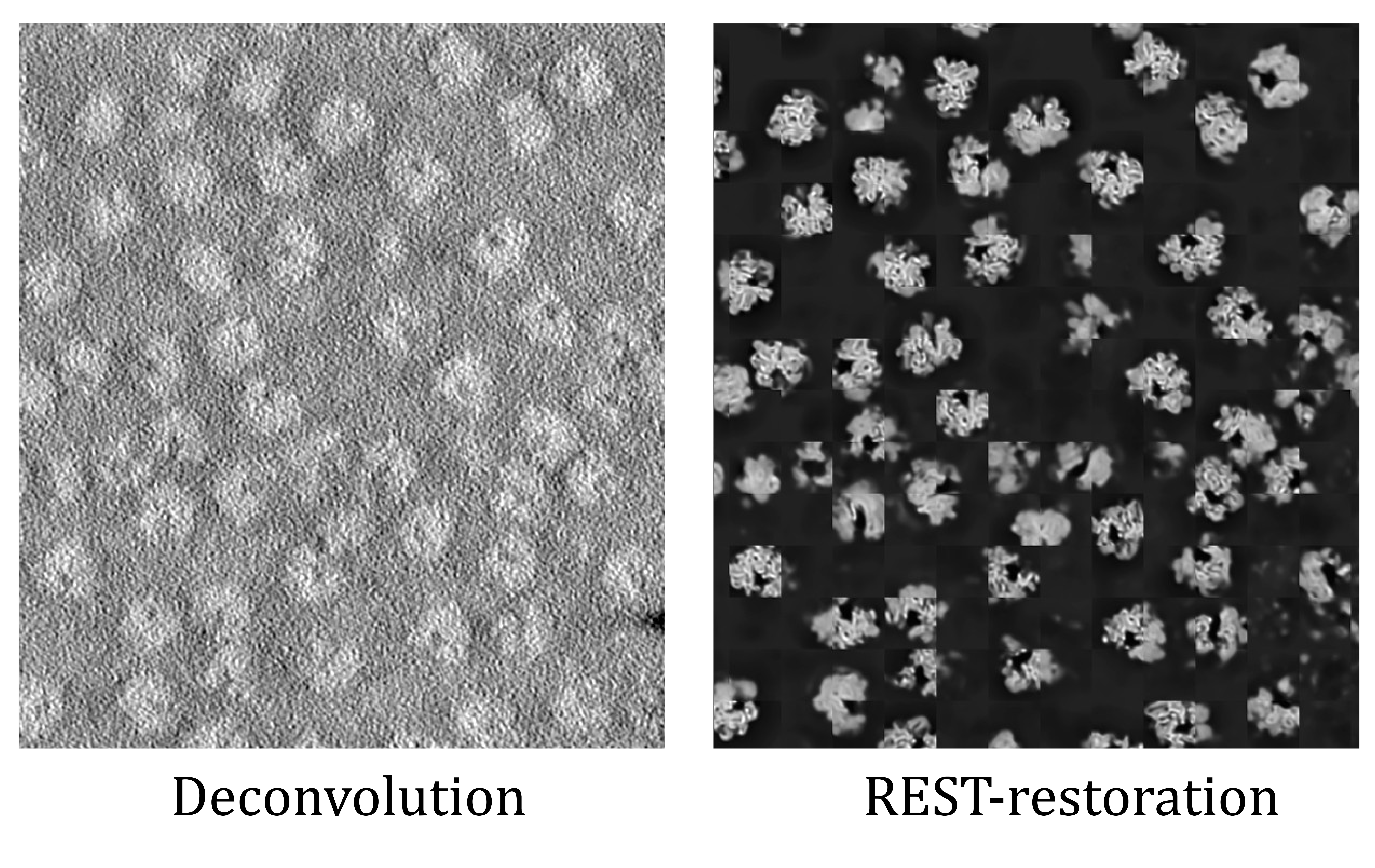
ribosome
nucleosome
Download the code.
Here, we recommend Linux system. Firstly, you should have conda
For example, if you work on the cuda version 10.1 and cudnn is 7.6.5.... (NVIDIA GeForce GTX 1080 Ti and NVIDIA GeForce GTX 2080 Ti .....), the tensorflow version should be 2.3.And we also tested the code on GTX 30XX with tensorflow=2.8 and cuda11.4, it also worked successfully.
conda create -y -n rest -c conda-forge python=3.7
conda activate rest
pip install -r requirements.txt
1). Do STA use Relion or other software
2). The subtomograms that participated in STA were extracted using Relion as the input of the training data.
3). According to alignment parameters in star files. used e2proc3d.py program to rotate and shift the averaged map to generate the ground truth. The command is like
e2proc3d.py --rot=spider:phi=-64:theta=28:psi=62 --trans=6.2,0.4,28.6 ribosome.mrc y_0.mrc
Here, ‘--rot=spider:phi=-64:theta=28:psi=62 --trans=6.2,0.4,28.6’ is the parameters of orientation which has been calculated from Relion star file, ‘ribosome.mrc’ is the averaged map from STA and ‘y_0.mrc’ is the ground truth of the particle according to the parameter.
4). Generate the training pairs of all particles and train them later.
You can directly use the pipeline of HEMNMA_3D in Scipion to generate the simulated subtomograms as the input and the volume used to generate the subtomograms as ground truth.
1). You need to import a PDB for the task of NMA.
2). Using the program of ‘Modes analysis&visualization’ to generate the Normal modes
3). Using the program ‘Synthesize volumes’ to generate the simulated data, in this program, you can set the parameters of volume number, voxel size, SNR, tilt range, and settings in CTF.
4). Extract the ground truth in the output named _‘*df.vol’ and use e2proc3d.py program to convert the file format from .vol to .mrc.
- Extract the simulated data in the output named ‘*_subtomogram.vol’and use e2proc3d.py program to convert the file format from .vol to .mrc.
Copy all files downloaded here in the project folder and execute them in the project folder. If you change a new batch of data for training, do it again.
1). Rename the raw particles or simulated particles to 1_00****.mrc and place them into subtomo folder. The name of each file should write in the subtomo.star.
2). Rename the ground truth to 1_00****.mrc and place them into subtomo folder in process2. The name of each file should write in the subtomo.star in process2.
3). Back to the project directory
4). Preprocess:
python generate_subtomostar.py subtomo 64 96; cp subtomo.star process2/.
python process1.py;
cd process2/;
python process2.py;
cd ..;
python process3_linux.py;
python splite_trainset.py;
or if your CropSize and CubeSize are all 64
sh onestep.sh
5). train:
python process_train.py --epoch 2 --step 1500 --num_gpu 4 --new_model_name new_model_name.h5 --initial_model initial_model_name.h5 ;
If you want to know each parameters meaning:
python process_train.py -h
usage: process_train.py [-h]
[--initial_model INITIAL_MODEL]
[--new_model_name NEW_MODEL_NAME]
[--epoch EPOCH]
[--step STEP]
[--num_gpu NUM_GPU]
refine your model using simulated data
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
--initial_model INITIAL_MODEL
Name of the pre-trained model. Leave empty to train a new one.
--new_model_name NEW_MODEL_NAME
Name of the model you want to rename. Leave empty to use results/model_iter00.h5.
--epoch EPOCH
The epoch for training. Maybe you need find a suitable parameters to train your data
--step STEP
The step of each epoch. Maybe you need find a suitable parameter to train your data
--num_gpu NUM_GPU
The number of gpu you want to use
1). Copy the input tomograms or sub-tomograms into tomoset folder
2). Execute the command :
python process5_generate_predict.py;
python rest.py predict for_predict1.star real_ribosome_strategy1.h5 --gpuID 0,1,2,3 --tomo_idx 0 --crop_size 96 --cube_size 64 ; #(single patch only need one GPU)
The test datasets have been shared in OneDrive Cloud Disk which can be downloaded from
In the test datesets, the folder named "Rest_material” contains five sub-dictionaries:
1_tomograms_recovered including the original tomograms and REST-restored tomograms recovered by the authors
2_evaluation4strategy1 including the original tomograms and the pre-trained model trained by the authors for restoring the tomograms
3_evaluation4strategy2 including the original tomograms and the pre-trained model trained by the authors for restoring the tomograms
4_othermap4evaluation including the other maps used in paper
5_tutorial_of_REST_workflow including two datasets (one dataset of simulated nucleosome tomogram and one dataset of real ribosome tomogram for tutorial.
All of the files can be downloaded individually.
How to work on the test data see the file ###guideline4evaluation.