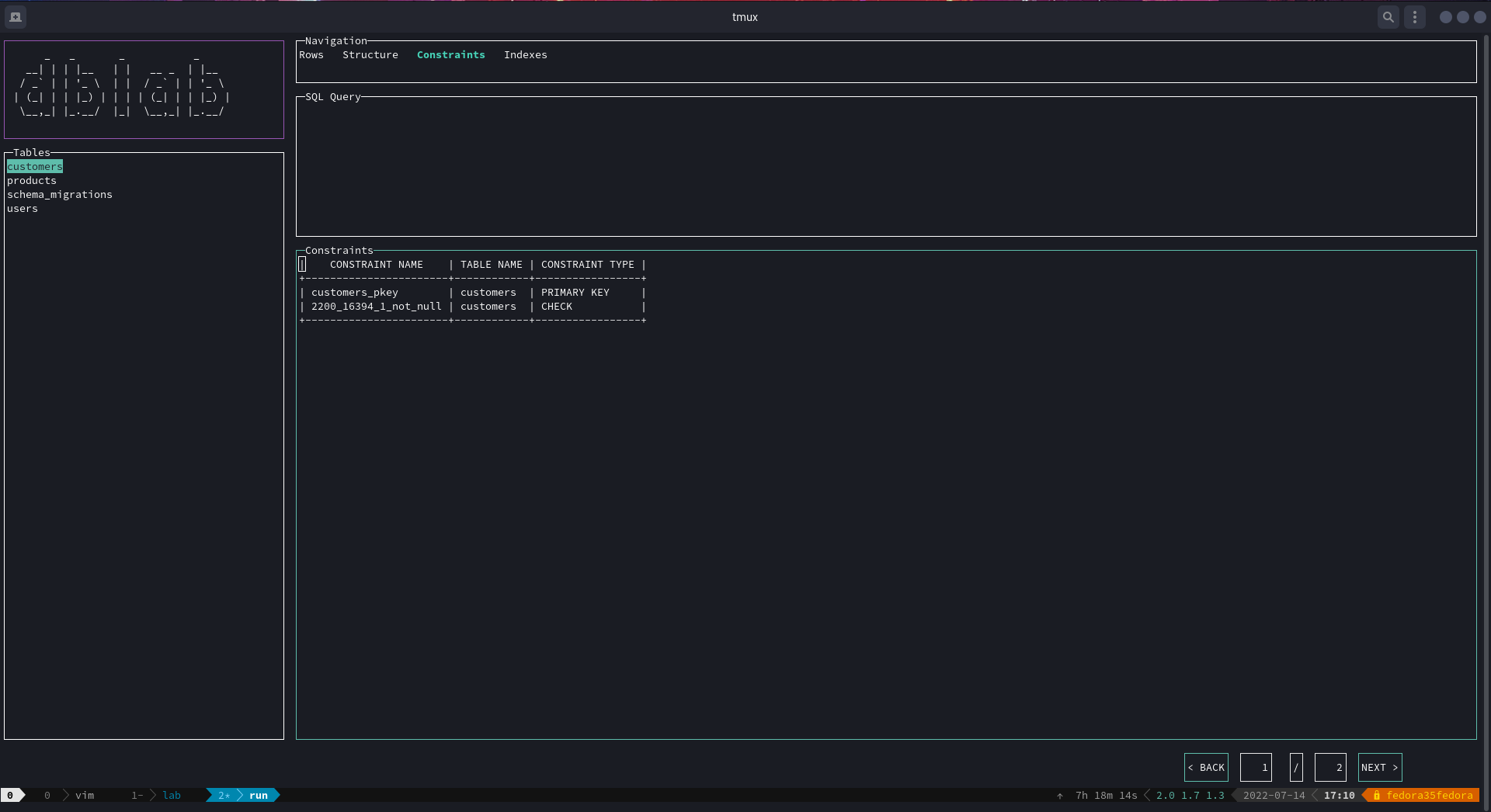
The same can be achieved for the constraints view by pressing Ctrl+F to go back and forth between the rows and the constraints panels.
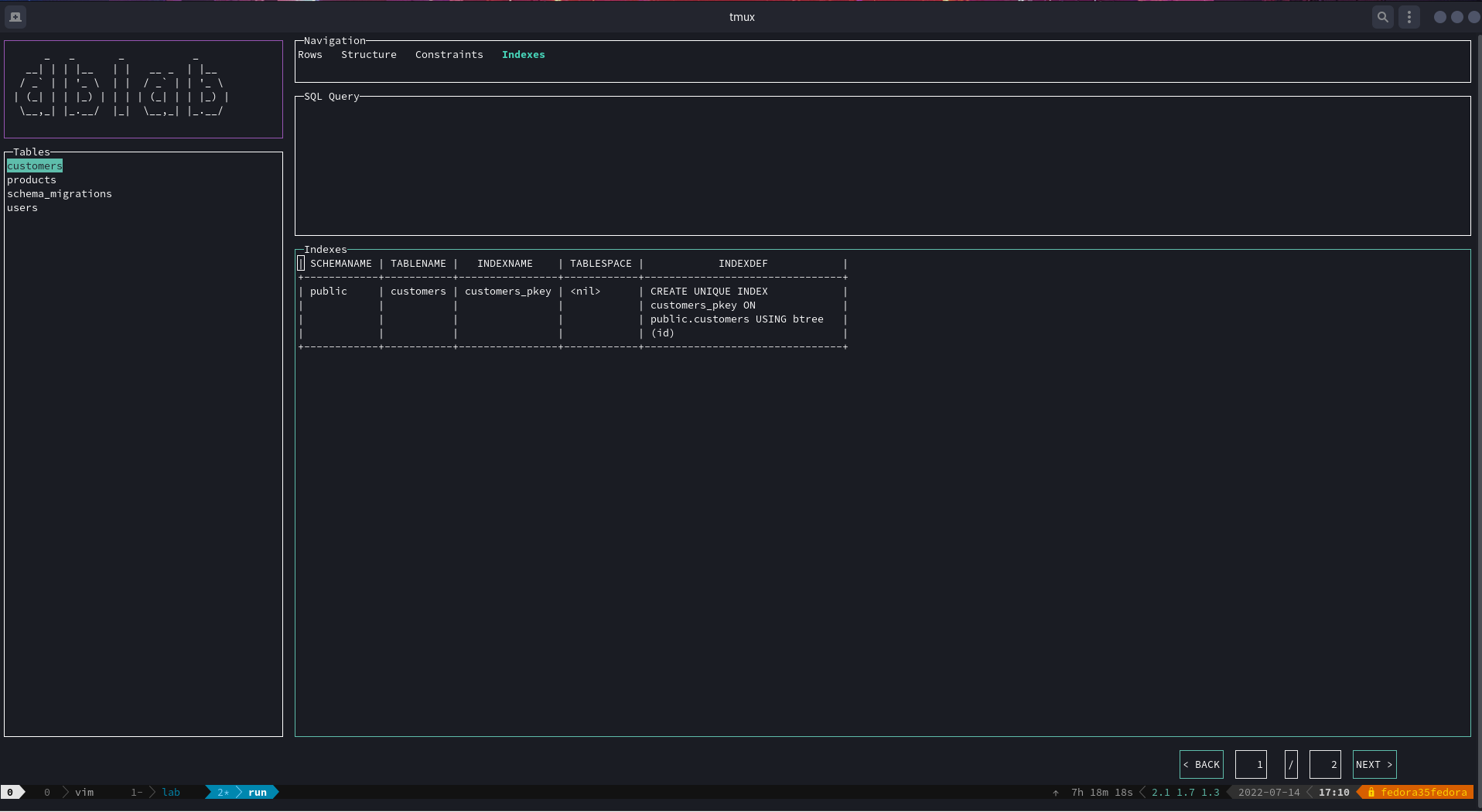
Now, there's a menu to navigate between hidden views by just clicking on the desired options:
As you may have noticed, navigation has already been added, so every time you query the content of a listed table, the result set is going to be paginated. This allows to the user dealing with large tables, optimizing resources.
Just hit the BACK and NEXT buttons to go back and forth.
Key Bindings
| Key | Description |
|---|---|
| Ctrl+Space | If the query panel is active, execute the query |
| Enter | If the tables panel is active, list all the rows as a result set on the rows panel and display the structure of the table on the structure panel |
| Ctrl+S | If the rows panel is active, switch to the schema panel. The opposite is true |
| Ctrl+F | If the rows panel is active, switch to the constraints view. The opposite is true |
| Ctrl+I | If the rows panel is active, switch to the indexes view. The opposite is true |
| Ctrl+H | Toggle to the panel on the left |
| Ctrl+J | Toggle to the panel below |
| Ctrl+K | Toggle to the panel above |
| Ctrl+L | Toggle to the panel on the right |
| Arrow Up | Next row of the result set on the panel. Views: rows, table, constraints, structure and indexes |
| k | Next row of the result set on the panel. Views: rows, table, constraints, structure and indexes |
| Arrow Down | Previous row of the result set on the panel. Views: rows, table, constraints, structure and indexes |
| j | Previous row of the result set on the panel. Views: rows, table, constraints, structure and indexes |
| Arrow Right | Horizontal scrolling on the panel. Views: rows, constraints, structure and indexes |
| l | Horizontal scrolling on the panel. Views: rows, constraints, structure and indexes |
| Arrow Left | Horizontal scrolling on the panel. Views: rows, constraints, structure and indexes |
| h | Horizontal scrolling on the panel. Views: rows, constraints, structure and indexes |
| Ctrl+c | Quit |
Contribute
- Fork this repository
- Create a new feature branch for a new functionality or bugfix
- Commit your changes
- Execute test suite
- Push your code and open a new pull request
- Use issues for any questions
- Check wiki for extra documentation
License
The MIT License (MIT). See LICENSE file for more details.